Lost checkouts, repeated form submissions, and confused customers often trace back to the exact root cause: ERR_CACHE_MISS. While many guides treat it as a simple browser glitch, for business sites, it usually reveals deeper hosting or configuration issues. This error occurs most often during form activity, the most risky part to get connection issues on.
It can occur on login and during CRM, but it also occurs during checkout. The error can also occur during the transfer of money. If misdiagnosed or ignored, it can result in abandoned carts or duplicate submissions. Any of these issues will result in a massive drop in user trust.
A common underlying cause for the ERR_CACHE_MISS error is a faulty hosting configuration. If there are issues in the server setup or errors in it, users can experience many different types of errors frequently.
Fixing the error does, however, require a dual approach. Proper configuration has to be done on both the browser accessing the website and the server that is hosting it. Before we start please ensure you understand what cache is and how to clear it.
Key Takeaways
- ERR_CACHE_MISS is usually a caching or header retrieval problem.
- Hosting errors often cause it: wrong cache-control headers, redirect loops, and SSL issues.
- Fixing requires a structured diagnosis across browser, CDN, and server.
- A reliable hosting provider, such as UltaHost, prevents most of these scenarios.
“Most ERR_CACHE_MISS cases come from inconsistencies between what the server tells the browser to cache and what the browser expects. Fixing headers and redirects at the hosting layer eliminates most occurrences.” – UltaHost Web Infrastructure Engineer.
What ERR_CACHE_MISS Actually Means (Hosting Context)
ERR_CACHE_MISS appears most often on Chrome when the browser can’t validate the existing cached resources properly. Since Chrome cannot read the cached resources, it tries to protect the user from any accidental duplicate submissions and throws out the ERR_CACHE_MISS error until it can be validated. It appears after form submissions and can be caused by several things.
For one, your server, CDN, or plugins could be sending mixed instructions about what should/shouldn’t be cached. This will confuse Chrome and trigger a revalidation, leading to a form resubmission error. Similarly, if your site does multiple redirects like HTTP → HTTPS → HTTP, Chrome keeps re-fetching the page and eventually returns ERR_CACHE_MISS. It can also be caused by general server instability (slow server, timeouts, etc.), CDN misconfiguration, corrupted caches, and cache plugins
Fix ERR_CACHE_MISS Quickly
Step-by-step guide to troubleshoot and resolve cache errors on your website.
Now that we know what the ERR_CACHE_MISS error is, let’s get into a step-by-step guide on how to fix it.
How to Fix ERR_CACHE_MISS (Complete Step-by-Step)
Now that we know what ERR_CACHE_MISS means, let’s get into how to fix it:
Step 1: Verify Browser-Side Causes (quick rule-out)
There are a few browser-side issues that are easy to fix and can potentially resolve the entire issue:
- Delete Browsing Data:
Follow these steps to clear your previous browsing data:
- Click the three dots at the top right of the Chrome browser.
- Click Delete Browsing Data.
- Select a time range (preferably all-time).
- Check the boxes for Cookies and Caches.
- Click Clear Data.
This will delete old, stale data and ensure you get a fresh restart of your browser.
- Test in Incognito:
Testing in Incognito helps you to root out the cause. Incognito mode completely disables all of your extensions and previous stored sessions, letting you get a clean entry onto the website. This can help verify if the problem lies with your browser settings or with something else.
- Disable Extensions:
Extensions can also interfere with the connection:
- Click the three dots at the top right of the Chrome browser.
- Hover over extensions, click “Manage Extensions”.
- Disable all the extensions you see on your screen.
You can re-enable the extensions if this doesn’t fix the issue.
- Update Chrome:
Sometimes, an outdated version of Chrome can come with its own bugs and glitches that could be causing the error. To update Chrome:
- Click the three dots at the top right, then click on Settings.
- On the sidebar, find and click on “About Chrome”.
This will automatically prompt Chrome to check for new updates.
- Test From a Different Network/Device:
The issue could also be from your internet or the device you are using in general. To pinpoint the issue, you can try using a different device, like your phone, to load the same website. You can also turn on and connect to your mobile hotspot to check if the issue is with your internet.
This step just reduces some noise before we get into a deeper diagnosis.
Step 2: Check Server Cache-Control Headers
- Inspect using Chrome Devtools → Network → Headers.
- Check for missing or contradictory cache-control directives. e.g., no-store on pages that utilize caching, must-revalidate conflicting with CDN caching or stale cached HTML, etc.
- Define clear, separate rules for static vs dynamic resources.
- Ensure forms endpoints are not cached.
- Standardize header behavior utilizing .htaccess/Nginx config.
Step 3: Fix SSL & Redirect Misconfigurations
One of the primary causes for the ERR_CACHE_MISS error is redirect loops and inconsistent HTTPS enforcement. If there are multiple redirect steps or if there is mixed content, Chrome keeps trying to re-fetch data and eventually just returns with ERR_CACHE_MISS.
There can also be SSL redirect issues if the SSL certificate has expired or doesn’t match the domain. If this occurs, Chrome refuses to trust it, and when Chrome can’t validate it, it forces revalidation cycles that keep failing until they give a form resubmission error.
Solution:
There are a few solutions to this. You should try to enforce one clean redirect path that is to be followed. One singular path ensures there are no looped redirects, and Chrome can cleanly validate everything. It should move from HTTP → HTTPS cleanly in one step with no bouncing.
You should also make sure that your SSL certificate is valid, properly configured, and matches the domain. This will let Chrome read it easily and properly.
An easy way to do all of these solutions at once is simply to utilize UltaHost and its free SSL configuration program. You can use their Free Migration Service to easily convert to their system and make use of their free SSL configuration that prevents any errors, as well as 24/7 human support to ensure that any future errors are also easily sorted.
Step 4: Check CDN, Proxy, or Server Cache Layers
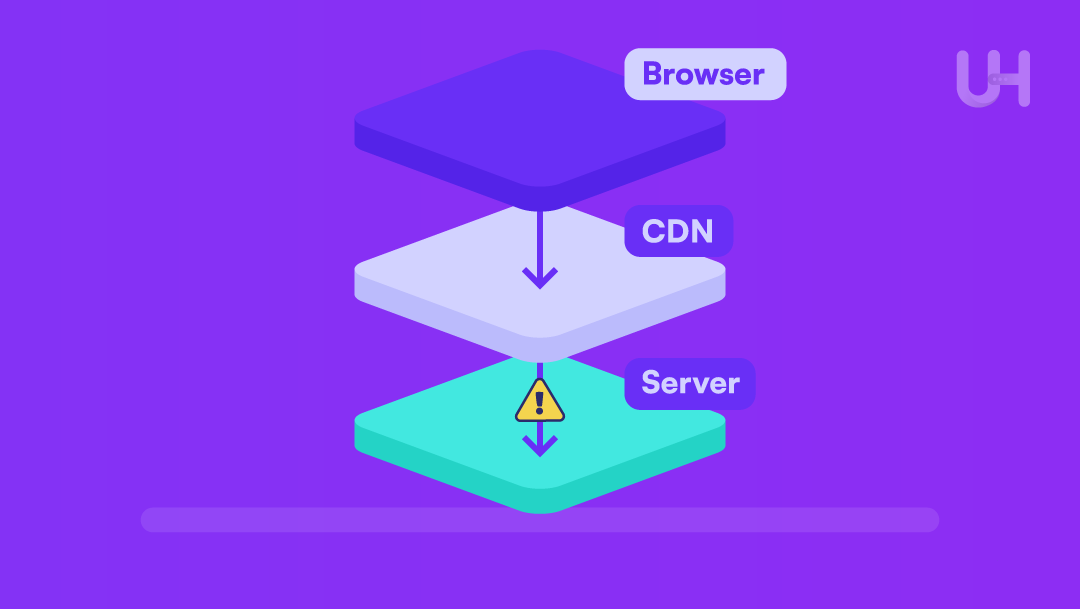
CDNs can also cause issues sometimes when they override cache-control unintentionally. They have their own caching rules, so sometimes they might cache files even when the server says not to. And since the browser receives mixed instructions from the CDN and the server, it gets confused and returns with ERR_CACHE_MISS.
Causes:
- CDN returns different cache headers than the origin, causing mismatches
- Dynamic HTML was mistakenly cached at the CDN layer.
Solution:
- First and foremost, you should try purging your CDN cache. This will eliminate old assets and mismatched headers. If purging the CDN cache doesn’t fix the issue, you can verify whether the issue truly lies with your CDN or not by temporarily disabling it.
- If the error is indeed caused by the CDN, you should try to match your CDN’s caching with the origin server. If there is a difference between the two, Chrome fails to confirm which one is correct and gives the error Chrome cache error.
- Just like CDN, reverse proxies like Cloudflare, Fastly, or Nginx can also cache content to improve speeds. Occasionally, they might accidentally cache dynamic pages or POST responses by mistake, causing Chrome to receive outdated or conflicting info.
Step 5: Review Form-Handling Code & Dynamic Pages
This step is critical for e-commerce stores and for CRMs, as form submissions are very important in them.
Causes:
- Caching confusion is causing double POST requests.
- Cache-incompatible PHP logic.
- The user’s session is mismatched with the server.
- Unexpected CSRF token regeneration.
Solutions:
- Use PRG patterns (Post-Redirect-Get), preventing accidental resubmissions.
- Do not cache form endpoints.
- Make sure CSRF tokens persist correctly until the form is submitted.
Step 6: Check Server Stability, Timeouts, and Errors
A slow server may cause Chrome to fail to retrieve cached resources, resulting in a Chrome cache error.
Causes:
- Overloaded servers struggle to handle requests fast enough.
- High CPU/RAM usage.
- Intermittent 500/502/504 entries in logs.
Solutions:
- Upgrading hosting resources.
- Optimize PHP-FPM, improving PHP performance and reducing timeouts.
- Remove or adjust the plugins causing slowdowns or errors.
- Enable OpCache.
Step 7: Reset & Rebuild Site Cache Layers
Outdated caches tend to send old and stale data to the browser. Similarly, multiple caching layers (plugin, server, CDN) conflict if not cleared. This can cause ERR_CACHE_MISS.
Solutions:
- Clear plugin cache so outdated data isn’t used.
- Clear server cache to remove stale data.
- Reset CDN cache.
- Rebuild minified assets.
Diagnosing Hosting vs Browser Root Cause
It’s important to diagnose whether the issue actually lies with the browser or the hosting. Fortunately, this is very simple to pinpoint.
- Monitoring Reports: If there are only a few reports, then the error may be an individual-level browser issue. However, if there are a lot of reports, then it may be a problem on the hosting side of things.
- Using logs + DevTools: We can utilize DevTools and logs to check headers, redirects, and error codes. If a consistent pattern forms across users, that shows a hosting problem.
- CDN Disabled Test: Temporarily disable the CDN. If the error completely disappears, then this means that the CDN was causing mismatched caching.
Each of these methods is tailored to help you identify hosting caching issues.
Preventing ERR_CACHE_MISS Long-Term
We can take some additional steps on the hosting side to ensure that ERR_CACHE_MISS is avoided in the long term:
- Ensure that all the layers follow consistent, stable caching rules.
- Avoid mixed content and redirect loops and ensure clean HTTPS enforcement.
- Use PRG for forms to prevent duplicate submissions and caching issues.
- Avoid caching dynamic content (forms, logins, checkouts).
- Monitor logs for header anomalies.
- Keep CMS/plugins updated.
The combination of all of these measures ensures a clean experience and permanent prevention of the Chrome cache error.
How UltaHost Helps Fix & Prevent ERR_CACHE_MISS
If you are the owner or manager of a website, there’s no doubt that consistent performance is always important. This can, however, be difficult to maintain as it relies heavily on unpredictable factors. To combat this, you can utilize a better hosting service that lets you solve these issues easily.
Resolve Website Cache Errors
Learn simple fixes to restore website functionality and avoid ERR_CACHE_MISS issues.
UltaHost is a top-of-the-line hosting service tailored for users who require consistent performance. Our WordPress Hosting Solutions ensure cache plugins and server stack always work smoothly together.
They use NVMe SSDs that ensure consistently high uptime and reduce timeout-triggered cache errors. They provide free SSL certificates and a clean HTTPS setup to reduce redirects and TLS-driven cache issues.
They also provide clean daily backups you can use in case of configuration issues, as well as 24/7, reliable human support that can quickly and easily diagnose any issue. Their reverse-proxy-friendly architecture also avoids CDN-origin mismatches.
Furthermore, UltaHost’s Free Migration Service makes moving from one provider to another extremely simple and easy to do.
FAQs
What causes ERR_CACHE_MISS?
Caching header conflicts, redirect loops, SSL issues, CDN misconfiguration, form resubmission behavior, or browser cache failures.
How do I fix ERR_CACHE_MISS in Chrome?
Clear cache, disable extensions, inspect headers, fix redirects, repair SSL, adjust CDN caching, and ensure dynamic pages aren’t cached.
Can hosting cause ERR_CACHE_MISS?
Yes. Incorrect cache-control headers, server instability, backend form-handling, or CDN conflicts frequently trigger it.
How do I prevent ERR_CACHE_MISS?
Standardize caching rules, fix redirects, avoid caching forms, maintain stable server resources, and ensure SSL consistency.
Does this error affect e-commerce checkouts?
Yes. It can interrupt form submission and harm conversions.








