Have you encountered corrupted video files on your Linux system? You may find it difficult to repair these files, especially if you prefer open-source tools that align with Linux’s flexibility and customization possibilities. We can help you address this issue and will present a list of three open-source video repair software solutions available for Linux environments. We have tested these tools extensively to verify that they provide the reliability and performance necessary for various video repair needs.
Top 3 Open-Source Video Repair Software for Linux
Despite Linux’s widespread adoption in various areas, the availability of video repair tools adapted to this platform remains limited. While users of other operating systems have many of the most effective video repair tools for damaged files, the Linux community faces a scarcity. After our tests and evaluation, we have identified only three open-source tools that stand out for their capacity and compatibility with Linux.
Pay attention: In this article, we will not provide detailed instructions on how to operate these open-source tools. We aim to familiarize you with their capabilities and offer a general overview of each software’s advantages and disadvantages.
FFmpeg
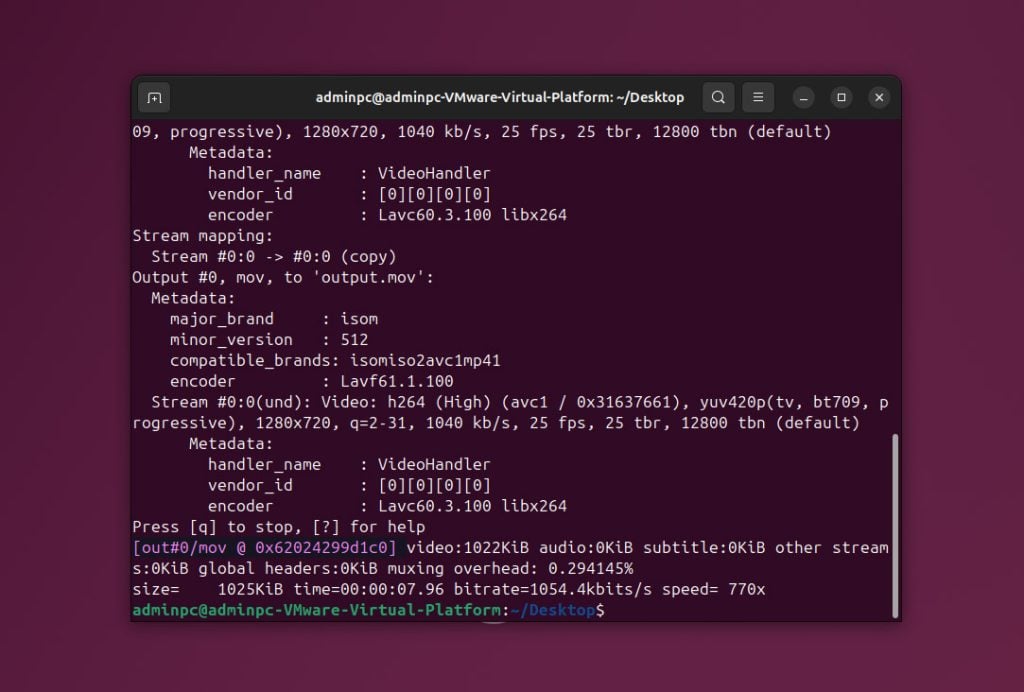
When it comes to video repair tools for the Linux operating system, FFmpeg stands out as a premier choice among video repair tools. FFmpeg was developed in 2000 and has grown into a leading tool that can repair, process, and convert video files. One of the distinct characteristics of FFmpeg is that it does not provide a universal command for video repair; instead, you need to select commands based on the type and conditions of the video corruption. This precisely handles various issues but requires specific knowledge about the problem. The software benefits from active updates, which improve its capabilities and adapt to new video technologies and formats.
Supported video formats: FFmpeg supports a vast array of video formats, including MP4, AVI, MOV, MPEG, WMV, FLV, MKV, WebM, QuickTime, XviD, DivX, MPEG-2, H.264, H.265, VP8, VP9, and many others.
Advantages:
- FFmpeg is a multifunctional tool that repairs videos and supports processing and conversion, which makes it a one-stop solution for multiple multimedia needs.
- It supports an extensive array of video formats and can handle nearly any file you might encounter on a Linux system.
- FFmpeg can address various types of video damage, such as corruption caused by truncated files, incorrect codec parameters, or damaged file headers.
- FFmpeg has a website with detailed command descriptions, user guides, and instructional materials to help you understand and utilize the software.
Disadvantages:
- To use the tool, you must invest time to learn and experiment with the different commands available on FFmpeg.
- To use FFmpeg successfully, you need to be well-informed about video corruption. You must also choose the correct recovery command, which can be difficult for beginners.
Untrunc
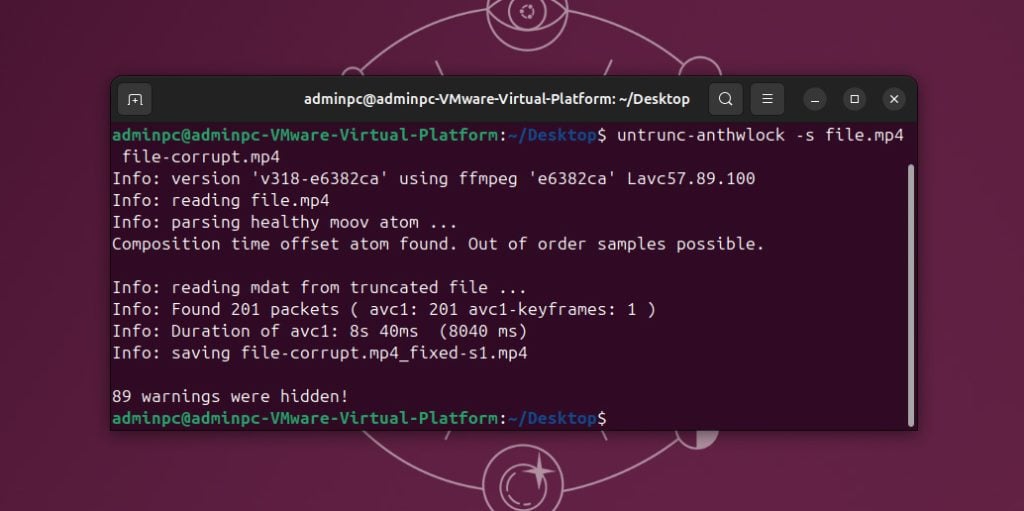
The next software we added to our list is Untrunc. Developed in 2013, Untrunc offers a specialized solution compared to FFmpeg. Unlike the broad capabilities of FFmpeg, Untrunc specializes in repairing videos that have lost and corrupted their meta atom, which is necessary for file structure integrity. To use Untrunc, you must have a corrupted video and an undamaged sample from the same recording device, as it uses the healthy file as a reference to repair the corrupted one. Also, Untrunc does not have an official website; all relevant information and updates for this tool are available on its GitHub repository or various online forums.
Supported video formats: Untrunc works with limited video formats, specifically MP4, M4V, MOV, and 3GP.
Advantages:
- Untrunc employs a standard command that removes the need for extensive research or knowledge of other commands.
Disadvantages:
- Untrunc only repairs damage related to lost and corrupted meta atoms and does not address other types of video corruption.
- While Untrunc’s information is accessible via GitHub, the absence of an official website means there is no centralized source of descriptions or official support, which can be inconvenient if you seek detailed guidance.
- Repairing videos larger than 2GB can take several hours, which may not be practical if you need quick fixes.
DivFix++
The last open-source software we identified is DivFix++. Unlike the previous two options, it requires a Linux distribution with GUI support because it features a graphical user interface. DivFix++ runs best on Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Mandriva, Fedora, and Debian for optimal performance. This software is the most specialized among those we have considered, as it exclusively works with AVI video files. DivFix++ reconstructs the index part of AVI files, which is necessary to preview movies that initially lack this component.
Supported video formats: DivFix++ exclusively supports AVI video files.
Advantages:
- DivFix++ can repair high-definition AVI files, which provides no loss in quality.
- The software features a simple graphical interface that does not require you to learn complex command syntax, making it accessible even to those with minimal technical experience.
Disadvantages:
- DivFix++ supports only AVI video formats, which limits its applicability.
- The last update to DivFix++ was several years ago.
- No official website provides complete information about DivFix++; all resources are available only across various user forums.
Is There an Online Video Repair Alternative?
In addition to open-source software, online services for repairing videos offer a convenient alternative that does not require installation on your PC. These services operate through a simple process where you upload the damaged file and a reference video, if available, and then download the repaired video once the service has completed its work.
One example of such a service is Clever Online Video Repair. This platform represents the versatility of online tools and can address a wider array of video damage types compared to software like Untrunc or DivFix++. Online services can also repair videos that do not play completely, an especially difficult issue. Typically, these platforms support a broader range of video formats, which underscore their adaptability and user-friendliness.
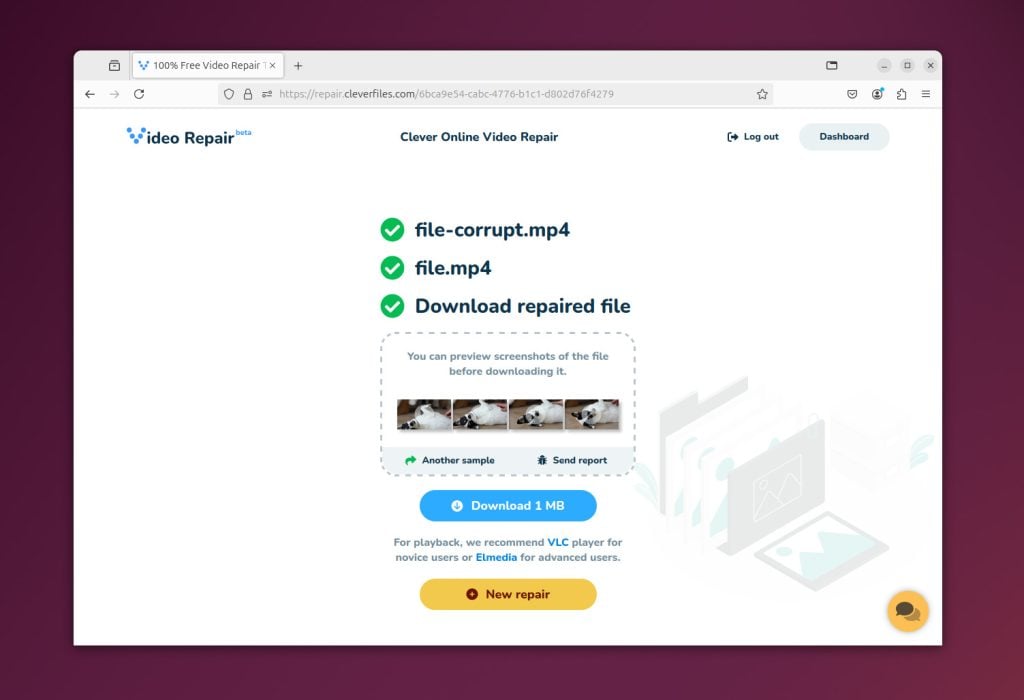
Advantages of online video repair services:
- You do not need to install any software, which saves space and time.
- They can repair a variety of damage types and support more video formats.
- The repair process is accessible from any device with internet access, which makes it ideal if you need quick fixes without the hassle of technical setups.
Disadvantages:
- If you upload sensitive or proprietary videos to a third-party server, it might pose security risks. Therefore, we recommend that you read the privacy policy of any service before you use it to verify it meets your security standards.
- A stable and fast internet connection is necessary to upload and download large video files.
- While some services offer free trials, more complex repairs might require payment.
Conclusion
In this article, we offer three options to help you choose the best open-source software for video repair on Linux. In summary, FFmpeg delivers extensive versatility if you are proficient in video diagnostics and command-line operations. Untrunc concentrates on recovering videos with missing MOOV atoms but requires a reference file to perform repairs. DivFix++ presents a user-friendly interface; however, it remains ideal solely for repairing AVI files.
If you seek convenience, online services like Clever Online Video Repair or others offer a quick and accessible alternative. These services handle a wider range of video issues without any installations. Whichever option you choose, evaluate your specific needs and the capabilities of each tool.
If you’re looking for a reliable hosting environment to run your Linux applications or software seamlessly, consider Ultahost Linux VPS Hosting. With optimized performance, robust security, and excellent scalability, it’s the perfect choice for Linux enthusiasts and professionals.
FAQ
Can these open-source tools handle batch processing of multiple corrupted video files?
Yes, FFmpeg can handle batch processing and allows you to repair multiple files at once through script automation. You can create scripts using FFmpeg commands in a shell script file or directly from the command line. These scripts can loop through directories of video files and apply repair commands to each video sequentially. In contrast, Untrunc and DivFix++ typically require you to operate on individual files one at a time.
Are there any online tutorials or communities that can help me learn to use these Linux video repair tools?
Numerous online resources, tutorials, and community forums are available for these tools. Websites like Stack Overflow, GitHub, and specific Linux forums host discussions and detailed guides. Users also share scripts and troubleshooting tips that improve learning and usage.
Can these open-source tools repair video files from external devices like USB drives and SD cards?
All these tools can repair video files from external devices. Depending on the tool used, you must mount the device on their Linux system and access the files through the command line or graphical interface.
Do any of these tools provide a preview option to check the video before final recovery?
None of the open-source tools like FFmpeg, Untrunc, or DivFix++ inherently provide a built-in preview option to check video file integrity before you complete the final recovery. These tools primarily specialize in the repair process itself. Any preview would typically require you to play the video with a media player after attempting the repair. However, many online video repair services, such as Clever Online Video Repair, offer a preview feature. These services allow you to view a portion of the video after you complete the repair, which allows you to assess the repair quality before you download the fully restored file.
Is technical support available for these open-source video repair tools?
Direct technical support is limited for open-source tools. However, community support is powerful, with forums, user groups, and sometimes even the developers providing advice and updates. For more formal support, you might consider commercial counterparts.
How do online video repair services work, and are they secure?
Online video repair services allow you to upload your damaged files to a server where the repair occurs. These platforms generally use secure protocols for file transfers (such as HTTPS) to protect data integrity and privacy. Nonetheless, you should review the service’s privacy policy and security measures to provide adequate protection before uploading sensitive or proprietary information.












