How to Install OWASP ZAP in Kali Linux
For ethical hackers and security enthusiasts, Kali Linu...

Node.js is a powerful JavaScript runtime environment for developing super-scalable and fast applications. Contrary to conventional installations that restrict JavaScript to only the browser, with Node.js, developers get to run JavaScript on the server, thus providing the advantage of having a single scripting language on both the front end and back end systems. With its event-driven, light, and lean architecture, Node.js fits into the best solution for real-time applications, APIs, and even microservices.
Debian users here have a way of supercharging their development environment with Node.js. With the combination of the stability of Debian and the flexibility of Node.js, there’s no better option for the developer who wants rock-solid performance without compromise. From personal projects to deploying enterprise solutions, Node.js on Debian offers seamless performance with up-to-date tools.
Here, you will get to learn each and every step required to install Node.js on Debian. So by the time you finish reading this article, you should know every step to take starting from the installation of the system and checking if Node.js has been installed.
Installing Node.js on Debian through the default APT package manager is the simplest. It is fairly simple to follow and works fine if you do not need the latest version of Node.js. Debian repositories usually contain a stable version of Node.js, which is good enough for a lot of use cases.
Be sure to have updated package index before you install any package. Therefore, execute this command:
sudo apt update
This command fetches the latest package information, ensuring you’re installing the most current version available in the Debian repositories.
To install Node.js, run:
sudo apt install nodejs -y
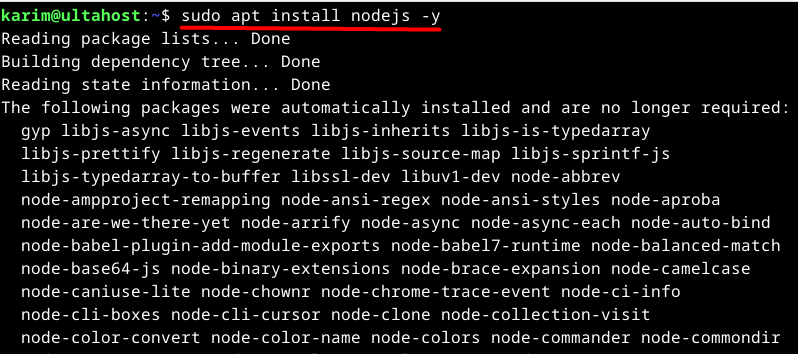
This command installs the Node.js runtime along with its dependencies. However, keep in mind that the version available in Debian’s default repository might not be the latest.
Install Node.js on Our Debian Linux Server!
Ultahost offers Debian Linux hosting with NVMe SSD storage. Use our best Debian Linux VPS to practice and improve your command line skills efficiently.
Node.js works hand-in-hand with npm (Node Package Manager), which helps you manage packages and dependencies for your projects. To install npm, use:
sudo apt install npm
After installation, verify that Node.js and npm were installed successfully by checking their versions:
node -v npm -v

The output will display the installed versions. If you see the version numbers, it means Node.js and npm are ready to use. You can also update the NPM version refer to our guide on how to update the NPM version.
This method is perfect if you need a stable and hassle-free setup. However, if you require the latest version of Node.js, consider using other methods, which we’ll discuss next.
A PPA (Personal Package Archive) is a repository that allows developers to distribute newer or custom software versions not available in the default Debian repositories. For Node.js, using a PPA repository ensures you get the latest or a specific version of Node.js directly maintained by the Node.js team. This method is ideal if you need features or fixes introduced in the latest versions.
The Node.js version in Debian’s default repositories may lag behind the latest releases. By using the PPA, you can install the most recent stable version of Node.js, which is especially important for developers working on cutting-edge projects or using features available only in newer versions.
The curl tool is required to fetch the NodeSource setup script. If it’s not installed, you can add it with:
sudo apt install curl -y
NodeSource maintains the latest versions of Node.js. To add their PPA repository, run:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg NODE_MAJOR=20 echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] https://deb.nodesource.com/node_$NODE_MAJOR.x nodistro main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install nodejs -y
To confirm the installation, check the versions of Node.js and `npm`:
node -v npm -v

The output will display the installed versions, which should match or be close to the latest stable release.
You can see that this method provides the latest versions of both nodejs and NPM because the PPA repository ensures you’re not stuck with outdated versions.
Read also How to Install Yarn on Debian.
Node.js is a versatile tool that brings many advantages to developers, especially when paired with the stability and efficiency of Debian. Below are the key benefits explained in detail.
Node.js uses the V8 JavaScript engine, known for its speed and efficiency. This ensures that applications run faster, making it ideal for high-performance tasks such as real-time data processing, APIs, and streaming services.
Node.js follows an event-driven, non-blocking model, allowing it to handle multiple requests simultaneously without consuming excessive resources. This makes it suitable for applications requiring high concurrency, such as chat apps or gaming platforms.
Node.js is cross-platform and works seamlessly on Debian. Developers can create applications that run across different environments, saving time and effort during deployment.
Node.js comes with npm (Node Package Manager), offering access to over a million open-source packages. This ecosystem helps developers speed up development by reusing libraries and tools rather than building everything from scratch.
With its lightweight design and support for microservices, Node.js is highly scalable. It allows developers to build modular applications that grow effortlessly with user demand.
Node.js has a vast and active community. Developers on Debian can find numerous tutorials, forums, and open-source projects to resolve issues and learn best practices.
Debian is known for its rock-solid stability and security. Pairing Node.js with Debian ensures your applications are built on a reliable foundation, reducing the risk of crashes or vulnerabilities.
Node.js is a powerful tool for building modern, efficient, and scalable applications, and Debian provides a stable and reliable environment for its installation and use. In this guide, we covered two main methods to install Node.js on Debian: using the default APT package manager and adding the NodeSource PPA repository. The first method is quick and straightforward for users who need a stable version, while the second ensures access to the latest features and updates.
Both methods cater to different needs, ensuring that you can choose what works best for your projects. By following the step-by-step instructions provided, you can download Node.js Debian seamlessly and take full advantage of its features. Whether you’re building APIs, real-time applications, or lightweight microservices, Node.js on Debian is a combination you can count on for performance and reliability.
If you’re a developer diving into app development, ensure your hosting setup can handle Node.js demands. Ultahost offers reliable NodeJS hosting with dedicated resources for guaranteed speed and stability, ideal for resource-intensive tasks.
Node.js is used to build server-side applications, APIs, and real-time services like chat apps and streaming platforms.
Use the APT package manager for a stable, system-maintained version or the NodeSource PPA for the latest features.
Yes, the NodeSource PPA allows you to select and install a specific version of Node.js.
You can update Node.js by re-adding the NodeSource repository and reinstalling the desired version.
Yes, npm is bundled with Node.js in most installation methods, including the PPA repository.
Yes, using Node Version Manager (NVM), you can manage and switch between multiple Node.js versions.
Yes, Node.js integrates seamlessly with Debian, leveraging its stability and security for reliable application performance.