You are in the middle of working on something crucial online – maybe uploading an important document due the next day, browsing to watch a newly-released marvel movie and then it appears: your screen is telling you addressing you with the enigmatic message; “400 Bad Request.” Your heart sinks.
What does this mean? Is your computer broken? Did you do something wrong? Is the website down? The confusion and frustration is too common for non technical users around the world.
The 400 Bad Request error is a common HTTP status code that you will come across. But it is also one of the most misunderstood.. Understanding what causes a 400 Bad Request error, and how to solve the issue is not always straightforward, but it does allow you to get back to work faster and keep frustration levels in check.
This blog will guide you through everything. We will break down the geek speak, figure out what is going wrong and guide you through with simple answers that really do get the issue resolved.
Key Takeaways
- 400 Bad Request highlights the server has received your request but it was not able to process it.
- 400 bad request occur mostly due to incorrect URLs, old browser cache and cookies, outdated DNS cache, and oversized file size.
- One of the most powerful initial solutions to 400 Bad Request errors is clearing your browser’s cache and cookies
- Flushing your DNS cache erases outdated network data that might be preventing you from connecting to the website
- Although 400 errors are strictly believed to be client-side errors, it can be possible for a server to generate one. It is possible that your web hosts or domain name servers could be having issues
- Keeping your browser up to date and regularly clearing cache can help in minimizing such 400 Bad Request errors
Launch Smarter, Scale Faster with Ultahost
Let Ultahost’s expert support team help you diagnose and fix the issue fast, so your website stays online and error-free.
What Is a 400 Bad Request Error?
A 400 Bad Request error is an Internet browser error message that’s way more straightforward than you would think.It’s actually a message from the web server, telling you the request you made contains incorrect syntax. In lay terms, it’s as if you sent somebody a letter when you didn’t have an address for them, or did so in a language they can’t understand.
What’s happening here? Technically, it’s the protocol that your web browser and the site you’re visiting use to bring pages to your screen. You are familiar that when you enter a URL, click a link, or submit a form in your browser, your browser generates an HTTP request to the server requesting some information or an action of some kind. This request consists of several components such as the URL, headers, cookies, and occasionally form data or files.
If there’s something in your request that doesn’t meet these requirements, like incorrect syntax, bad characters, damaged or broken data, or missing mandatory information based on how you sent the request, the server will step back the received image to with a status code of 400 and tell you it’s not going to process this message.
Common Causes of 400 Bad Request Errors
It is important to know what causes a 400 Bad Request error in order to solve and prevent it.
1 Common URL Formatting Mistakes
A bad URL is one of the most common causes for this error. This is easier to have happen than you may think, sometimes a wayward character, a space not where it should be or special characters that are not encoded correctly can cause the server to get confused.
URLs containing illegal characters or improper encoding can trigger the error, as servers expect special characters to be correctly formatted.
- Copy and paste the URL that contains characters your browser doesn’t recognize.
- URLs that are excessively long or contain consecutive percentage signs without proper encoding will fail to process correctly.
Another common reason is the saved data in your browser, such as cookies and cache files. Though it’s meant to enhance your browsing experience by memorizing locally data and quickening page loads, this may get bad or older over a time.
If your browser attempts to contact a server with invalid or out of date cookies, it cannot be assured that the session is valid and as such you will see a 400 error. Caches and cookies can get old or become corrupted, it’s usually when you’re trying to visit websites that you haven’t visited in a while, but also after a website has changed its authentication systems,
3DNS Cache Issues Causing 400 Bad Request Errors
DNS records are saved on your computer so that websites load faster. But when a website updates it’sIP address, those records that are cached on your system become obsolete and there will be a redirection between what your computer has in it’s memory and the website’s actual DNS information.
4 File Size Limits Triggering 400 Bad Request Responses
If you upload files to your website and the file size is greater than what can be handled by server resources the 400 Bad Request error may occur. The server refuses the request because it is too large to be processed in an efficient manner, so the upload does not finish.
| Repeated 400 errors eventually harm user trust and search engine crawl efficiency. While they don’t always impact rankings directly, unresolved client-side errors increase bounce rates and reduce overall site reliability, both of which search engines take seriously. |
How to Fix 400 Bad Request Error: 6 Proven Methods
1 Method 1: Check and Correct the URL
The first (and most straightforward) step to diagnosing a 400 Bad Request error is to carefully review the URL.
This may sound like a given but bad URLs are shockingly common and easy to let slide. A good number of users flub out typing web addresses or fail to realize when a link copied and pasted has bad formatting on it.
Steps to check your URL:
- Double check any special characters in the URL which are typed into your browser’s address bar.
- Absent any extra spaces, particularly leading and trailing you may have in the URL.
- Ensure that special characters are encoded correctly (use %20 for a space, etc.)
- Make sure the domain name has proper formatting
- If you’ve copied the URL, try writing it in manually_INSTEAD.
- Try searching for the page if you know you have the correct URL.
One of the best ways to fix 400 Bad Request errors is by clearing your browser’s cookies and cache, as outdated data or some corrupted file in there might be causing this problem.
- Cookies are little data files that websites store in order to remember your preferences and login information.
- Browsers save copies of web pages, images, and other resources to make websites load faster when you return.
When you clear your cache and cookies, what you’re doing is resetting your browser’s relationship with the site in question. This action wipes out any conflicting cached data, which could be what is triggering the server to reject your requests.
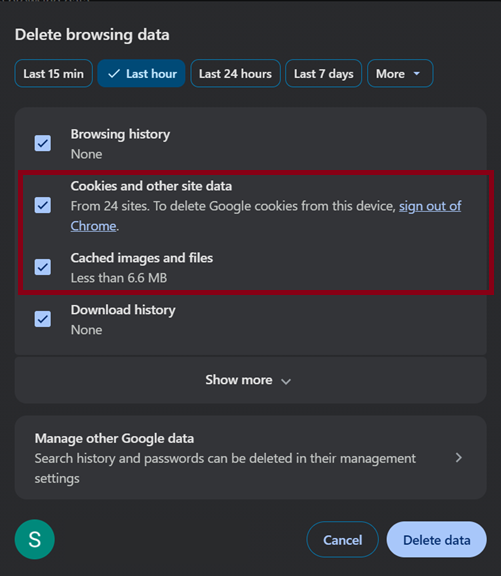
Steps to clear cache and cookies in Chrome:
- Click the three dots icon in the top-right corner of Chrome
- Navigate to History
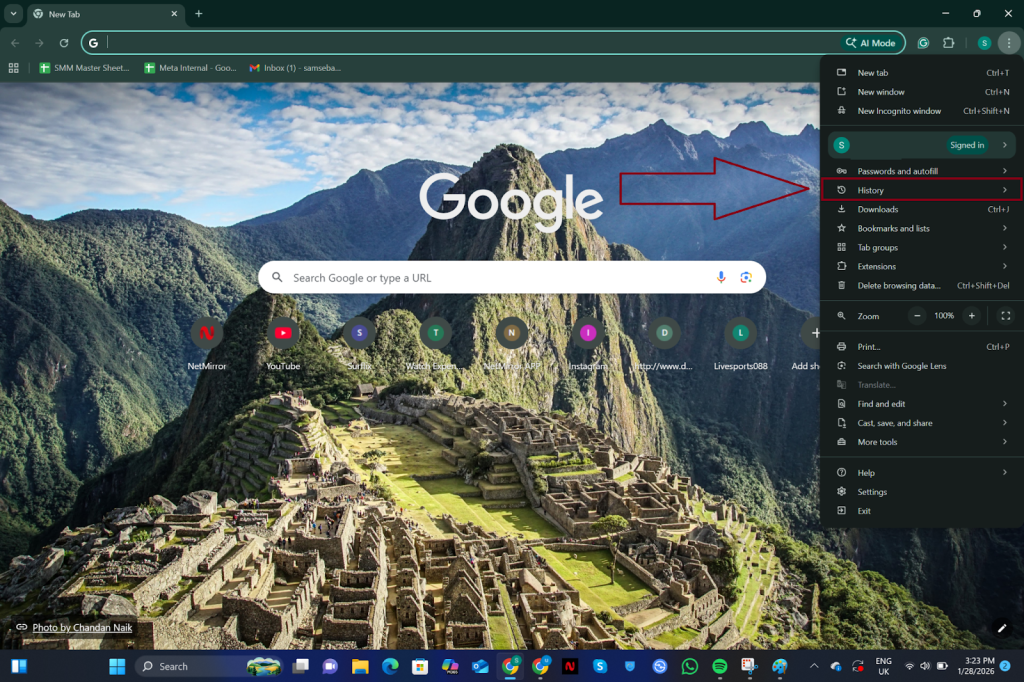
- Check the boxes for “Cookies and other site data” and “Cached images and files“
- Click “Clear data” button and wait for the process to complete
- Restart your browser and try accessing the website again
3Method 3: Flush Your DNS Cache
Clearing your DNS cache is an important troubleshooting step that everyone should learn, as this can help to test the connections between your computer and the internet, something most people are completely in the dark about. Your OS has locally cached DNS records. This cache accelerates your internet connection by bypassing the need to resolve IP addresses each time you visit a previously accessed site.
But when websites change their IP addresses, or your DNS cache becomes outdated, your computer may point to non-existent or out of date data, resulting in 400 errors.
Finding fresh DNS information If your cache is empty, the computer doesn’t have a ready answer, so it conducts a search process to find this answer.
Steps to flush DNS cache on Windows:
- Press the Windows key and type “cmd” in the search bar
- Right-click on “Command Prompt” and select “Run as administrator”
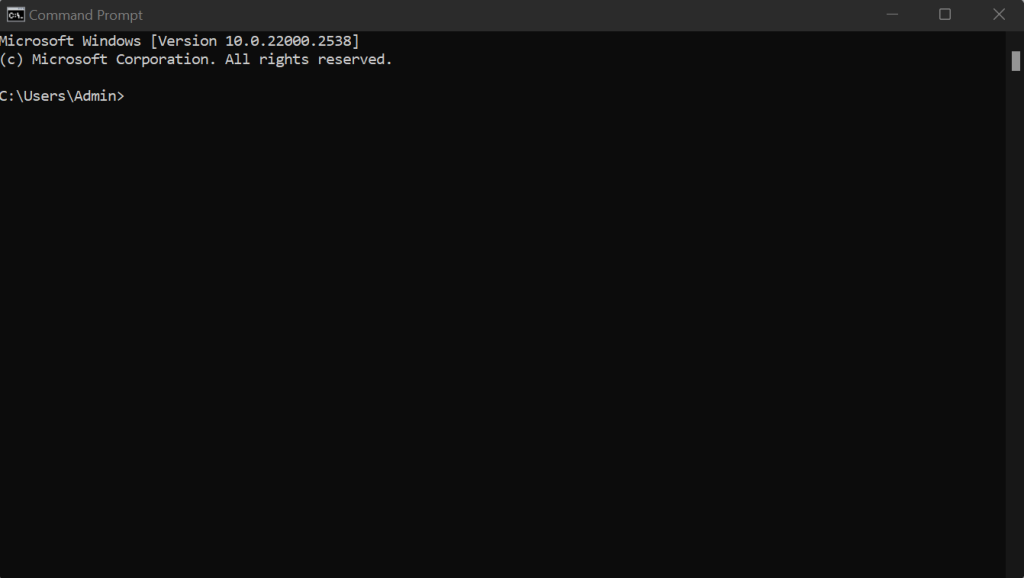
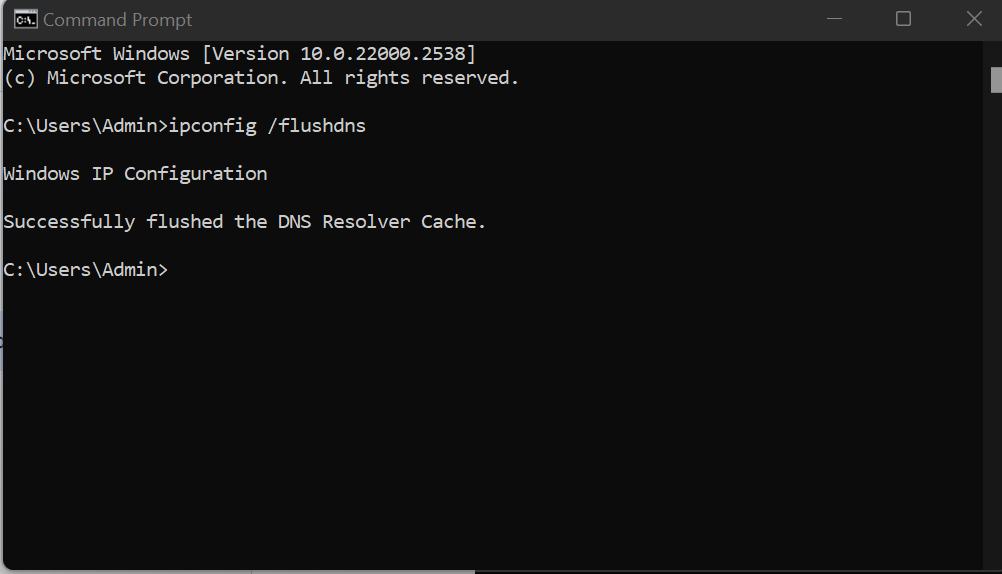
- Type the command: ipconfig /flushdns
- Press Enter and wait for the confirmation message
- You should see “Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache”
- Restart your computer to ensure changes take effect
- Try accessing the problematic website again
4Method 4: Disable Browser Extensions
Browser extensions add features and functions to your web experience, but they can interfere with how the browser itself makes a connection to or serves information from a website. There are also add-ons that mess with the HTTP headers, block content of certain types, strip out or add cookies, or modify other things about how requests to servers are made.
Steps to disable extensions in Chrome:
- Click the three-dot menu icon in the top-right corner
- Hover over “Extensions” and select “Manage Extensions”
- You’ll see a list of all installed extensions
- Toggle off the switch for each extension to disable them temporarily
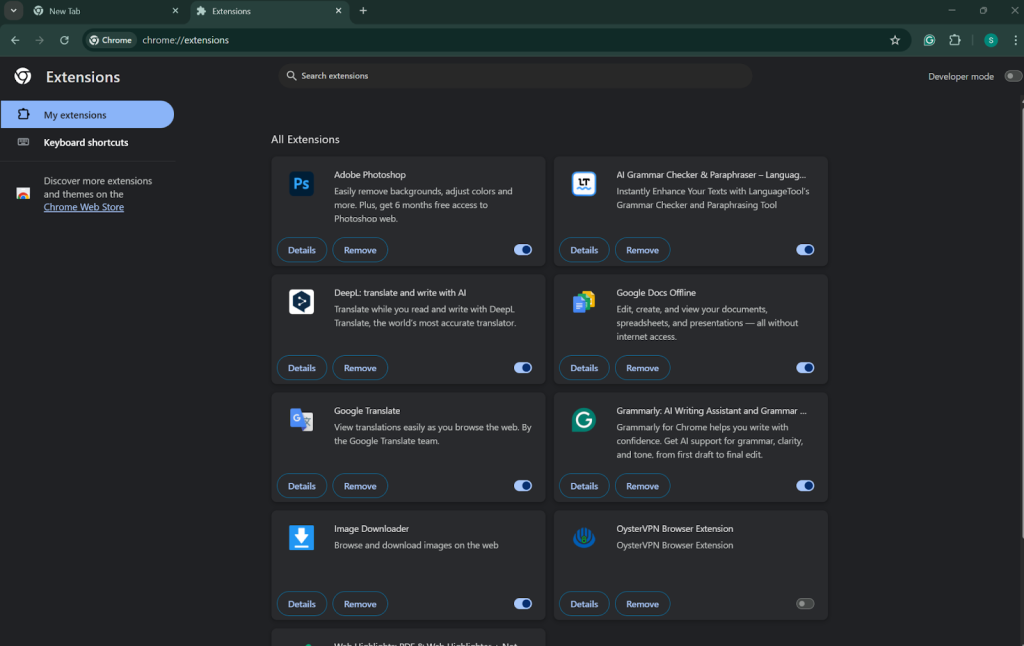
- Try accessing the website that was showing the 400 error
- If the error disappears, re-enable extensions one at a time
- Test the website after enabling each extension to identify the problematic one
- Once identified, consider removing the problematic extension or looking for alternatives
- Check if the extension has available updates that might fix the issue
5Method 5: Check File Size When Uploading
The server will return a 400 Bad Request response if the file exceeds the maximum upload file size, and compressing the files or increasing PHP memory limit are likely your best options. The problem is that this file size limit isn’t always communicated clearly on the site, meaning that users will often not learn about it until they hit it.
Steps to resolve file size issues:
- First you better consider uploading small test file to determine whether the issue is being cause by it
- If you have a problem, read the site docs or help section to find file size limits
- For images: Compress using tools like TinyPNG, JPEG Optimizer or reduce dimensions
- For video: Consider encoding with HandBrake or uploading to YouTube/Vimeo instead
- If documents are the issue: Trim down large images, compress embedded objects, or save in an alternative format
- For audio: Compressed MP3 or SoundCloud is good.
- Try to split it into more files and smaller size of file if possible.
- Also see if there is another way to upload (i.e. FTP) if the file needs to be that big.
6 Method 6: Try a Different Browser or Device
Web requests, cookies and cache are treated differently by different browsers, each with its own oddities and compatibility problems. What’s triggering a 400 error in Chrome could be accepted without complaint by Firefox or Safari. Also, testing using a different device will make you drill to the basement of whatever is actually causing you the 400 bad request.
Steps to test with different browsers/devices:
Update your original browser to the latest version before switching permanently
- Download and install an alternative browser if you don’t already have one (Firefox, Edge, Safari, Opera)
- Open the alternative browser without signing in or importing settings
- Navigate to the website that was showing the 400 error
- Test the same action that triggered the error originally
- If using a mobile device, try both Wi-Fi and cellular data connections
- If the website works in the alternative browser, the issue is likely browser-specific
- If the error persists everywhere, it’s probably a server-side problem
- In case of server issues, wait and try again later or contact the website’s support team
Turn errors into opportunities for optimization
Understand how 400 Bad Request errors affect performance and SEO, and see how UltaHost can help you diagnose and fix them with ease..
From a hosting infrastructure standpoint:
Modern hosting environments can detect and log 400 errors in real time, making proactive monitoring essential. With proper server logs and request filtering in place, most 400 Bad Request issues can be identified and fixed before they affect end users

Final Thoughts
The 400 Bad Request error can be scary at first, but with this set of troubleshooting methods in your toolkit, you now have the tools to deal with it confidently as you brush off the dust and move right along!
Start with the basic fixes such as examining your URL and clearing out your cache, and then proceed to the intermediate measures like flushing DNS or trying in a different browser. Just be patient and persistent, and you’ll be back online, and productive. in no time.
FAQs
What’s the difference between a 400 Bad Request error and a 404 Not Found error?
The 400 Bad Request error is an HTTP status code that means the request you sent to the website server, was somehow incorrect or corrupted and the server couldn’t understand it. A 404 Not Found error indicates that while the server itself understood the request it received from your browser perfectly well, the page or other resource you’re looking for was simply not there at that location.
Can a 400 Bad Request error be caused by server problems?
Yes, they can be caused at times due to server side problems (like misconfigurations, strict server limits or temporary server glitches). This is unlikely though, in contrast to the case of client-side factors. If you have tried all the troubleshooting steps on your end, it is probably an issue on the server side and only the website owner can quickly resolve that.
Why does the 400 error only appear on one specific website?
If you only encounter the 400 Bad Request error on one or a few websites, it may be something related to that server and not your computer.
Will clearing my browser cache and cookies delete my important data?
Clearing your cache and cookies will sign you out of most websites, so in that sense you’ll have to log back in using your username and password. It will clear some website preferences and customization. But it won’t erase your bookmarks, saved passwords (if you are using a password manager) or downloaded files.
Is it safe to disable all my browser extensions?
Yes, turning off browser extensions temporarily is a 100% safe and it is a common diagnostic process. Disabling extensions does not remove them or their data, it only disables them temporarily. You can re-enable the feature in a single click at any point.








