How to Flush You DNS Cache?
Much like a phone book a domain name system (DNS), bridges the communication gap between humans and computers by matching domain names to their respective Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. Although the main focus of this article is on “how to flush your DNS cache?“, it is important to first understand what DNS and the DNS cache are, so that we can understand the process of how to do it and why it’s necessary.
Let’s now go over the main topics that will be covered in this article:
- What is DNS?
- What is DNS Cache?
- How to Flush DNS Cache?
- Flushing Windows DNS
- Flushing MAC DNS
- Flushing Linux DNS
- How to Flush Browser DNS?
- Flushing Google Chrome Cache
- Flushing Yandex DNS Cache
- Flushing Safari DNS
- What to do if you still experience problems with your internet connection.
What is DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a system that divides the internet space into various segments and assigns a unique DNS address to each computer. Every website on the internet has a different DNS server.

Internet site names are expressed using IP addresses, which consist of numbers and can be confusing for users who are not familiar with computer languages. DNS is used to resolve specific domain names into IP equivalents to make it easier for people to use.
All domain names are associated with an IP address, and the process of searching for this IP address associated with a domain name is carried out by authoritative DNS servers. The address of a website is linked to the IP address of that website through the DNS server provider’s name servers.
What is DNS Cache?

DNS cache, also known as DNS resolver cache, is a database maintained by the operating system that temporarily stores the results of a DNS resolution request. The purpose of this cache is to speed up the resolution process by avoiding the need to query a remote DNS server every time a host name is requested.
Over time, the information stored in the cache may become outdated or stale, causing issues with accessing certain websites or slowing down the overall performance of the computer. To prevent these issues, it is recommended to periodically clear the DNS cache. Clearing the cache allows the computer to retrieve the most up-to-date information from the remote DNS server and ensures that internet browsing is faster and more efficient.
How to Flush DNS Cache?
There are different methods for flushing the DNS cache for a fast and secure internet experience. These methods can vary depending on your computer’s operating system and the type of internet browser you use. However, flushing the DNS cache is a simple process that can be performed easily on all systems. By following a few simple steps, you can obtain your current DNS address. There are three types of operating systems that are widely preferred by users in today’s technology. These are Windows, MAC, and Linux operating systems.
The steps for flushing the DNS cache are different for each of these, but they are all quite easy. Now, the UltaHost team will explain in detail how to flush the DNS cache in these three operating systems:
- Flushing Windows DNS:
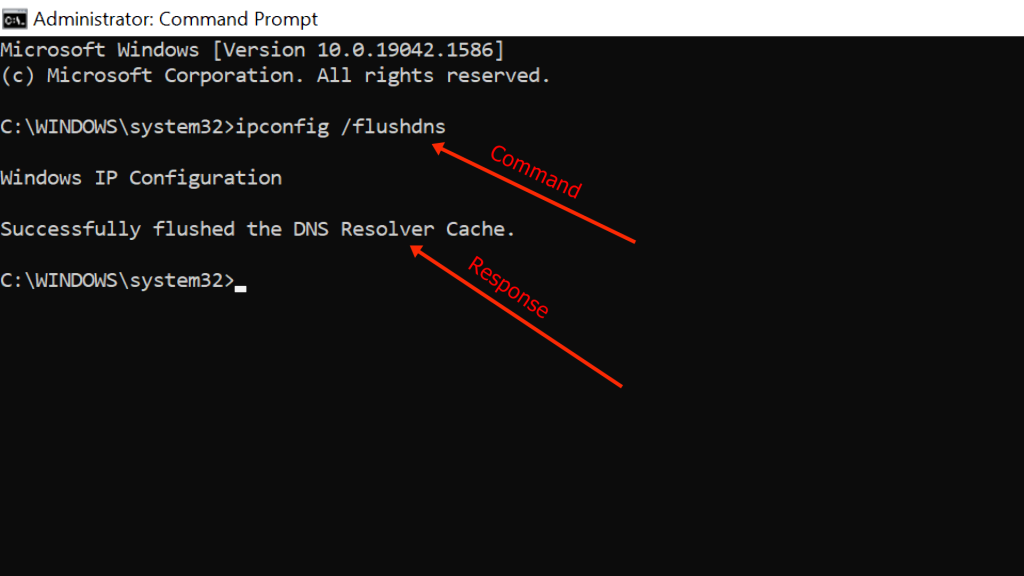
On your Windows computer, follow the Start > Run path or use the Windows + R keys to open the Run dialog. Type “cmd” in the dialog box and press OK. In the opened console, execute the following commands in sequence. Make sure to press enter after each command.
- ipconfig /flushdns
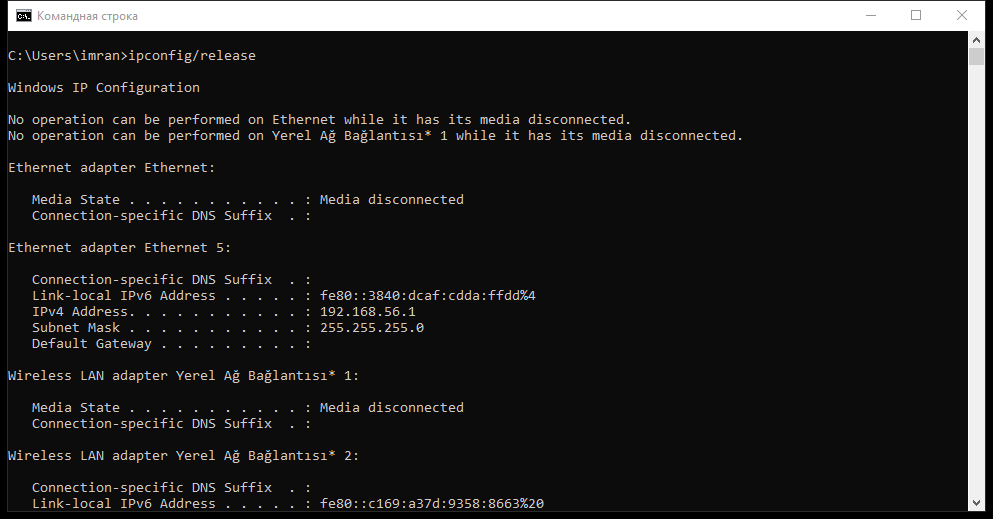
- ipconfig /release
- exit
This process will clear the DNS cache on your computer.
- Flushing Mac DNS
In the search bar, type “Terminal” and in the opened window enter the appropriate commands for your operating system. Then press enter to easily complete the DNS flush process.
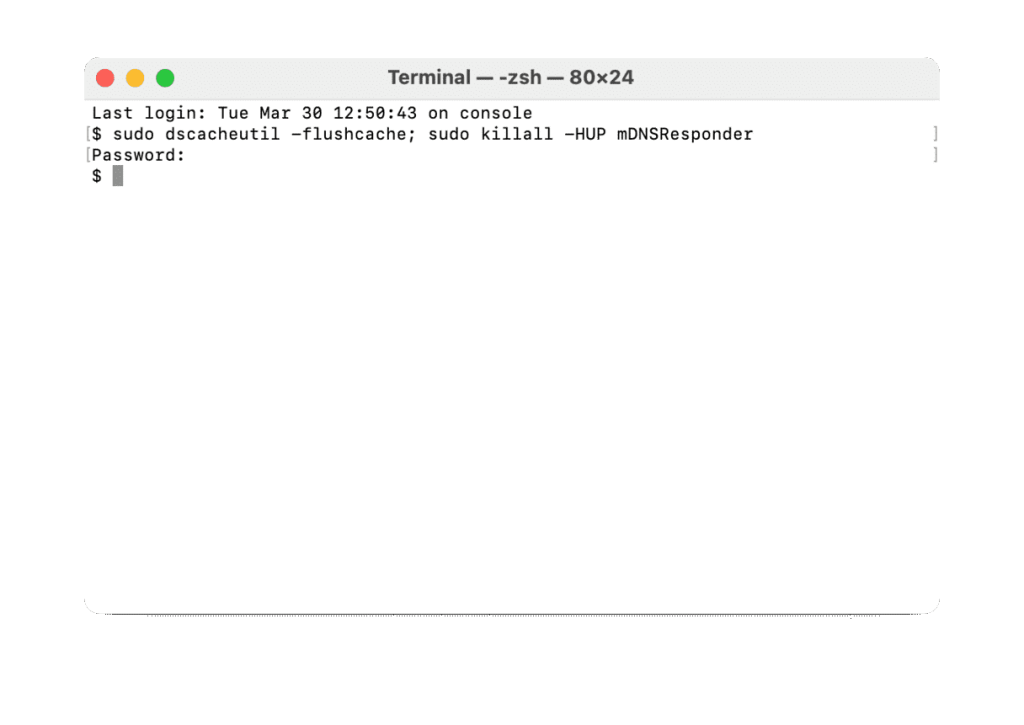
• Mac OS X 10.5.1 and earlier versions: sudo lookupd –flushcache
• Mac OS X 10.6: sudo dscacheutil –flushcache
• Mac OS X 10.7, 10.8 and 10.9: sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
• Mac OS X 10.10 Yosemite: sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
- flushing Linux DNS:
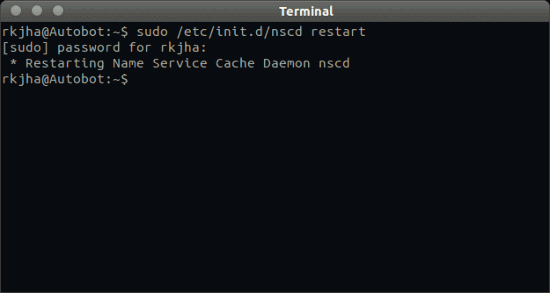
In a computer using Linux operating system, flushing the DNS cache is very simple. You just need to type /etc/init.d/nscd restart in the command prompt opened with the root command. After flushing the cache through the operating system settings, you can check by using your web browser. There will be a noticeable improvement in your internet speed after the DNS cache is flushed.
How to Flush Browser DNS?
Sometimes, clearing the DNS cache only through the operating system may not be enough. If you still face similar slowdowns and issues after clearing the cache, cleaning your browser cache can also be helpful. Clearing the DNS cache in various internet browsers is also simple with a few steps. It is useful to examine some of the commonly used browsers in terms of usage. For users of Internet Explorer, which is one of Microsoft’s official applications, the cache clearing process may show small variations according to the version of the browser. For clearing the DNS cache in older versions of the browser, go to Tools > Options > General, and click on Browsing History. You can easily perform the cache clearing process through the “Clear” option in this section.
In the newer versions of the browser, when you click on the “Tools” option in the top tabs and select “Delete Browsing History,” the page that opens make sure to check the options “Preserve Favorites website data,” “Temporary Internet Files and Website Files,” and “Cookies and Website Data.” Then, you can easily complete the process by clicking the “Clear” button.
Flushing Google Chrome DNS Cache
If you use Google Chrome, click on the three dots or three lines button located just below the close button. This will give you access to the control and customization panel. Select “History” and select the time range you want from the window that opens when you click “Clear Browsing Data” in the left-hand side of the window that opens. After checking the options in the menu, simply complete the process by clicking the “Clear Data” button.
Flushing Yandex DNS Cache:
In Yandex browser, navigate to Settings > Other > Clear History, reach the “Clear these items” list, select the time range you want to clear cache and make sure to check the option “cached files.” If you only want to clear browser cache, don’t forget to turn off all other options. Finally, complete the process by clicking the “Clear” button. Note: The process of clearing the cache in Yandex browser can be easily completed in a few steps.
Flushing Safari DNS Cache:
If you use Safari browser, you can clean your DNS cache by first going to your browser’s settings through the gear button in the upper right corner. Then, you can complete your process by using “Preferences” and “Reset Safari”. In the window that appears, you can check other history data as desired and successfully perform the process by pressing the reset button.
Many browsers have similar processes for clearing the DNS cache with just two to three steps. Mozilla Firefox users can clear their recent history from the browser tools and Opera users can easily clear their history from Tools > Settings > Clear Personal Data section. After successfully completing both the browser and the computer’s DNS cache-clearing process, you can observe a positive impact on the speed of the browser.
What to do if you still experience problems with your internet connection.
If you still experience the same after flushing your DNS cache, the first thing to do is to try and restart your router. This should help reset the connection, as well as clear any temporary errors that may have occurred during the process of flushing the DNS cache. If this does not fix the issue, then it may be necessary to call your ISP (Internet Service Provider) or consult their online support resources for assistance in troubleshooting the issue. Additionally, if you are able to access other websites without difficulty while having trouble with one particular site, it could indicate a problem specific to that website’s hosting provider or an issue related to its server configuration. It could also be a sign of a larger problem such as a network-wide issue or even malware causing interference with your internet connection.
Flushing your DNS cache is an important process that you should do on a regular basis in order to keep your computer running smoothly. Flushing your DNS cache can help resolve certain issues that you may be having with your internet connection or with specific websites.
As Ultahost, we are passionate about sharing our knowledge. We believe that both reading and listening are important for fully understanding a topic. That’s why, after you finish reading our blog, we encourage you to click on the provided link to watch a related video.
We truly appreciate your dedication in following our blogs and hope you find the information helpful. Thank you so much for being a part of our community…