Did you know that most of the world’s data is new? In fact, over 90% was generated over the last half a decade. This mammoth data volume needs storage space. That is where data centers enter the frame. In this article, we delve deeper into the technology, understand data storage, and discuss data center tiers.
At their core, data centers are buildings for housing massive computer systems. They are ranked by their capability and categorized for ease of use. Let’s walk you through the different data center tiers and explain everything you need to know to choose the right data center near you. Let’s start!
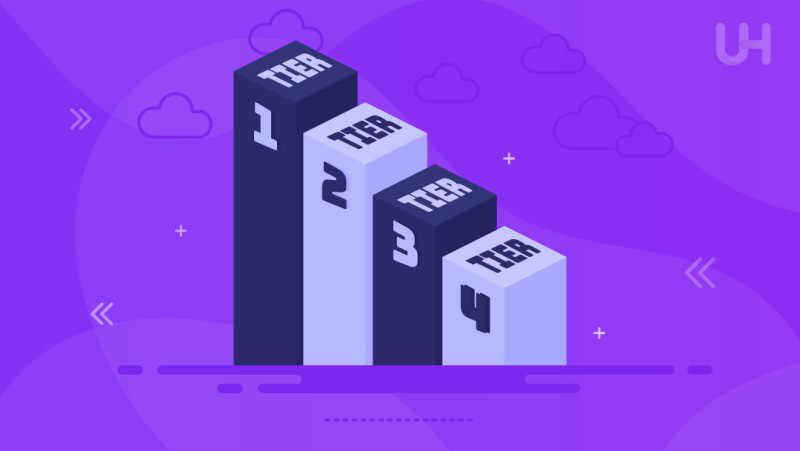
What are Data Center Tiers?
Data Center Tiers classify its performance, redundancy, and reliability. They help businesses align their IT infrastructure with operational needs. The Uptime Institute has defined four primary tiers, each representing different levels of availability and uptime guarantees. Let’s quickly glance at the classification:
Tier 1: Basic Capacity
A Tier 1 data center provides the essential components for data hosting but offers minimal redundancy. It ensures a 99.671% uptime, equating to about 28.8 hours of annual downtime. This setup is suitable for small businesses with non-critical applications that can tolerate planned downtime for maintenance. However, it lacks the robust backup systems of higher tiers, so unexpected disruptions can lead to service outages.
Tier 2: Redundant Capacity
Tier 2 data centers improve reliability by introducing partial redundancy in power and cooling systems. With 99.741% uptime and about 22 hours of downtime per year, they are ideal for mid-sized businesses that need a balance between cost and uptime but can still manage occasional downtime. These centers have backup systems in place but lack full equipment for concurrent maintenance.
Tier 3: Concurrently Maintainable
Tier 3 data centers take redundancy a step further by allowing concurrent maintenance without affecting operations, making them highly reliable. They offer 99.982% uptime, meaning only about 1.6 hours of annual downtime. With multiple power and cooling paths and N+1 redundancy, Tier 3 is the enterprise favorite. Since they can’t afford major interruptions for critical applications.
Tier 4: Fault Tolerant
The pinnacle of data center performance, Tier 4 facilities provide full fault tolerance with 2N+1 redundancy. This means that even in the event of a failure, there’s a backup system ready to take over without disrupting services. With 99.995% uptime, translating to just 26 minutes of downtime per year, organizations that require constant availability, such as financial institutions and government agencies, use Tier 4 data centers.
Is There a Tier 5 Data Center?
Tier 5 is the newest data center standard. It comprises all the criteria of a Tier 4 data center and adds a few new requirements. While the Uptime Institute has yet to officially announce its existence, there have been discussions about what it would look like.
Tier 5 data centers must include the ability to run the network without water, implement an external air pollution detection system, operate as Green Data Centers that run on renewable power, install permanently mounted stored energy system monitors, provide securable server racks, and meet many more requirements.
Data Center Tiers Explained: Who Sets the Tiers?
The Uptime Institute sets the standard for classifying data center tiers. Here are the factors that the authorities consider.
- Redundancy and Uptime: The amount of time annually that a data center is expected to function and the measures taken to prevent downtime.
- Efficiency and Sustainability: How efficiently a data center utilizes available resources and adapts to new technology.
- Cost: The total cost to run a data center
- Security: The security measures enforced to protect user data from unauthorized access.
What is the Role of Data Centers in Web Hosting?
Data centers play a critical role in web hosting by providing the infrastructure needed to store, process, and deliver websites to users around the world. Here’s how data centers underpin web hosting.
Physical Infrastructure
At the core of web hosting are the physical servers that host web applications. Data Centers house these servers in highly secure, climate-controlled environments with robust power supplies and internet connectivity. This ensures that websites remain accessible and protected from physical threats like unauthorized access, fires, hardware failure, etc. So, if you are using a WP secure hosting plan, chances are, it’s housed in a physical data center.
Redundancy and Reliability
Data centers are designed with multiple layers of redundancy for power, cooling, and networking, ensuring that websites experience minimal downtime. Depending on the tier of the data center, redundancy systems like backup generators and multiple internet connections are in place to prevent outages.
Higher-tier data centers (e.g., Tier 3 and Tier 4) offer higher uptime guarantees, which is crucial for businesses that require their websites to be accessible 24/7. We recommend upgrading to a dedicated hosting server to handle increasing traffic needs. You can also use an uptime-checking tool to track recent website downtime.
Scale Your Business with MAC Dedicated Servers
Ultahost’s Macintosh dedicated server hosting plans allow you to use Apple software without purchasing Mac hardware, Enjoy our powerful and cheap Mac OS Bare Metal servers.
Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow, their hosting needs can change. Data centers offer scalable resources, allowing web hosts to add more storage, bandwidth, or computing power as needed. This flexibility is crucial for websites with fluctuating traffic, such as eCommerce platforms during peak seasons. This is why we recommend upgrading to a High RAM VPS for eCommerce businesses.
Security
Data centers provide robust security measures, including firewalls, encryption, and physical security protocols. These protections safeguard the servers that host websites from cyberattacks, data breaches, and physical intrusions. This is especially important for businesses handling sensitive data like customer information or financial transactions.
Efficiency and Sustainability
Modern data centers are built with energy efficiency in mind. Hosting providers leverage innovations such as energy-efficient cooling systems and renewable energy sources to minimize their environmental impact, which is becoming an increasingly important factor for businesses.
Conclusion
Data centers provide an essential framework for streamlining business operations. Therefore, it’s crucial that you ask the right questions to potential storage and web hosting partners to ensure the complete safety of sensitive data. Ultimately, whether you should opt for a Tier 1, 2, 3, or 4 data center will depend on your requirements and budget. So, you must evaluate your business needs before choosing.
Looking for a powerful web server for your high-traffic website? Choose Ultahost’s SSD Dedicated Server for robust performance and cutting-edge security. Enjoy managed servers, SSD NVMe storage, and DDoS protection, starting at just $74.83/month.
FAQ
What is a data center?
A data center is a facility that houses servers and IT infrastructure to store, manage, and process data.
What does a data center do
Data centers manage, process, store, and disseminate large amounts of data for organizations, businesses, and governments.
What does Tier mean in a data center?
A data center “Tier” refers to its classification based on uptime, redundancy, and performance.
Which is the best data center tier?
Tier 4 is considered the best because it offers the highest level of redundancy, fault tolerance, and uptime (99.995%).
How do I find the right data center tier for my business?
The right data center tier depends on your business’s needs, uptime requirements, and budget. Smaller businesses with less critical operations may opt for Tier 1 or 2, while companies needing high availability and minimal downtime should consider Tier 3 or 4.
What is a Tier 5 data center?
A Tier 5 data center is an unofficial term used by some companies to describe data centers that go beyond Tier 4 standards.
What is the difference between Tier 4 and Tier 5?
While Tier 4 offers fault tolerance and redundancy, Tier 5 (unofficial) adds advanced features like enhanced security, sustainability initiatives, and more robust disaster recovery measures.