Digital transformation places unprecedented demands on unprecedented data centers, forcing them to be ever more agile, efficient, and scalable. Hyperconverged infrastructure leads this revolutionary approach that converges computing, storage, and networking into a single, software-defined system. HCI simplifies operations and reduces complexity, changing how organizations manage their IT infrastructure.
In this article, we will explore how hyper-converged infrastructure is really changing data centers, how the basic entity works, and its many benefits that also come along. We will look deeper into its key components, compare these with traditional converged infrastructure, and discuss some of their practical applications across different fields.
What is Hyperconverged Infrastructure?
Hyper-converged infrastructure represents the next-generation IT architecture, with storage, computing, and networking combined in one block, united by a common management plane. While traditional data center architectures have servers, storage systems, and networking equipment implemented as hardware silos, HCI uses software-defined technologies to deliver these functions in virtualized constructs. This, in turn, consolidates management, improves efficiency, and provides an open, modular architecture that is scalable according to needs.
A central tenet of HCI is a solution that relies on commodity hardware and sophisticated software capability. An organization can abstract out dependencies on physical hardware and deploy infrastructure that scales flexibly to dynamic workloads without expensive proprietary solutions. This paradigm shift enables the alignment of IT resources with operational demands.
How Does HCI Technology Work?
HCI works by abstracting traditional IT components through virtualization concepts and then combining them as an integrated platform. Virtualization software’s core role is pooling resources from multiple hardware units and creating VMs and storage environments. Algorithms then orchestrate these to ensure optimal performance and utilization.
Another important piece of HCI is SDN (Software-Defined Networking) and SDS (Software-Defined Storage). These technologies let the administrator manage network traffic and data storage via software interfaces without having to tinker with hardware configurations. In other words, they make infrastructure agile, responsive, and adaptive to each workload change without administrative interference or any downtime.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure vs Converged Infrastructure

As organizations evaluate various ways to modernize their data centers, it is important to understand some key differences between hyper-converged and converged infrastructure.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure
HCI does not require separate hardware silos for computing, storage, and networking resources but integrates these resources into one solution. Managed through a software-defined layer, HCI simplifies infrastructure management, bringing unmatched scalability. Besides, its modular design helps an organization increase resources in increments, thus aligning costs with growth. Furthermore, HCI will be ideal for organizations embracing hybrid cloud models since it perfectly integrates with cloud platforms.
Converged Infrastructure
Converged infrastructure, though containing compute, dedicated storage server, and networking in a single entity while maintaining all of these modules as independent entities inside itself, performs on an operationally independent module but requires dependency interrelation; generally, they get vendor lock-in. CI simplifies operation for rather static, predefined workloads without flexibility or expandability that can be needed in more dynamic environments with an HCI solution.
Key Components of Hyper Converged Infrastructure
Transitioning to hyperconverged infrastructure requires rightly understanding what it is and the components that make it all possible.
Hypervisor
The hypervisor is a virtualization layer that abstracts compute resources and assigns them to virtual machines. It provides a means of effectively utilizing resources, isolating workloads, and dynamic scaling, hence achieving optimal performance for diverse applications.
Nodes
The nodes are the building blocks of HCI. Each node is a package of computing, storage, and networking resources. Clustering such nodes working in cohesion to provide infrastructure as single systems adds resilience and redundancy to it.
Power Your HCI Technology with 10Gbps Speed!
Looking to supercharge your hyperconverged infrastructure with lightning-fast connectivity? UltaHost’s Fast 10Gbps Dedicated Server delivers the speed and reliability your business needs to optimize performance.
Compute
In HCI, the compute resources address the processing capability of applications and workloads. Resources are spread across nodes to ensure balance and scalability within the infrastructure.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN abstracts and centralizes network management, which permits dynamic configuration and data traffic optimization. It also ensures that virtualized components can communicate with each other efficiently while reducing hardware dependencies.
Software-Defined Storage (SDS)
SDS pools the storage resources across all nodes into one virtualized resource pool, thus offering data management flexibility, better performance, and easier disaster recovery.
Benefits of Hyperconverged Infrastructure
Indeed, the adoption of hyper-converged infrastructure brings some key benefits that meet today’s IT challenges.
Scalability
Hyper-converged infrastructures are supposed to enable an organization to scale up its resources seamlessly and uninterruptedly when the demand increases. In contrast to a traditional architecture, which requires planning and up-front investments, in HCI, a node is added to the system with very minimal effort, thus enabling modular growth. This allows organizations to scale incrementally without overprovisioning, reducing waste, and supporting economic expansion. In this regard, the feature is priceless for businesses working with variable workloads and also growth-oriented operations.
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most striking advantages of HCI is cost-effectiveness. By consolidating storage, networking, and computing into a single, integrated solution, HCI removes the need for expensive legacy hardware. Besides, operational costs reduces because fewer IT specialists manage the infrastructure. Automation within HCI systems reduces labor costs even more by making administrative tasks easier. These savings, over time, can greatly improve the return on investment for businesses using HCI solutions.
Data Protection and Resilience
HCI systems are designed with strong data protection features, natively providing redundancy and disaster recovery. HCI distributes Data across nodes so that operations cannot be disrupted in case of a hardware component failure. Advanced backup and recovery solutions in HCI platforms make it easier to restore critical systems faster. Moreover, these features make HCI a perfect choice for organizations where data integrity and uptime are top priorities.
Automation and Efficiency
Intelligent software integration in HCI means a high degree of automation in the said context. This is where administrative tasks, such as provisioning, scaling, and updating, can be done on the systems with little or no human intervention. Smoothing reduces human errors and speeds up IT processes, freeing the IT staff time for more strategic pursuits. Automation ensures consistency in performance and adds to overall operational efficiency.
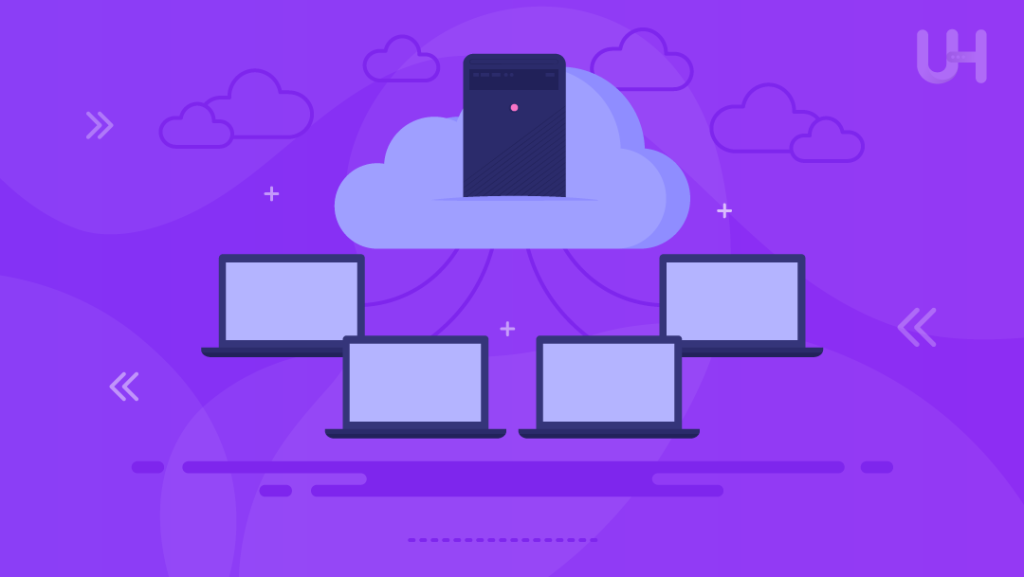
Compatibility for Hybrid Environments
HCI is fully compatible with both hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, hence becoming the perfect fit for modern data centers. This means businesses can integrate public and private cloud platforms into their environments with flexibility, fully adapted to the needs of a particular business. Lastly, it enables companies to take the best of two worlds without compromising performance and security: on-premises control with the scalability option of cloud solutions.
Use Cases for HCI Technology
With its flexibility, hyper-converged infrastructure fits into many industries, applications, and more.
Healthcare
HCI technology is in demand in the healthcare sector, with large volumes of sensitive patient data. For instance, EHRs require high-performance, scalable solutions, ensuring data privacy, as do other medical technologies like telemedicine and diagnostic imaging. With such demands, HCI provides a secure and highly centralized infrastructure while providing ease in disaster recovery. It further simplifies compliance with the regulatory standards of HIPAA and makes it easier for healthcare providers to keep up-to-date with their legal requirements.
Financial Services
Real-time data processing and analytics are some of the most important features in financial services for fraud detection, transaction processing, and market analysis. HCI provides the low-latency performance such time-critical applications require. This is enhanced with built-in data protection to protect sensitive customer information, ensuring business continuity during outages or cyberattacks. Scalability within HCI means that financial institutions can easily thrive with growing transaction volumes and a swelling customer base.
Retail
HCI in retail is used to achieve high-level supply chain management, inventory tracking, and customer relationship management systems. The rise in e-commerce calls for infrastructure that can bear traffic volumes and also provide real-time visibility into customer behavior. With HCI, data from various channels seamlessly integrates, ensuring an efficient customer shopping experience. It can support edge computing applications for in-store processes, such as self-checkout systems and in-store analytics.
General Business Uses
HCI technology serves a wide range of general business needs, providing a foundation for modern IT environments. Key applications include:
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): A virtual desktop infrastructure provides a convenient, high-performance VDI while simplifying management by increasing security.
- Data-Intensive Applications: Provides high computing and storage VPS for analytics, AI, and machine learning workloads.
- Edge Computing: It brings compute power closer to the source of data generation, which means higher velocity with reduced latency.
- Hybrid Cloud and Multicloud Strategy: It seamlessly integrates on-premise infrastructures with cloud platforms for flexibility and scalability.
Conclusion
Hyperconverged infrastructure represents a milestone in modernization within the data center. Compute, storage, and networking in one platform give HCI an unparalleled ability to scale, be cost-efficient, and be resilient. The ability to adapt to different kinds of workloads and to support hybrid cloud environments makes it a cornerstone for future-ready IT strategies. Adoption of HCI is not an option but an absolute necessity for any organization to stay competitive in a digitally aggressive landscape.
For businesses aiming to maximize the efficiency of their hyperconverged infrastructure, leveraging NVMe VPS from UltaHost offers unparalleled speed and performance. Experience faster data access, reduced latency, and seamless scalability.
FAQ
What is hyper-converged infrastructure?
HCI combines computing, storage, and networking into a unified, software-driven system for easier management.
How is HCI different from traditional setups?
HCI integrates hardware components into one system, reducing complexity and costs.
Does HCI work with hybrid clouds?
Yes, HCI integrates seamlessly with hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Which industries use HCI most?
HCI greatly benefits healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and general businesses.
Is HCI good for SMBs?
Absolutely. HCI’s scalability and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal choice for SMBs looking to modernize their IT infrastructure without overspending.
How does HCI protect data?
It offers built-in redundancy, disaster recovery, and backup for data protection.
What are HCI’s key components?
Key components include hypervisors, nodes, compute, SDN, and SDS.