The Domain Name System is a silent orchestrator in the vast expanse of the World Wide Web. It conducts a symphony of connectivity, defining the online experience. This guide embarks on the journey to decode the nuances of DNS.
The Primary Role of DNS
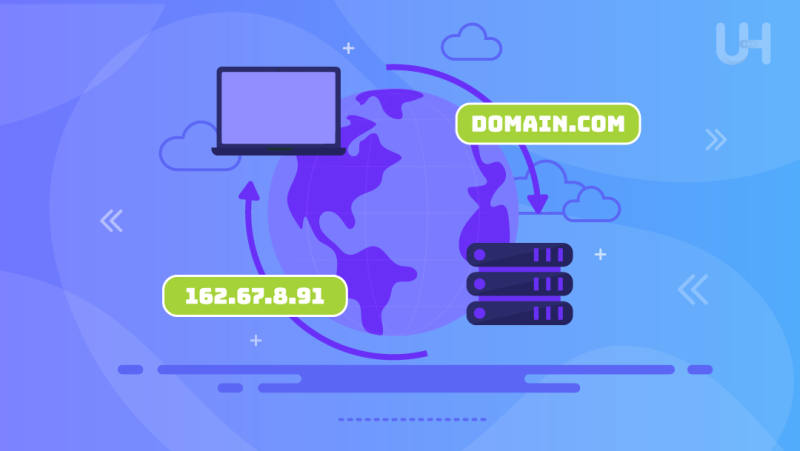
The Domain Name System (DNS) operates as the translator of user intent, converting domain names into numerical language of IP addresses. This translation facilitates effective communication between the servers hosting the websites and the user device.
DNS Cache: Meaning & Aspects to Consider
A DNS cache is a temporary storage area on a network or device where previously resolved domain names and their IP addresses are stored. DNS caching’s purpose is to boost the process of domain name translations into corresponding IP addresses.
Although DNS caching plays a pivotal role in accentuating the efficiency of web browsing, an outdated or overloaded DNS cache may lead to problems, impacting the overall experience. Some aspects to consider are:
- Performance Advantages DNS cache stores previously resolved domain names and IP addresses, resulting in faster resolution. When the website is revisited, the device can quickly retrieve the IP address from the cache instead of performing a new lookup. Hence, the loading time is reduced.
- Problems with Outdated and Overloaded Cache On the one hand, the DNS cache reduces loading speed. On the other hand, it leads to stale entries and slow updates. If the cache contains incorrect and outdated information, it results in connectivity issues. This primarily happens when websites change their IP addresses, but the cache retains the old entry. Additionally, some systems do not update the DNS cache as frequently as required. So, changes do not reflect instantly.
DNS Cache Clearing
With time, devices accumulate a cache of outdated DNS records. Clearing the DNS cache is an effective troubleshooting step to implement if you encounter issues like difficulty accessing websites or slow browsing. Clearing the cache ensures that the device fetches the accurate and latest IP address information so that connectivity issues are remedied, and browsing speeds are accelerated.
Here are the steps to clear the DNS cache:
macOS To clear cache and reset DNS Mac manually, you have to know the macOS version you are running and then use the Terminal app. Check the macOS version by clicking on the Apple logo and selecting About This Mac. The steps for Ventura, Monterey and Big Sur are:
Launch Terminal > enter sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder > enter password > press Return.
Windows On Windows, you can clear the DNS cache by opening Command Prompt as an administrator and entering ipconfig /flushdns. Press Enter.
How to Configure DNS Settings?
1. Selecting the apt DNS Server
ISPs assign a default DNS server, but you can opt for a more secure and swifter alternative. Open DNS and Google DNS are popular choices.
2. Configuring the Settings
On macOS:
Go to System Preferences > click Network > choose your active connection > select Advanced > click the DNS tab > add your preferred DNS server.
On Windows:
Open Network and Sharing Center > select your active connection > click Properties > choose Internet Protocol Version 4 Properties > select Use the following DNS server addresses > enter your preferred DNS server.
What is DNS Security?
DNS security extensions serve as the guardians of the online sanctum, preventing malicious activities like cache poisoning and DNS spoofing. By integrating security extensions, you can fortify your web interactions and ensure your safety while browsing the Internet.
Thanks to a robust DNS infrastructure, you can enjoy a reliable and swift Internet experience. Resolution of domain names will be expedited, and your online activities will be turbo-charged with a well-configured DNS setup.
DNS Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks
You will face roadmaps along the way when traversing the digital realm. The common DNS problems and solutions are:
- Slow and lethargic browsing – The solution to this is to switch to a faster DNS server and clear the DNS cache.
- Error-laden IP resolutions – Flushing the DNS cache will resolve this issue. This problem is caused because the DNS cache stores inaccurate and outdated DNS information. Also, you must double-check the configured DNS server addresses.
- Inaccessible DNS server – Switch to a different DNS server or check your Internet connection to resolve this problem.
The Bottom Line
DNS is the GPS for your online sojourn, and it is essential to understand how it works to orchestrate your digital experience. Configuring and clearing DNS will ensure a secure, faster, and reliable browsing experience.
Hopefully, this guide clarifies the meaning and significance of DNS. Also, now you know how to clear the DNS cache on your device so you can have an incredible experience when surfing the Internet.
Have you faced any issues with DNS while browsing the web? Do you have any suggestions for users wanting to change the DNS server? Leave your comments without hesitation.
Understanding DNS is just the beginning of your online journey. Ultahost offers a seamless transition from knowledge to action with our exceptional domains. Your digital identity starts here. Explore our domain solutions and embark on a future where your online presence truly stands out. Don’t just understand DNS; own it with Ultahost domains today!