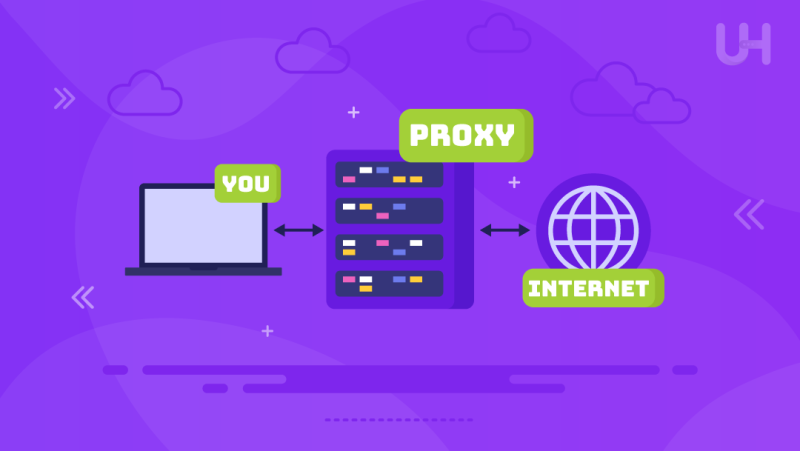
A proxy server is a type of computer that acts as an intermediary between a user’s device and the internet. These proxy servers are responsible for sending user requests to the internet on their behalf, reporting back the results to the latter. Therefore, the proxy server functions as a security gate by concealing the user’s actual IP address and providing other services such as security, privacy, and caching. Apart from that, proxy servers are also efficient in safeguarding sensitive information over the Internet, assisting in the management of privacy, and aiding in the management of the network. The proxy server conceals the identity of the user; hence, the user does not suffer any direct contact with the websites they wish to visit.
The proxy server also manages internet traffic by filtering certain content and restricting access to dangerous sites. Most of today’s web browsers incorporate this server to ensure that browsing is both secure and efficient. In this blog post, we will cover the definition of proxy servers and their function.
What is a Proxy Server?
Proxy serves as a link/uniting website for the internet and proxy service users. In simple bass terms, a proxy server is a computer that acts as a gateway between the user and the web. The user makes his/her request from the proxy server, which in turn serves the request with that of a web server. The web server responds to the request and sends the proxy server the needed information from the web document. There is increased security and privacy for the user. Proxy servers test all the traffic on a certain network, therefore enhancing performance. Proxy servers streamline the delivery of static files, ensuring that even pages burst open when they are rendered and that there are no needless delays on freestanding pages with their summonses to come online.
Basic Function: Acting as an Intermediary
As such, a proxy server works as an intermediary between a client and a server. In case you wish to visit a certain website, the proxy server will get the information from the website that you aim to visit. Furthermore, It fetches the response or data from the web server and objectively sends it to your device. They also offer middleware services such as managing transactions, sending messages, and connecting to other databases. It is this way of communicating that is indirect control, which thus monitors the control of the flow and movement of data. Enhancing the security of information systems and administering traffic to the internet over a network helps improve performance.
For instance, consider a user who wants to visit a certain website. First of all, a proxy server submits a request to the server, collects the intended web page, and subsequently streams it back to the user. Ordinarily, this entire process is done automatically, where it becomes unnoticeable, yet the efficiency of the interaction between the user and server is preserved.
Types of Communications Facilitated by Proxy Servers
Proxy servers enable diverse types of communication, particularly for browsing the internet.
- HTTP Requests: The most popular communication method with the internet is HTTP. When you browse a website and make a request through your browser, the proxy server passes that HTTP request to the relevant website server. The server retrieves the information that you need and sends it to you, after which that information is returned to you. This is how the process circulates for all sites that do not have secure connections.
- HTTPS Requests: This is the same as HTTP, but it applies to securing websites. The encrypted nature of HTTPS requests ensures that the information that is sent from the user to the website and vice versa is secured. Proxies that service HTTPS requests have to decrypt the secure data, process the request, and then re-encrypt it before sending it to the user for access. Again, this enables data security and privacy while browsing.
- Other Services: Aside from HTTP and HTTPS, a proxy server can provide other services. For example, if a user wants to transfer files, they may process FTP (File Transfer Protocol) requests or even email their requests. Certain proxy servers are specifically dedicated to games, streaming, or circumventing specific geographic network restrictions.
IP Address Concealment
Proxy servers conceal a user’s dedicated IP address; this is one of the greatest benefits of a proxy server. While utilizing a proxy server, the websites and services that are visited would only see the proxy server’s IP address instead of the user’s actual IP address. Such practice ensures privacy and protects identity while surfing the internet.
For example, if you employ a proxy server in a foreign country, websites may assume that your traffic originated from that country, not from your location. This would be useful to try bypassing geo-restrictive conditions, such as accessing content exclusively available in certain regions or for anonymity. Furthermore, concealing one’s actual IP address may prevent potential cyber-attacks, tracking, and unsolicited targeted ads.
Protect Your Online Privacy with DDoS-Protected VPS
Are you ready to enhance your online security? With Ultahost’s DDoS-Protected VPS Hosting, you get incredible protection from a VPS as well as powerful DDoS protection. Keep your sensitive data and website protected from unnecessary breaches.
How does a Proxy Server Work?
Proxy servers serve as the boundary between the user’s device and the internet. Below is an explanation of how proxy servers work in steps.
Step 1: The User Sends a Request for Information
It starts when a user wants to visit a page or resource on the internet. A user types the address of the site on the search bar, or he or she uses an app that needs some information. There are different types of requests that are sent, and one of them is called the disposing request, where the user gives the address of the site or service that he or she wants to use.
Step 2: The Proxy Server Receives the Request
They do not go straight to the server of the requested website; rather, they first go to the proxy server. A proxy server will be one that sits between a user and a search engine. It receives requests made from the user’s device. The server checks what information a user wants and how best to serve it.
Step 3: The Proxy Server Forwards to the Destination Server
The proxy server subsequently makes the request to the destination server, that is, the web page or service that the client desires to fetch. At this stage, the proxy server can change the request by hiding an IP address so that identity protection is properly adhered to. The proxy server will not have any information about the client’s private internet protocol (IP) address. Hence, he will always respond to the proxy’s queries.
Step 4: The Destination Server Sends Information Back to the Proxy Server
The proxy server receives all the necessary data from the servers. After this, the proxy server should capture the server information. That is the webpage to be served or any other data requested. In all these processes, the user remains incognito, and his details are kept under cover.
Step 5: The Proxy Server Forwards The Data Back to the User
The proxy server completes the task by sending the response back to the user’s device. The user can now access the needed content, be it a web page, video, or file. Depending on the type of proxy being used, the user’s IP address is hidden, and extra security measures like encryption are provided.
Modifying Request and Response
In addition to this, proxy servers can manipulate both requests and responses in several different ways:
- Caching: If multiple clients request the same content at the same time, one of the proxy servers can store frequently requested content. This enables the proxy server to quickly serve the content without burdening the main server.
- Filtering Content: Proxy servers can restrict access to certain websites or ads using filtering rules. This can be implemented for security purposes where the organization’s policy enforces such restrictions.
- Compression and Optimization: Some of the proxy servers compress the data or optimize its contents for users with slower internet connections to improve overall performance.
Altering both the request and response helps a proxy server improve performance, manage access to the material, and increase security.

Types of Proxy Servers
There are many different types of proxy servers, and each serves a different purpose based on the requirements of the individual or network. Proxy types vary from those focused on user anonymity to others that enhance the performance of servers. Most users tend to look for proxy solutions that can be relied on to find the best proxy tailor-made for their needs. Let’s explore the key types of proxy servers and their functions.
Forward Proxy
As the intermediary between a device and the Internet, a forward proxy hides the user’s IP address for privacy. It ensures that only the proxy’s IP is visible, thus masking the user’s identity. Proxies serve a very important function when it comes to monitoring network activity and blocking certain websites. They are mostly used by corporations to monitor web traffic. Moreover, proxies help users who may want to access content that is restricted in their geographical region.
Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy performs the actual opposite of what a forward proxy does by managing the incoming traffic of a web server. It is positioned between the client and the server and controls the requests sent by users to the server. For the purpose of load balancing, a reverse proxy is very helpful. It prevents any one server from becoming overworked or overloaded by splitting the user requests among different servers. Apart from larger websites optimizing their performance, reverse proxies are often used to enhance website security.
Transparent Proxy
A proxy is said to be transparent when it does not change any requests or replies sent by the user as compared to the destination server. It simply captures and facilitates the exchange of traffic. As an example, businesses and educational institutions may be monitoring proxies in order to control internet usage or block access to certain websites. Many users, businesses, and educational institutions tend to prefer this approach because it is completely automated and leaves the user with no configuration to make. This proxy type is usually adopted in educational institutions where there is a need to monitor the content accessed.
Anonymous Proxy
Anonymous proxies prevent tracking by hiding devices’ IPs to ensure the user’s identity and location are not traceable. This makes them reliable for users who do not wish to expose any personal details restraining them from freely browsing the net. Anonymity is guaranteed while using this proxy type; hence, they are commonly used for anonymous browsing to control the serving of targeted ads or data captured from websites.
High Anonymity Proxy
A high anonymity proxy also called an elite proxy, hides the user’s IP address and level of activity on the internet. It provides the user with the greatest security possible to the user. This ensures that the websites that the user is visiting do not flag the proxy being used thus making the activity being done on the internet completely inconspicuous. High Anonymity proxies are useful when users don’t want to be tracked, for securing private information online surveillance or for browsing sensitive information where tracking is to be avoided.
Web Proxy Server
Proxy servers meant specifically for web traffic are known as web proxy servers. Web proxy allows the user to navigate and access web pages by allowing the connection to go through the proxy server. Due to web-based or geographic censorship, Web proxies serve as an easy way to overcome barriers. Web proxies are accessible for any user who browse casually on the internet ho wants to keep his identity hidden or wants to browse restricted content. In addition, they do help in masking the identity of the browser.
Web Proxy Server Explained
A web proxy server is a type of proxy that specifically manages web traffic. It operates as a middleman between a user’s browser and a certain website they intend to visit. After users ask for a certain webpage, the web proxy server goes ahead to ask the specific website for the page and sends the webpage back to the user’s browser while also masking the user’s real IP address.
How Web Proxy Servers Handle HTTP and HTTPS Traffic
Web proxy servers can manage both HTTP and HTTPS traffic. In the case of HTTP traffic a web proxy receives an unencryption request and retrieves an unencrypted answer. With HTTPS traffic, a proxy sets a secure connection between a user and the proxy server, which guarantees no information is altered as it moves through the conduit. The proxy sends the request to the destination server as encrypted and captures the response back to the user as encrypted.
Advantages of Using a Web Proxy Server
Proxies can unblock restricted websites, improve privacy, and shield web traffic.
Bypassing Content Restrictions
Web proxies are commonly used to evade internet restrictions. Such proxies serve to circumvent filters in settings like schools, offices, or areas with strict censorship accessible to the general populace. Proxy servers allow users to navigate around these barriers and access the content they need.
Accessing Geo-blocked Content
Proxy servers assist users in overcoming geographical limitations associated with certain content sites. Proxy servers make it possible to cross geo-blocked limitations by impersonating the user’s IP address, thereby providing access to restricted services or news websites in other countries.
Enhancing Privacy by Hiding the User’s IP Address
Utilization of the Proxyrack Residential Proxy provides users with more privacy by concealing one’s IP address. This enhancement of privacy makes it impossible for web users to trace the IP address used by the user, enabling them to practice online security through identity concealment and surveillance evasion.
Use Cases
Let’s discuss the use cases of proxy server:
Accessing Region-Specific Content
Perhaps the most recognizable use of proxy web servers is for accessing region-specific content where websites and certain streaming services restrict use based on a customer’s geographical location. By using web proxy servers, customers can access content that might not be accessible in their country as long as the web proxy server is located in a different region.
Enhancing Security in Public Wi-Fi Networks
Proxy servers also have their value in secured browsing through proxies where a user is protected during hijacking using public Wi-Fi networks. Public networks are mostly unsecured which brings the users at risk of cyber attacks and hackers. With the web proxy, there is encryption of a user’s internet traffic making it possible for the user to escape the interception of sensitive data like passwords or personal details.
Protecting Corporate Networks from External Threats
Proxy servers filter the incoming web traffic, enabling only the safe content to access the network and blocking all malicious websites that can compromise the network, so proxy servers are frequently used by businesses. Proxy servers are also useful in policy because some employees abuse browsing policies, proxy servers aid in enforcing policies by blocking access to certain types of websites guaranteeing safe browsing.
Benefits of Using a Proxy Server
Proxy servers add another layer of security by hiding identities and protecting users against threats from the internet. They also improve the rate of access control, allow users to escape geographical constraints on the internet, make the internet more accessible, and enhance browsing speed.
Improved Security and Privacy
Proxy servers protect the user’s IP address, thereby enhancing security and privacy. By encrypting, data is protected from hackers. Also, proxies can provide some level of protection against some forms of cyberattacks, such as DDoS attacks, by cleaning the traffic that comes to the user’s network of malicious traffic.
Access Control and Filtering
Proxy servers help with filtering and access control, meaning restricting access to certain information. They can help in blocking useful websites that may expose users to harmful or inappropriate content. In business environments, proxies are used to implement organizational rules.
Bypassing Geo-restrictions
Proxies assist users in evading geographical restraint noise. They make it possible to reach their sites or content that is restricted based on geographical boundaries. Users are also able to view content restricted from their regions by going through proxy servers situated in those regions.
Caching for Faster Browsing
Proxy Servers can keep content that is frequently accessed by users in their cache so that they do not have to constantly search for them on the internet. This gloriously helps reduce the loading times of websites and improves the general speed of browsing, especially for users who repeatedly visit the same websites.
Boost Your Website’s Security with Cloudflare VPS!
If you want to maximize your website’s capability and security, Ultahost’s Cloudflare VPS Hosting offers additional speed, Cloudflare’s network reliability, and an extra layer of protection.
Different Proxy Server Protocols
Proxy servers utilize a variety of methods to control internet traffic, each method tailored to specific requirements. Knowing the available methods helps in choosing the best method for a particular case.
HTTP Proxy
Almost all proxies filter HTTP traffic, pass requests from clients to web servers, and serve data back to clients. Only a small fraction of the users who use HTTP proxies even know they are proxies. These are the basic kinds of HTTP proxies. Their major downside comes from their lack of ability to encrypt or handle sensitive HTTPS traffic which is popularly used today. Don’t risk your data privacy. Proxies that perform these activities are absolutely useless without providing sufficient protection.
HTTPS Proxy
An HTTPS proxy improves the safety of a user’s internet communication. It takes care of HTTPS traffic and encrypts all information transferred between the client and the destination server. The key distinction between HTTP and HTTPS proxies is that an HTTP proxy allows the transmission of non-encrypted information while an HTTPS proxy does not, safeguarding sensitive details such as passwords and credit card numbers. As such, HTTPS proxies are critical for secure browsing and online transactions. This also makes them more preferable than HTTP proxies in terms of privacy protection.
SOCKS Proxy
SOCKS proxy is a type of proxy that is adaptable and supports a variety of traffic. These include HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and many others. Unlike HTTPS and HTTP proxies, SOCKS have no regard for the information they are given and, therefore, do not check it or alter it. This characteristic makes them suitable for a wide variety of purposes. SOCKS proxies are frequently used for peer-to-peer file sharing, gaming, and web application firewalls or network limitations that may prohibit certain types of traffic. Because they are non-web based and can easily bypass sophisticated network filters, SOCKS proxies serve best when dealing with non-web protocols.

Common Proxy Server Uses
There are various ways to utilize a proxy server and achieve specific purposes. With the assistance of a proxy server, users and companies can bypass content restrictions, ensure privacy, and manage the flow of internet traffic. Discussed below are some of the most popular applications for proxy servers:
Bypass Content Restrictions
Proxy servers are predominantly used to bypass geographical restrictions. Later serves can easily avoid geographical content limitations by routing their internet traffic through a proxy server based in a different location. For instance, streaming services that are not available in certain countries can be accessed using proxy servers.
Anonymous Browsing
Proxy servers are commonly used for anonymous browsing. Proxy helps enhance security levels for the IP addresses of companies and individuals and ensures that no one tracks their online activities. By hiding the user’s actual IP address, it becomes impossible for websites to obtain and track browsing data, enabling effective data collection blockage. This becomes highly important when people try to safeguard sensitive information from vulnerability, especially during browsing.
Corporate Use Cases
Most companies utilize proxies to ensure that employees do not access harmful or irrelevant websites. Proxies prevent employees from accessing inappropriate sites and filtering harmful content. Moreover, it prevents from malware, viruses, and other threats from incoming web traffic. Proxies can monitor the internet for employee usage so as to provide insight into employee activities, which helps enforce security measures.
Ad and Tracker Blocking
Through proxy servers, users are able to avoid ads and prevent websites from tracking data using HTTP cookies. It provides users with a better and smoother browsing experience. Furthermore, users are able to retain their privacy by minimizing the personal data relinquished to third parties and advertisers. Many proxies offer advanced features for blocking pop-ups, banners, and other forms of advertisements, which enhance the online experience.
Potential Drawbacks and Risks of Proxy Servers
- Privacy Loss: For some proxies, logging customer data, such as user activity, may lead to loss of privacy. It is particularly for free-of-charge and unreliable proxies that store data for advertising purposes.
- Reliability Issues: Proxies may lead to slower connection speeds. Unreliable proxy service providers lead proxies to unexpected outages, security breaches, and the leaking of sensitive data.
- Security Risks: Through traffic interception, ruthless proxies can disclose critical details such as login credentials or private information. If not properly encrypted, proxies leave behind a pathway for hackers or unauthorized users to access information.
- Compatibility Issues: Proxy traffic detection and blocking is a common occurrence on multiple websites and applications. Therefore, it makes them either work inefficiently or not at all. This results in the denial of access to some online resources and creates further complications with authentication.
How to Choose the Right Proxy Server
Different factors in alignment with your requirements dictate the selection of a proxy server. To assist you with your quest for a working proxy service, here are some pointers to first think about.
Factors to Consider
- Speed and Reliability: Uninterrupted proxies with fast loading times and good connection speed have become crucial in the current era. Online work, streaming, and browsing require a proxy to be operational at all times. Choose a proxy service with access to unmatched uptime and surely stable services meant to aid users with their needs.
- Security Features: Look for a provider with a deep concern about sensitive data, such as personal info. They tend to use encryption to transmit sensitive documents, which guarantees undisclosed data transmission. Other than the need for base security structures, some enable cost-friendly SSL certificate encryption. It comes with advanced features like anti-malware shielding.
- Location and Access to Specific Geo-Restricted Content: Area boundaries-content can be readily provided access for content restriction. The restriction line region needs a bypassing region that deserves open varieties of different places across countries.
Compare Features
- Reliability: Choose proxies that have a good-standing history and reputation for uptime and responsiveness.
- Pricing: Pricing changes with the proxy type and the volume of needed servers. Use subscription options to determine the cost-benefit balance.
- Customer Support: Good customer support is vital for addressing emerging problems in real-time and thus needs to be sought actively.
Conclusion
Proxy servers are essential in ensuring security and improving the browsing experience. Proxy servers facilitate anonymity, access to geo-blocked sites, and securing sensitive information. It is, therefore, very important to carefully examine requirements before selecting a proxy server. Today, understanding the functioning of proxy servers is crucial for both individuals and corporates. Consider all available options and select proxy servers that are tailored to your ideal online experience.
If you’re looking for consistent and reliable network access, UltaHost’s IP-dedicated servers will suit your needs. Increased security and protection for your consistent performance are guaranteed with a dedicated IP. Secure your online presence with UltaHost’s powerful dedicated servers for uninterrupted performance.
FAQ
What is a proxy server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user’s device and the internet, enhancing privacy and access.
How does a proxy server work?
It forwards user requests to websites and returns the responses, masking the user’s IP address.
Why should I use a proxy server?
Proxy servers offer privacy, bypass content restrictions, and add security when browsing online.
What are the types of proxy servers?
Common types include forward proxies, reverse proxies, transparent proxies, and web proxy servers.
What is a web proxy server?
A web proxy server allows users to access websites anonymously by masking their IP addresses.
Can proxy servers help bypass geo-restrictions?
Yes, proxies can access geo-blocked content by routing traffic through different locations.
Do proxy servers slow down internet speed?
Some proxies may slightly reduce speed, especially if overloaded, but high-quality proxies are faster.