The world we live in is a digital world with pros and cons. Cybersecurity has always played a major role in safeguarding individuals’ identities and personal information at any cost. In the case of cybercrimes, if cybersecurity fails to protect individuals’ data, many businesses would go to a loss. Phishing is one of the most common types of cybersecurity attacks that uses deceptive techniques to manipulate users to get access to all their confidential information.
Cyber attackers use phishing emails to distribute malicious links so that they can easily extract users’ access credentials, bank account numbers, and other sensitive information. It is easier to trick someone on the web using this widely popular technique instead of breaking through the computer’s defenses.
For the prevention of such phishing attacks, detecting and learning more about these will help.
What Is a Phishing Attack?
The term “Phishing” is generally used for a fraudulent practice that involves stealing sensitive information of businesses or individuals. Attackers do it by disguising themselves as trusted entities. A Phishing Attack is a social engineering tactic used to steal personal information like usernames, passwords, and bank account details. Attackers pose as a trusted source to trick victims, much like bait lures a fish.
Phishing tricks victims into easily opening an email, message, or any other form of communication. Clicking on such malicious links leads to the installation of malware or the freezing of the whole system. It may also reveal sensitive information and can be a part of some ransomware attacks. Such fraudulent attacks have catastrophic results including identity theft, stealing of funds, and even unauthorized purchases. An organization or individual targeted by such an attack may face significant financial losses, reduced market shares, lowered reputation, and customer trust. Every business that faces a phishing attack has a hard time recovering from the loss.
Try using Ultahost’s highly secure WordPress servers to protect your WordPress website from ransomware attacks. Take advantage of our dedicated WordPress Hosting Secure solutions to protect your site from malware, DDoS attacks, and malicious traffic.
How does phishing work?
Phishers usually use different public sources to gather information on targeted personalities or organizations. These include LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, etc. These sources are used to collect information on victims like personal details, work history, hobbies, interests, routines, and more. These uncover the targeted victim’s name, his/her job title, email address, and location. An attacker can then create a seemingly legitimate phishing email using all this data.
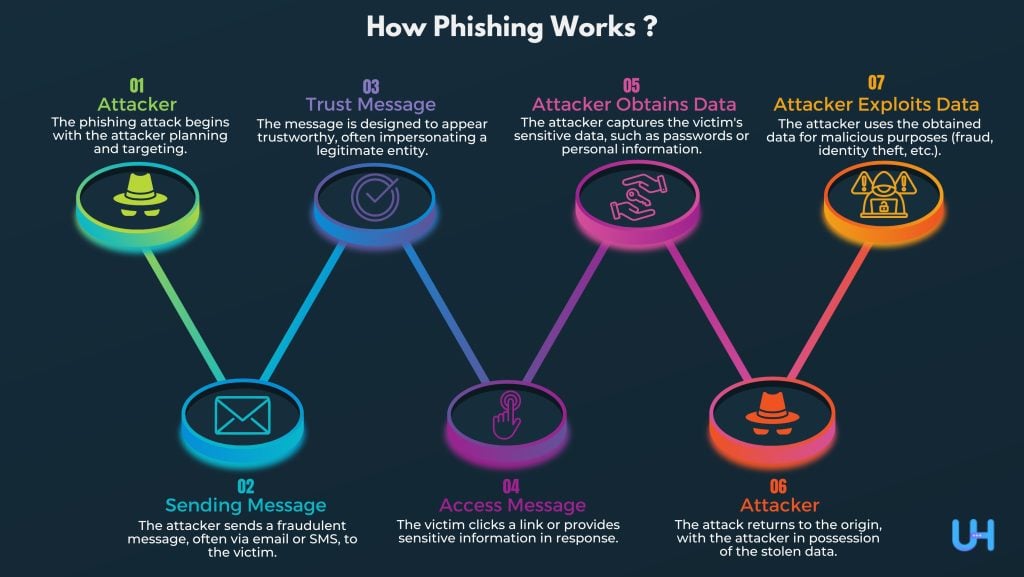
Attackers use different ways to trick users. A typical victim may receive a message seemingly from a reputable organization or contact. If the victim clicks on that malicious link or file, it either directs them to a fake website or installs malware on their device. On such fake sites, victims often divulge their financial and personal data. Attackers also impersonate themselves as an authoritative agency and use phone calls to steal information. Sometimes, they even use AI-generated voices of authoritative personalities to gather confidential information. However, most of the phishing emails generally appear fake as they are poorly written. Only some phishing emails seem legitimate due to the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools like chatbots.
Common Techniques Used for Phishing
Phishers use a wide variety of techniques to make their attacks seem believable to their victims. The most common phishing techniques are as follows:
- Deceptive Phishing: Phishers use psychology to manipulate victims to achieve their targets. A phisher may use social engineering techniques such as deception, bribery, coercion, etc. for such purposes.
- Typo-squatting and URL hijacking: Phishers often use domains and URLs very similar to that of a legitimate, trusted domain. This is known as “Domain Hijacking“.
- Crafting Spoofed Emails: Attackers often design spoofed emails that have names of targeted users’ trusty individuals as their display names.
- Link Shortening: Attackers often use link shortener tools like bit.ly to conceal the target destination of a URL. Phishers use this trick to direct users to a phishing page through such links.
- Link Hiding: Phishers often scam users by hiding phishing links in text or images that seem harmless. These links direct users to phishing pages.
- Malicious Redirects: Phishers often craft malicious redirects to direct users to other phishing pages instead of the real ones. Attackers make malicious redirects mostly when the original URL of that page becomes unavailable or outdated.
Types of Phishing Attacks
Phishers have invented a wide variety of techniques to increase their success rates. Here are 12 types of phishing scams that attackers implement:
Email phishing scams
Most of the phishing attacks are sent to targeted users via emails. Attackers usually register fake domain names that are very similar to those of reputable organizations. They create fake domains by altering characters (e.g. my-bank.com instead of mybank.com), using subdomains (e.g. mybank.host.com), or by using any trusted organization’s name in place of email usernames (e.g. [email protected]). Attackers send thousands of convincing emails, tricking recipients into downloading infected files or clicking malicious links. Phishers use spoofed emails and URLs that mimic the original, replicating wording, signatures, logos, and typefaces to appear authentic.
Another technique that phishers follow is creating a sense of urgency. This includes giving deadlines to recipients such as threats for account expiration.
Phishers send messages via emails to achieve the following goals:
- For the targeted user to click on links that direct to a malicious website for malware installation.
- For the targeted user to download an infected file and use it to support malware.
- For the targeted user to click on links to a fake website and divulge their personal information.
- For the targeted user to respond and then provide personal data.
For secure and dedicated email hosting solutions, Ultahost provides users with the best Email Hosting Server. This hosting server helps host business emails with the proper security and promotion of websites.
Spear phishing scams
Attackers know most of the personal information of the victim in spear phishing. Such a method of phishing is regarded as a personalized scam. This is currently the most effective type of phishing accounting for more than 90% of phishing attacks. Such extra information helps to make the phishing attack successful by representing the message as being authentic. Special knowledge that the phisher knows already about the victim includes:
- Name of the victim
- Location of victim
- Place of employment of the victim
- Job title of victim
- Email address of the victim
- Specific information about the victim’s job role
- Reliable and trusted colleagues, family members, or other contacts, and samples of their writing
- References to co-workers or executives at the victim’s organization
By gathering all this data, the attacker creates a seemingly legitimate email or message to trick the victim into performing authoritative tasks and activities such as transferring funds. The victim easily provides sensitive information such as valid login credentials to the attacker this way.
Whaling phishing scams
Whaling attacks are a subtype of spear phishing scams that particularly target senior management executives to steal large sums of confidential information. Phishers conduct thorough research on their victims to craft believable messages that appear genuine, aiming to get access to their privileged environment. A typical whaling attack targets people who have the authority to create payments in the form of a command. Such people can authorize large payments from vendors and the attackers can get those payments if they mimic the vendor properly. Attackers also send whaling scam emails to users that appear to come from one of the executives or important members of the organization or company and credit monitoring services can be an effective tool to detect and respond to financial fraud resulting from these attacks.
Cloning phishing scams
Cloning Phishing scams take place when the attacker takes control of a victim’s system within an organization to send email messages from a trusted sender to the victim. For this, the phisher creates a clone or copy of a legitimate email and replaces attachments or links in it with the malicious files and links. Then, the attacker uses these previously delivered, seemingly legitimate emails with a spoofed email address containing a link or an attachment to trick users into clicking on the malicious links and files. These spoofed emails must be from senders that the victim trusts such as financial institutes, accredited businesses like Amazon, etc.
Pharming phishing scams
Pharming attacks involve cache poisoning of domain naming systems by hijacking the Domain Naming System (DNS) server functionality. This phishing technique redirects victims from an authentic website to a malicious one. Users get tricked and they automatically try logging into fake websites providing their valid access credentials.
Evil Twin phishing scams
Evil twin attacks occur when hackers lure victims into connecting to a fake Wi-Fi network that seems like a trustworthy access point. The victims try to connect with the seemingly legitimate Wi-Fi hotspot which is the duplicate hotspot with the same name as the real Wi-Fi network. This Evil twin network sends out radio signals and the attackers get access to all the victim’s personal information including usernames, IDs, and passwords as soon as the victim connects to it. Moreover, attackers also have the power to target the victim’s device with their fraudulent attempts.
Smishing and Vishing scams
Such phishing attacks use mobile phones instead of written tools for communication.
Smishing (SMS Phishing) scams
SMS Phishing attacks are mobile-oriented phishing attacks that use fraudulent text messages to convince and lure victims to divulge their account information or install malware on their devices. Usually, the attackers demand the victim to click on specific links, and call or send email messages to get access to their confidential data. Smishing is not easily identifiable as link shortening is easy on mobiles as compared to other devices.
Vishing (Voice Phishing) scams
Voice Phishing attacks involve phishing through voice-based media including Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and telephone services. This type of phishing uses speech synthesis software to create voicemails for victims. Such kind of voicemails are left to notify the victims of any suspicious activity in their bank accounts. Vishing also includes fraudulent phone calls in which the attacker pretends to be a scam investigator from any credit card company bank or any other trusted entity. The scammer uses calls to ask for the victim’s personal information and account credentials for the verification of their identity in some cases. Criminals may also ask to transfer money to a safer account that is the scammer’s account and is not secure.
Angler Phishing scams
Angler phishing attacks are one of the most common ways to trick consumers which attackers pose as legitimate organizations or companies on social media. They mimic well-known companies by creating fake accounts on social media with similar account handles from legitimate organizations and even the same profile picture to confuse consumers. Scammers take advantage of consumers’ tendency to request assistance from certain brands or file complaints using their social media accounts. The consumer audience contacts the scammers in place of the real brand company. In this case, the attackers may request personal information including confidential access credentials from the victims pretending to analyze their issue. The phishers may provide a malicious link for a gift card or discount or one directed to a fake customer support page.
Pop-up Phishing scams
Pop-up attacks are those in which an offer or a warning message appears as a pop-up notification on various Apple and Android devices. This pop-up link directs the users to a malicious website tricking them into divulging their data through the site.
Calendar Phishing scams
In such types of phishing attacks, scammers attempt to fool the victims by sending fake calendar invites. These seem as common event requests that can be automatically added to device calendars. However, even such invites contain malicious links that direct users to fake websites.
Page hijacking Phishing scams
Page hijacking attacks are those in which users get redirected to pages that are duplicates of the page they want to visit. The attackers use these compromised websites to install malware through cross-site scripting.
Secure Your Website with Robust Hosting!
If you are looking for a solution to protect your web applications and site from malicious attacks, look no further! Ultahost offers fully managed Cloudflare VPS hosting with 24/7 unlimited support for unparalleled security, site performance and reliability.
How can phishing be prevented?
A few steps can easily protect you from phishing attacks. These tips are for both individual users and enterprises:
Vigilance of Individual Users
Users should be vigilant enough to easily recognize spoofed messages. Spoofed messages may contain subtle mistakes such as spelling mistakes, changes in domain names, etc. that can expose the original identity of such messages. Individuals must know the actual reason for receiving such emails and if there is no specific reason, they should think and investigate it.
Important Measures Taken for Enterprises
A few measures can mitigate phishing attacks for enterprises:
Two-Factor Authentication Method (2FA)
It is one of the most effective methods to counter phishing scams as it adds another layer of extra verification in case of logging into sensitive sites and applications. 2FA is based on two things: what users know (passwords, usernames) and what device they have for 2FA (smartphones, tablets). It is difficult to get entry alone via 2FA and this prevents misuse of access credentials.
Strict Password Management
Authorities must assign their employees the task of frequently changing their passwords and avoiding the reuse of passwords for multiple sites and applications. Enforcing strict password management policies using 2FA helps prevent phishing attacks on organizations.
Layering Security Controls

Experts recommend using all kinds of security controls to prevent phishing attacks from reaching end users. The following online business security tools aid with using different security controls:
- Antivirus software
- Antispyware software
- Antiphishing toolbar (installed in browsers)
- Network and Desktop Firewalls
- Gateway Web Security
- Gateway Email Filters
- Spam Filters
Email Security, Verification, and Filtering Solutions
Always set an email authentication standard for email security and verification. Enterprise mail servers must confirm if the inbound emails are verifiable or not. Enterprises use the “Domain Keys Identified Mail protocol” to block all unknown messages except for those messages that are digitally signed. Another email verification method that companies use is “Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance protocol (DMARC)” which effectively blocks unsolicited emails. Such email security solutions automatically block and isolate suspicious emails.
Many email filtering solutions protect from email messages containing malware codes or malicious payloads. Enterprises use sandboxing tools to check if these emails contain malicious codes, links, attachments, or any kind of spam content for the detonation of such emails.
Employee and Security Team Awareness Training
It is highly important to train employees of an organization and keep them ready for an encounter with any upcoming phishing attacks in the future. Employees along with the company’s security team must be educated on understanding signs of phishing and identifying various phishing attacks so that they immediately report such suspicious incidents to the higher-ups. For this reason, educational campaigns can be set up to help employees learn to enforce secure practices such as not clicking on external email links; in case of any such incidents. This helps diminish the threats of phishing attacks as well. In addition, employees should be cautioned to avoid opening suspicious emails from unknown senders and clicking on suspicious links, files, and attachments to prevent getting into phishing scams. Employees can also learn to avoid phishing properly through interactive security awareness training aids like Proofpoint Security Awareness Training and Cofense’s PhishMe.
Organizations should encourage their staff members to look for trust badges or stickers from renowned cybersecurity or antivirus companies before dealing with a random website. Websites having such kind of authentic badges are serious about security and can never be malicious.
Internet resources (such as Anti-Phishing Working Group) also help learn and combat phishing by providing advice on spotting, avoiding, and reporting phishing scams efficiently. Moreover, sites such as FraudWatch International and MillerSmiles.co.uk publish the latest phishing emails circulating on the web.
Phishing Attacks Testing Simulators
Simulator training services for phishing attack testing help the company’s security team and employees evaluate their learning through security awareness training programs. End users can get a better understanding of phishing attacks via such training services. Employees get to be tested regularly for phishing attacks by conducting such tests which makes them proficient at identifying the real scams.
Limiting User Access to Privileged Systems
Cybercriminals mostly target high-value sites and accounts to get their valued access credentials. Phishers try to get sensitive information about such privileged areas. Limiting and restricting user access in such high-value systems helps to prevent the leakage of sensitive data. The principle of least privilege only gives access to users who need it instead of giving it to extra users around.
Conclusion
In short, phishing attacks are types of cybersecurity attacks in which the attackers impersonate themselves as harmless entities, sending malicious messages. They use different phishing techniques to exploit various trends and industries including emails and messages. Identifying such fraudulent attacks is crucial and this can only be possible by spreading awareness and educating about phishing attacks among enterprises and employees.
With the right tools and techniques, individuals and businesses can protect themselves from phishing attacks. Consider exploring Ultahost’s Anonymous VPS Hosting solutions for an additional layer of security. Ultahost ensures your online activities remain private and secure, further safeguarding your digital presence.
FAQ
What is a Phishing Attack?
A Phishing Attack is a social engineering tactic used to steal personal information like usernames, passwords, and bank account details. The attackers pose as trusted entities in such scams.
How does Phishing work?
A typical phishing victim may receive a message seemingly from a reputable organization or contact. If the victim clicks on that malicious link or file, it either directs them to a fake website or installs malware on their device.
What are the common techniques of Phishing?
Phishers use different deceptive techniques like URL hijacking, link shortening, link hiding, creating spoofed emails, and malicious redirects. They use such ways to trick victims and lure their confidential information.
What are the different types of Phishing Attacks?
Phishers boost their success rates by using various phishing techniques, including email phishing, spear phishing, whaling, cloning, pharming, and more.
What is Spear Phishing?
“Spear phishing” is a type of phishing where attackers use personal information about the victim, making it a personalized scam.
What is the difference between Smishing and Vishing?
Smishing attacks use fraudulent text messages to trick victims into revealing account information or installing malware, while vishing involves phishing via voice-based media, such as VoIP and telephone services.
How can businesses prevent Phishing?
Businesses can prevent phishing by methods like 2-factor authentication, proper security tools, email filtering, and limiting user access to privileged systems.









