How to Use the which Command in Linux
The which command in Linux is a simple yet powerful uti...
Bash scripts are powerful tools that allow you to automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows on Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux and macOS. Essentially, a Bash script is a plain text file containing a series of commands that the Bash shell can interpret and execute sequentially. These scripts can perform a wide range of tasks, from simple file operations to complex system administration tasks, making them invaluable for system administrators, developers, and power users alike.
Learning how to create Bash scripts is a crucial skill for anyone working with Unix-like systems. By automating tedious and time-consuming tasks, you can significantly improve your productivity and efficiency. Additionally, Bash scripts can help ensure consistency and reduce the risk of human error, making them essential for maintaining reliable and secure systems.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take a step-by-step approach to creating your first Bash script from scratch, covering everything from understanding the Bash environment to writing script logic, debugging, and deployment.
Before diving into creating Bash script tutorial, it’s essential to understand the Bash environment and its core components. Bash, which stands for Bourne-Again SHell, is a command-line interpreter and scripting language widely used in Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux and macOS. It serves as the primary interface between the user and the operating system, allowing users to execute commands, automate tasks, and write scripts.
Following are the steps given below on how to make a bash script:
Step 1: Text Editors and IDEs
When it comes to creating and editing Bash scripts, you have several options. You can use a simple text editor, such as Nano, Vim, Emacs, Sublime Text, or Visual Studio Code, which provides syntax highlighting and other features to enhance your Bash scripting experience.
So first, ensure that you have an editor installed on your Linux distribution. If you are a beginner then start with either nano or vim text editor and they are lightweight and easy to use. For example, you can execute the below commands to install them on Ubuntu:
sudo apt install nano sudo apt install vim
Step 2: The Shebang Line
One of the crucial aspects of Bash scripting is the Shebang line (#!). This line, typically placed at the beginning of a Bash script, specifies the path to the interpreter that should be used to execute the script. For instance, #!/bin/bash tells the operating system to use the Bash interpreter located at /bin/bash to run the script. Without the Shebang line, the script may not execute correctly or may use a different interpreter, leading to unexpected behavior.
So first you need to open the terminal and create a bash file using nano or vim that we discussed earlier:
nano bash_script.sh Vim bash_script.sh
This will create and open a file with .sh extension and next you need to write a shebang line:
#!/bin/bash
After that, you need to write any code that you want and then save and exit a file. For example, you can use a simple Bash script as below:
#!/bin/bash echo "Hello, World!"
Step 3: Making a Bash Script Executable
Next, you need to ensure that the Bash script is executable and you have the necessary permission. This is generally required for non-sudo users. To make a Bash script executable you can use chmod command followed by the script name:
chmod +x bash_script.sh

Step 4: Execute the Bash Script
After writing the Bash code, it’s time to execute it to check whether it’s working correctly or not. To do that you can use any of the below commands:
./bash_script.sh
bash bash_script.sh
Step 5: Testing and Debugging Bash Scripts
Proper testing and debugging are crucial when write Bash scripts. You should thoroughly test your scripts to ensure they work as expected and handle edge cases and errors gracefully. Techniques like using the set -x command to enable script tracing, leveraging the echo command for debugging output, and utilizing Bash’s built-in error-handling mechanisms can help you identify and fix any issues in your scripts.
Creating Bash Script on Our Linux VPS today!
Ultahost provides Linux VPS hosting with NVME SSD storage. You can write bash scripts to automate in our VPS for streamline your process.
Let’s suppose we have created a Bash script with the name bash_script.sh using the nano text editor:
nano bash_script.sh
Next, we will first write the shebang line in bash_script.sh:
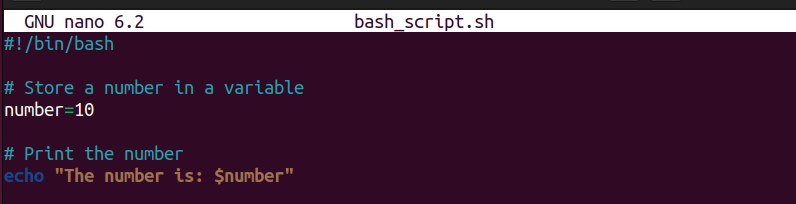
After that, you need to write a code that you want to execute. Below the Bash script example shows you can store any random number inside a variable and display it on the terminal:
#!/bin/bash # Store a number in a variable number=10 # Print the number echo "The number is: $number"
If you want to give execution permission to non-root users then you can use chmod command, otherwise, you can ignore this step:
chmod a+x bash_script.sh

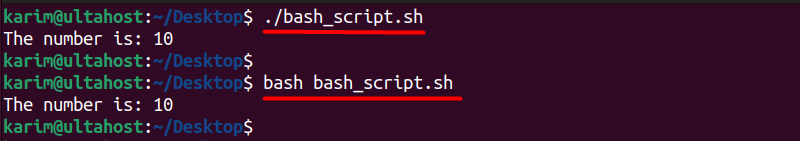
Finally, you need to execute the Bash script on the terminal by executing either of the below commands:
./bash_script.sh bash bash_script.sh
Read also What Is the .bashrc File in Linux?
In addition to the Shebang line, it’s essential to understand the basic Bash commands and syntax. Bash scripts are composed of commands that can be executed directly in the terminal or combined into more complex scripts. Some common Bash commands include:
Bash also supports variables that allow you to store and manipulate data within your scripts. Variables are declared by assigning a value to a name such as variable_name=value. Additionally, Bash provides control structures like if statements, for loops, and while loops, enabling you to write more sophisticated scripts with conditional logic and iterations.
By understanding the Bash environment, the significance of the Shebang line, and the basic commands, syntax, variables, and control structures, you’ll be well-prepared to start creating your own Bash scripts and automating various tasks efficiently.
Bash scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks and streamlining workflows on Linux and Unix systems. This guide covered creating Bash scripts from scratch, including understanding the Bash environment, writing script logic with variables and control structures, and debugging techniques. Mastering these skills enables efficient task automation, consistent execution, and reduced human error.
This guide has provided a step-by-step approach to creating your own Bash scripts. Remember, the more you practice and apply what you’ve learned, the more proficient you’ll become. Embrace the power of Bash scripting and unlock the potential for automation and efficiency in your Unix-like system workflows.
Bash scripting offers a powerful way to automate tasks on your server. However, managing complex scripts or troubleshooting errors can be time-consuming. For server management experience consider Ultahost’s fully managed dedicated servers help to create, debug, and even automate your Bash scripts.
A Bash script is a text file containing a series of commands that are executed by the Bash shell. It allows users to automate tasks and perform complex operations by writing a sequence of instructions.
You can create a Bash script file using a text editor such as Vim, Emacs, Nano, or even a simple text editor like Notepad on Windows. Just save the file with a .sh extension, indicating it’s a shell script.
The first line of a Bash script is called the shebang (#!) line. It specifies the path to the shell that will execute the script. For example, #!/bin/bash indicates that the script should be executed using the Bash shell.
You can make your Bash script executable using the chmod command. For example, chmod +x script.sh grants execute permission to the owner of the file. After this, you can run the script directly by typing ./script.sh.
Variables in Bash scripts are placeholders for storing data. They are defined using the syntax variable_name=value. Variables can store strings, numbers, or any other data type.