How Much Does a Website Hosting Cost in 2026,...
Did you know that choosing the wrong plan can increase ...
The Apache HTTP Server commonly known as Apache is one of the most widely used web server software on the internet. Web Host Manager short for WHM is a powerful web based tool that allows web hosting providers to manage their servers efficiently. One of the essential tasks for server administrators is to monitor the status of the Apache server to ensure that it is running smoothly and efficiently.
In this article, we will explore how to view the Apache status in WHM and why it is important to monitor Apache status.
Before diving into the steps to view Apache status in WHM, let’s understand why monitoring Apache status is important:
Install WHM on Our Cheap Linux VPS!
Enjoy the reliable performance of the best Linux system along with the flexibility of a virtual server. Experience fast speeds and low delays.
Check Apache WHM is a straightforward process. Here are the steps to access the Apache status WHM:
To begin, you need to log in to your WHM account. WHM is typically accessed through a web browser using a URL such as https://yourserverIP:2087 or https://yourdomain.com/whm. Enter your WHM username and password to log in.

Once you are logged in, you will be greeted with the WHM dashboard. From here, follow these steps:
In the left-hand sidebar, locate the “Server Status” section. This section contains various tools for monitoring your server’s health and performance.
Click on the “Apache Status” link. This will take you to the Apache status page, where you can view detailed information about your Apache server.
The Apache status page provides a wealth of information about your server’s current state. Here are some key points and sections discussed below:
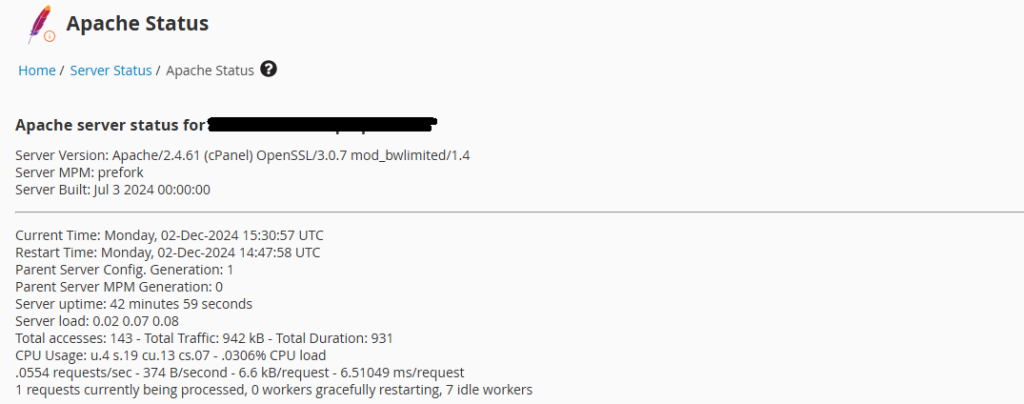
The Server Version and Build section displays the version of Apache running on your server, along with details about the build.
The Current Time shows the current server time.
Restart Time indicates the last time the Apache server was restarted. This information is useful for determining how long the server has been running without interruption.
The Total Accesses Displays the total number of requests served by the Apache server since it was last restarted.
The Total kB Shows the total amount of data (in kilobytes) served by the Apache server since it was last restarted.
Uptime indicates how long the Apache server has been running since the last restart.
The ReqPerSec represents the average number of requests served per second.
The BytesPerReq shows the average amount of data served per request.
The Busy Workers indicates the number of Apache worker processes currently handling requests.
The Idle Workers represents the number of idle worker processes waiting to handle requests.
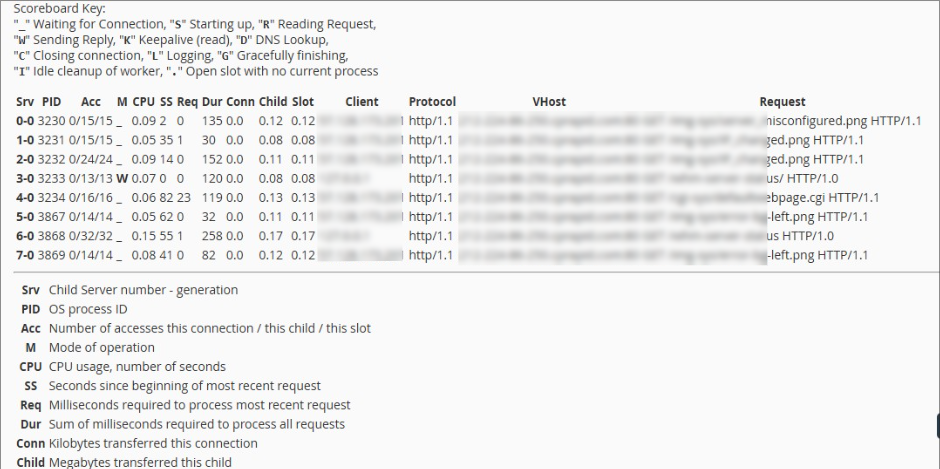
The Scoreboard section provides a visual representation of the current state of Apache worker processes. Each character represents a different state, such as waiting for a connection, processing a request, or being idle.
Read also How to Check Apache Version in Linux.
In addition to the basic Apache status, WHM offers advanced monitoring tools that provide deeper insights into your server’s performance and health. These tools can help you identify and address issues before they impact your server’s performance.
WHM provides detailed information about resource usage, including CPU and memory usage. To access resource usage information:
In the left-hand sidebar, navigate to the “Server Status” section.
Click on “Server Information” or “Server Status” to view detailed statistics about your server’s resource usage.
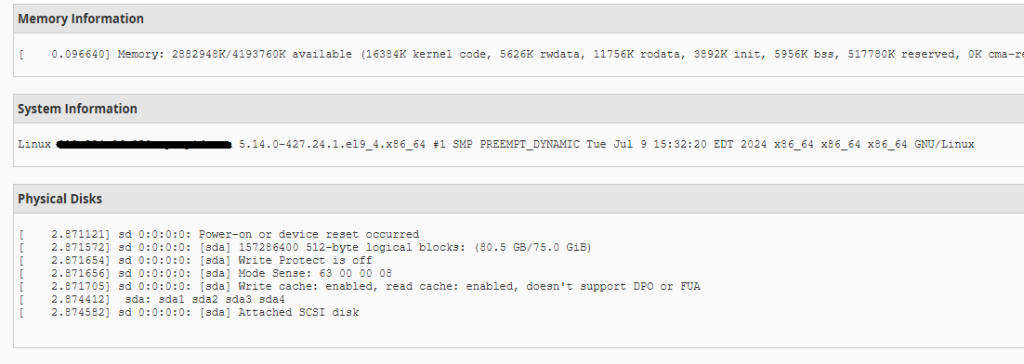
This information can help you identify resource-intensive processes and optimize your server’s performance.
Apache error logs are essential for troubleshooting issues with your server. They provide detailed information about errors and warnings generated by the Apache server. To access Apache error logs:
In the left-hand sidebar, navigate to the “Logs” section.
Click on “Apache Error Log” to view the error logs.
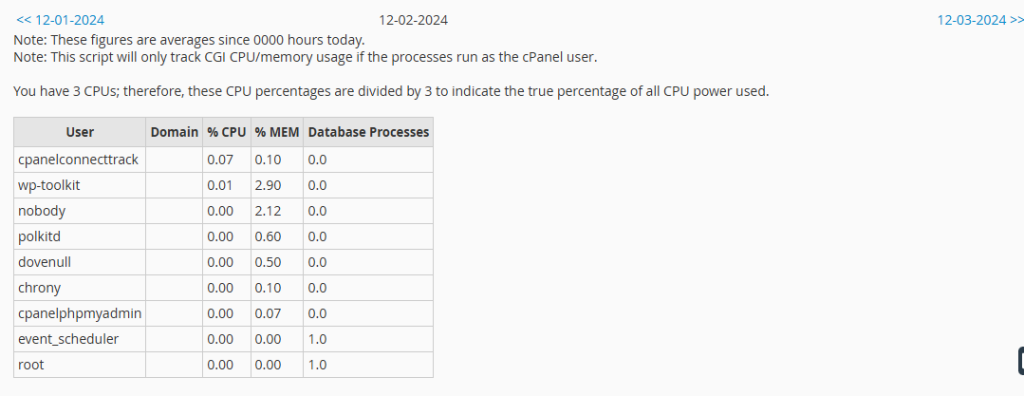
Reviewing error logs regularly can help you identify and resolve issues that may be affecting your server’s performance.
Monitoring unlimited bandwidth usage is important for ensuring that your server is not exceeding its allocated bandwidth. WHM provides tools for monitoring bandwidth usage:
In the left-hand sidebar, navigate to the “Account Information” section.
Click on “View Bandwidth Usage” to view detailed information about bandwidth usage for each account on your server.
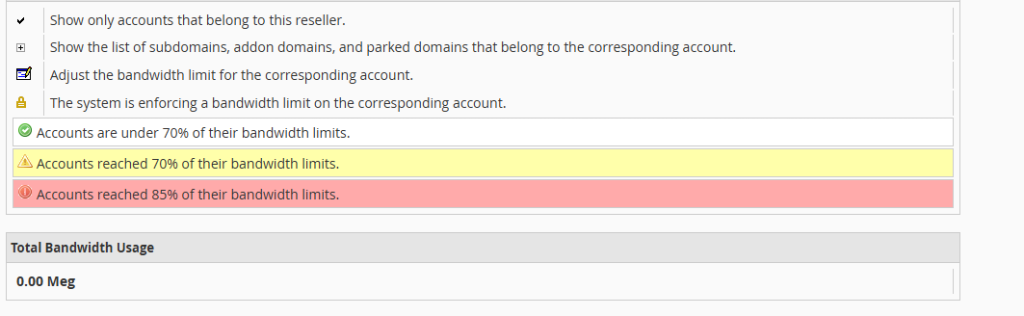
This information can help you manage bandwidth usage and avoid overage charges.
Monitoring Apache status in WHM is an important task for server administrators. It provides valuable insights into server performance, helps identify and resolve issues, and ensures that your server runs efficiently. By regularly checking Apache status, and reviewing logs you can maintain a healthy and secure server environment.
Apache offers flexibility and a wide range of customization options. Ultimately, the ideal web server for you will depend on your project’s specific needs. Rent VPS hosting from Ultahost that scales with your resources to accommodate your growing demands. Explore our VPS plans to find the perfect option for you.
Apache status in WHM shows real-time information about your server’s web traffic and performance.
To monitor server activity, spot issues, and ensure your websites are running smoothly.
Log in to WHM, search for “Apache Status,” and click on it to view detailed stats.
It shows active connections, requests, CPU usage, and server processes.
Yes, you need WHM admin privileges to check Apache status.
No, but it helps identify issues so you can take action elsewhere in WHM.
Yes, most WHM versions include the Apache status feature by default.