How to Install Sublime Text on Ubuntu
Sublime Text is a popular, feature-rich text editor des...
Yarn is a popular package manager for JavaScript and Node.js projects, offering faster installation speeds, improved security, and better dependency management compared to its predecessor, npm (Node Package Manager). In this step-by-step guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about installing Yarn on Ubuntu, ensuring you can take advantage of its benefits for your development workflow.
By the end of this article, you should be able to confidently install and manage Yarn on your Ubuntu system, and understand the key concepts and best practices for using Yarn effectively.
Before install yarn Ubuntu, it’s important to ensure your Ubuntu system is up-to-date and that you have the necessary permissions to install packages. Here are the prerequisites you should check:
Update your Ubuntu system
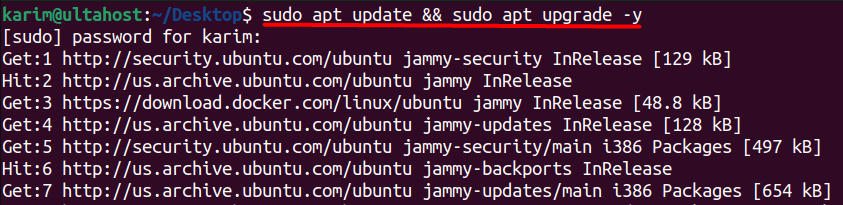
Make sure you have the latest updates and patches installed. You can do this by running the following commands in your terminal:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Administrative Privileges
Installing packages typically requires administrative permissions. Make sure you have sudo access or are logged in as the root user.
Install Node.js and npm
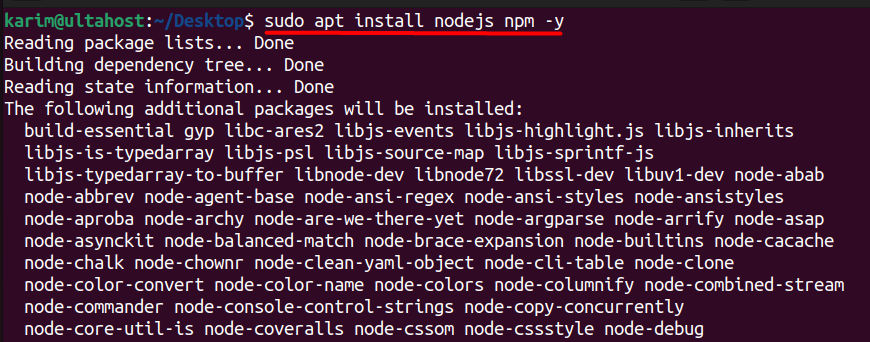
Yarn is designed to work with Node.js and npm. Make sure you have Node.js and npm installed before proceeding. You can install them by following our Node.js installation Ubuntu guide or using a package manager like apt:
sudo apt install nodejs npm -y
Once you’ve confirmed that your system meets these prerequisites, you can proceed with installing Yarn.
Install Yarn On Our Ubuntu VPS!
Experience the reliability of the world’s top Linux distribution paired with the flexibility of a virtual server. Enjoy lightning-fast speeds and minimal latency.
Before we dive into how to install yarn in Ubuntu, let’s take a moment to understand why package managers like Yarn are essential tools for modern software development, especially in the JavaScript ecosystem.
Package managers enable developers to easily manage and install dependencies required by their projects. These dependencies could be libraries, frameworks, or tools that provide additional functionality or streamline development tasks. In the case of Yarn, it serves as both a package manager and a lock file generator.
Here are some key benefits of using Yarn over traditional package managers like npm:
Understanding these benefits will help you appreciate why Yarn is a popular choice among developers, especially those working on large-scale or collaborative JavaScript projects.
The easiest way to Yarn install Ubuntu is by using the repository. This method is recommended, as it ensures that you’re installing a trusted and verified package.
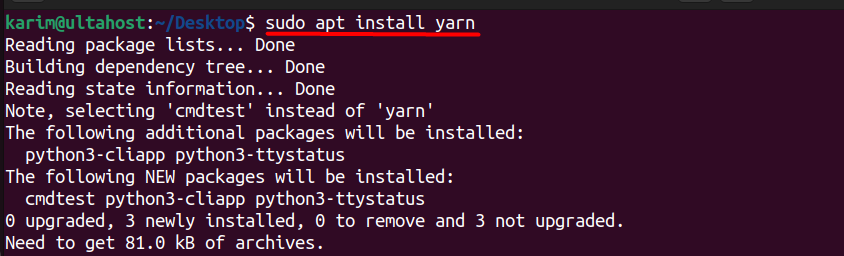
To install yarn once the package list is updated, run the following command:
sudo apt install yarn
After the installation is complete, verify that Yarn is installed by running:
yarn --version

The output 0.32+git indicates that the command installed a pre-release version of Yarn rather than an official stable release. The +git suffix indicates that this version of Yarn was built from the source code available in a Git repository.
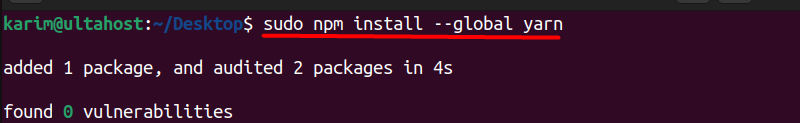
NPM is a command-line tool used for managing JavaScript packages. It comes bundled with Node.js and allows you to install, update, and manage packages. We can use NPM to install Yarn globally on our Ubuntu machine:
sudo npm install --global yarn
Global installations make the package available system-wide, which means you can run Yarn from any directory on your system without specifying its path.
Read also How to Install Tmux on Ubuntu.
Once Yarn is installed, you will need to know some basic commands to manage your projects effectively. Here are some commonly used Yarn commands:
These commands will help you get started with managing your project dependencies and scripts using Yarn.
Installing Yarn on Ubuntu can be accomplished using two straightforward methods. The first method involves using the Ubuntu repository, which ensures a trusted and verified installation. By simply running sudo apt install yarn after updating your package list, you can easily get Yarn up and running. The second method uses NPM, the default package manager for Node.js, allowing you to install Yarn globally with the command sudo npm install –global yarn. This approach makes Yarn accessible from any directory on your system, providing flexibility and convenience.
Both installation methods offer distinct advantages, catering to different user preferences and requirements. Utilizing the Ubuntu repository is ideal for users who prefer a stable and verified installation, while the NPM method is perfect for those who seek a more flexible, globally accessible setup. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can seamlessly integrate Yarn into your development workflow, enhancing your project management and dependency handling capabilities.
While installing Yarn on Linux is straightforward managing dependencies and ensuring compatibility across different server environments can be technical. Upgrading to Ultahost’s best Linux server plan empowers you with a robust solution that helps you to install with the latest package managers and repositories, simplifying Yarn installation and updates.
Yarn is a package manager for JavaScript, created by Facebook, designed to be more reliable and faster than npm (Node Package Manager).
You can install Yarn on Ubuntu using the following steps:
Yes, you can install Yarn without adding a repository by downloading the Debian package directly from the Yarn website and installing it using dpkg. Here’s how:
You can update Yarn to the latest version using the following command: yarn self-update
If you encounter permission issues, ensure you are running the installation commands with sudo or as a root user.