How to Install Python on MacOS
Python is a powerful, versatile, and beginner friendly ...
Python is one of the most widely used programming languages owing to its simplistic nature. Its functionality stretches from web scraping, data evaluation, to scripting and automation. Its adoption is high amoung developers, local and foreign alike, because it is flexible and has a wide range of libraries.
When working with Python, it is mostly the case that you have to deal with external data or user interactions. In these situations, there is a possibility of using standard input or stdin. This makes it possible to perform dynamic data processing because a program can read input from the command line or other such sources. This is vital to enable the making of interactive scripts, task automation, and real-time data analysis.
This tutorial will cover everything you need to know to read from stdin using Python. We will study the features of stdin and how to use it, utilizing different use cases as examples.
Python provides several methods to read input from stdin. Each method serves different use cases, allowing you to choose based on your requirements. Below, we explain the most common approaches with practical examples and detailed explanations. Before getting started refer to our guide on how to install Python on your Windows 10 system.
The input() function is the simplest way to read input from stdin. It waits for the user to type a value and press Enter, then returns the input as a string.
# Prompt the user for their name
name = input("Enter your name: ")
print(f"Hello, {name}!")
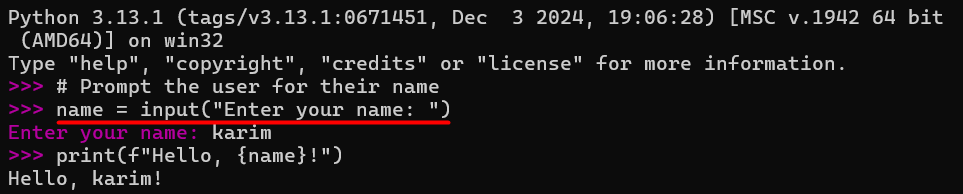
In this code, the input() function displays the prompt (`”Enter your name: “`). It waits for the user to enter text and captures the value as a string. The print() function outputs the personalized greeting using the captured input.
The sys.stdin module allows you to read data as if stdin were a file. This method is useful when reading multiple lines or large input streams:
import sys
print("Enter multiple lines (Ctrl+D to end):")
# Read all lines from stdin
lines = sys.stdin.readlines()
print("You entered:")
print("".join(lines))
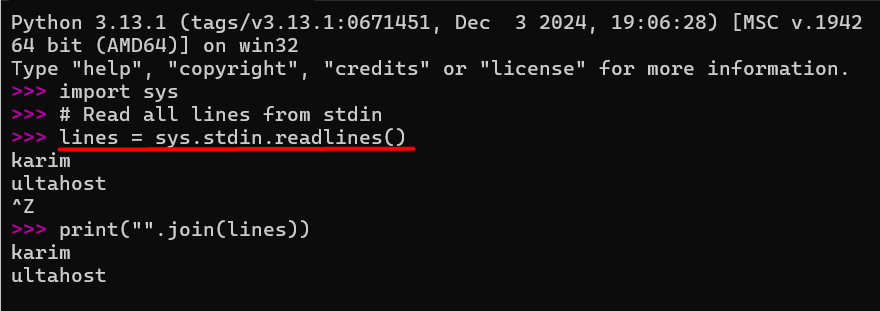
In this Python code, sys.stdin.readlines() reads all lines from stdin until the user (ends input with Ctrl+Z and then press enter on Windows). The lines are stored in a list, which you can process as needed. The print(“”.join(lines)) function combines the lines and displays them.
Experience Ultahost’s Top-tier Python Hosting!
Experience top-tier Python hosting, optimized for developers with seamless integration and superior performance for your projects.
The sys.stdin.read() function reads all input until EOF (End of File) and returns it as a single string. This method is ideal for reading large chunks of data.
import sys # Read the entire input as a single string data = sys.stdin.read() print(data)
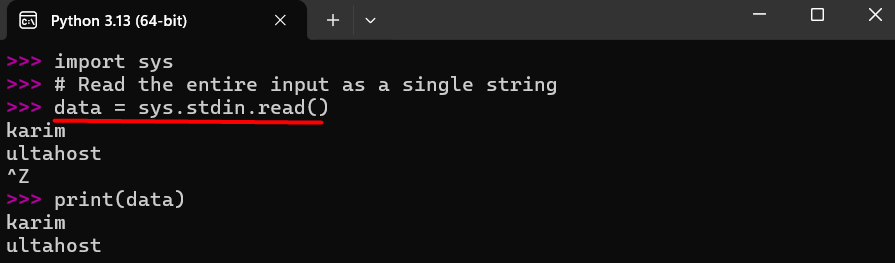
This method captures all input at once, unlike readlines(), which splits the input into a list. It is useful for processing piped input from another command.
The fileinput module in Python is designed to handle reading from files and stdin (standard input) uniformly. This allows you to write flexible Python scripts that can process input from both files and the terminal (stdin), without needing to write separate logic for each case:
import fileinput
print("Reading from stdin or files:")
for line in fileinput.input():
print(f"Line: {line.strip()}")
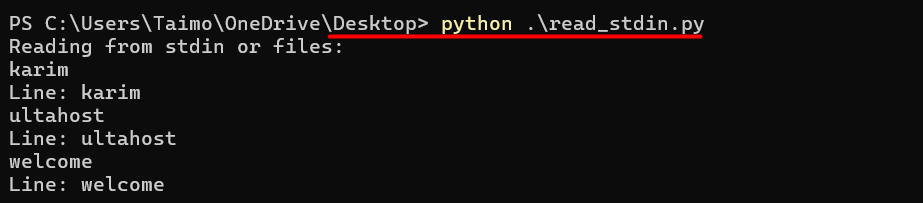
In this code, the fileinput.input() function handles both stdin and file input gracefully. The loop iterates through each line, allowing you to process data line by line. The line.strip() function removes leading and trailing whitespace for cleaner output.
To execute this script, first create a script file with .py format and then navigate to the path where you save the script file. After that launch the terminal or command prompt to execute the prompt.
Learn also How to Install NumPy using Python.
The Python input() function is commonly used for simple, interactive scripts where the user provides input one line at a time. It is ideal for straightforward scenarios, such as capturing user responses or processing single lines of data.
For more complex cases involving multi-line or structured input streams, the sys.stdin.readlines() method can be employed. This approach reads all lines of input and returns them as a list, making it suitable for processing input data line by line.
If handling large datasets that require bulk input, sys.stdin.read() is a better choice. This method reads all the input at once and stores it as a single string, providing an efficient way to work with extensive data.
Lastly, the fileinput module is useful for scenarios where input might come from both standard input (stdin) and files. It processes input line by line, offering a versatile solution for combined input sources.
By understanding these methods, you can confidently handle any stdin requirements in Python. Select the one that best fits your task for efficient input processing.
Stdin plays a crucial role in various real-world applications. Here are a few examples where reading from stdin proves helpful:
Python scripts that are designed to be executed from the terminal can use stdin to accept user input or data from other programs. This is common in utilities that perform tasks like text processing or file manipulation.
With stdin, you can pipe data from one program to another. For example, you could use cat file.txt | python script.py to process the output of a shell command.
Python can be used to read and process log files in real-time, filtering out specific information or parsing the data.
When working with stdin, there are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
Python gives us several ways to handle input through stdin, each useful in different situations. If you need simple user input, the `input()` function is your go-to. It’s straightforward and works well for one-line inputs. For multi-line input or larger chunks of data, sys.stdin.readlines() is a better option, reading input line by line until you signal the end. If you’re dealing with a lot of data at once, sys.stdin.read() captures everything in one go, which is perfect for large or piped input.
Lastly, the fileinput module lets you read from both stdin and files in a unified way, which is handy when you want flexibility without extra complexity. Each method has its strengths, so knowing when and how to use them can make your programs more efficient and adaptable. Whether you’re working with small inputs or processing big data, these options cover a wide range of needs.
Choosing a VPS provider can be a difficult task, with so many options available. That’s why Ultahost understands your specific needs and requirements, and brings you a perfect solution. Get the best free VPS servers with a free trial for Linux or Windows, ultra-fast speeds, and immediate setup.
Stdin stands for standard input, which is a way for a program to receive data from external sources, such as the terminal or files. It’s often used to read user input or pipe data from other programs. Python allows easy access to stdin via methods like input() and sys.stdin.
The input() function waits for the user to type something and press Enter. It returns the input as a string. You can use it to gather single-line input interactively in your script.
sys.stdin.read() captures all input as a single string, while sys.stdin.readlines() reads input line by line into a list. Use read() for bulk data and readlines() for line-by-line processing.
Yes, you can use the `fileinput` module to read from both files and stdin seamlessly. This allows your program to handle input from different sources without separate logic for each.
You can exit stdin input by sending an EOF (End of File) signal. On Windows, press Ctrl+Z and then Enter; on Linux/macOS, press Ctrl+D.
Stdin is useful for interactive scripts, reading large datasets, or piping data between programs. It’s often used in command-line tools or when processing input from external files.
Yes, stdin can be used to read real-time data, such as logs or streaming input, making it useful for applications like monitoring systems or automating workflows.