How to Deploy Your First App in Django
Django is a web framework for Python which offers a cle...
Python is powerful and versatile programming language handling dates and times within itself effectively. Whether you are adding timestamps to log entries, scheduling tasks, or presently seeking the capacity of marking-in time and showing the current value of date and time, Python is there to make things easier for you.
This tutorial presents numerous ways to get the current date and time in Python by using built-in modules and third-party libraries.
Python Standard Library provides classes that enable developers to effectively manipulate dates and times. No external dependencies need to be installed as the datetime module belongs to the Python Standard Library.
This guide assumes that you have already installed Visual Studio Code on Windows system with a Python extension for efficient coding.
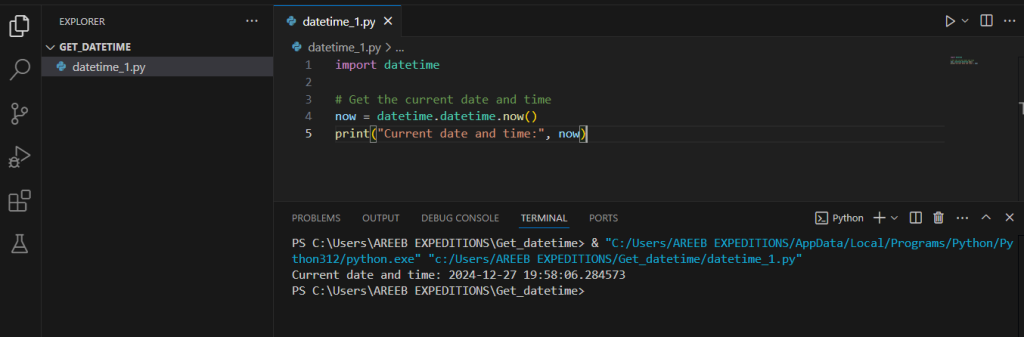
The datetime module includes the datetime class, which can be used to Python get current datetime:
import datetime
# Get the current date and time
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print("Current date and time:", now)
This will output something like:
You can format the date and time using the strftime method, which converts the datetime object to a string based on a specified format:
formatted_now = now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print("Formatted date and time:", formatted_now)
The %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S format string represents the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second.
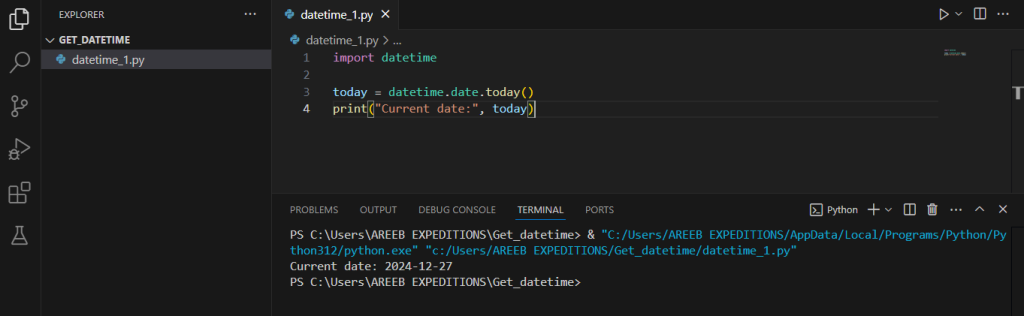
If you only want to get current date in Python, you can use the date class:
today = datetime.date.today()
print("Current date:", today)
Similarly, you can get the current time using the time class:
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().time()
print("Current time:", current_time)
Experience the Peerless UltaHost Python hosting!
Perfectly designed for developers seeking optimal performance and seamless integration with Python’s ecosystem. Our services are designed to support your projects with efficiency and ease.
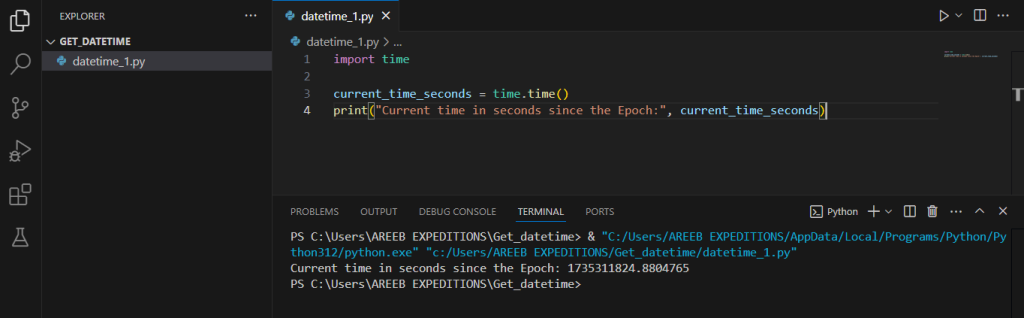
The time module provides various time-related functions. To get the current date and time, you can use the time module’s time function, which returns the current time in seconds since the Epoch (January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 UTC).
import time
current_time_seconds = time.time()
print("Current time in seconds since the Epoch:", current_time_seconds)
This will output something like:
You can convert the time in seconds to a readable format using the ctime function:
readable_time = time.ctime(current_time_seconds)
print("Readable current time:", readable_time)
The gmtime and localtime functions convert a time expressed in seconds since the Epoch to a struct_time object in UTC or local time, respectively:
gmtime = time.gmtime(current_time_seconds)
localtime = time.localtime(current_time_seconds)
print("GMT time:", gmtime)
print("Local time:", localtime)
The calendar module provides functions related to calendar operations. Although it is not specifically designed to get the current date and time, it can be useful for various date-related operations.
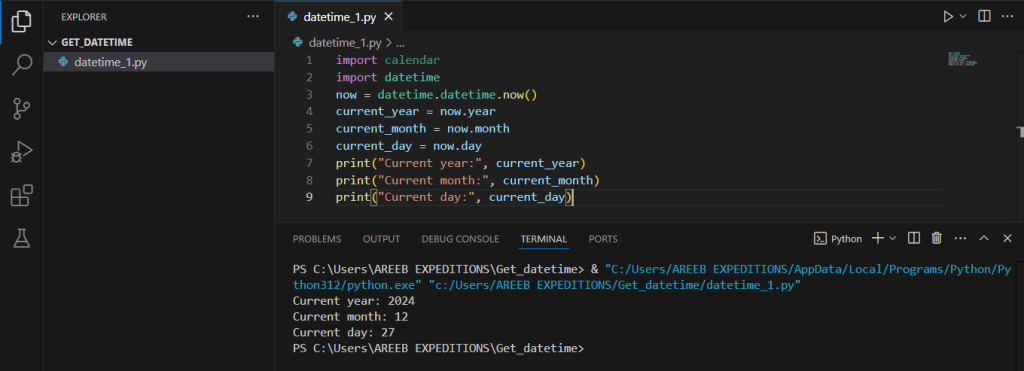
You can get the current year, month, and day using the time or datetime module and then use the calendar module for additional operations:
import calendar
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
current_year = now.year
current_month = now.month
current_day = now.day
print("Current year:", current_year)
print("Current month:", current_month)
print("Current day:", current_day)
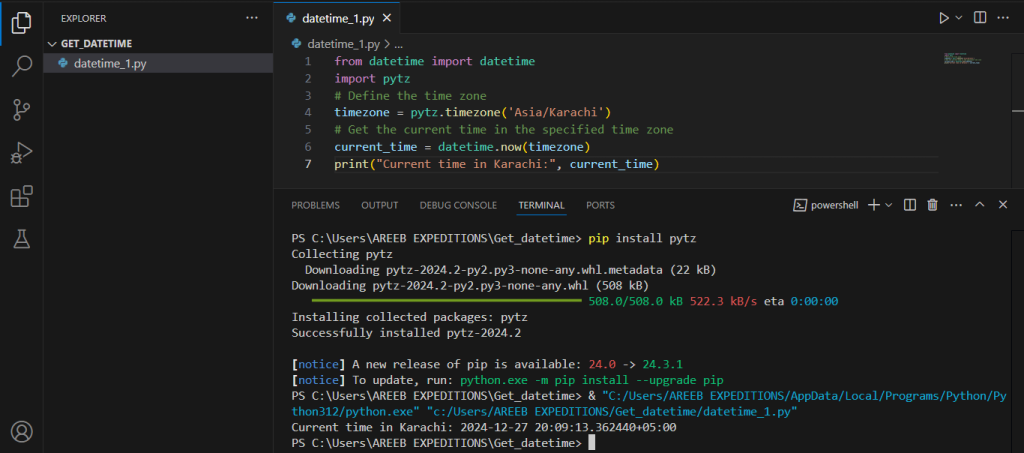
For handling time zones, the pytz library is an excellent third-party package. It allows you to get the current time in different time zones.
You can install the pytz library using pip:
pip install pytz
Here’s how you can get the current time in a specific time zone using pytz:
from datetime import datetime
import pytz
# Define the time zone
timezone = pytz.timezone('Asia/Karachi')
# Get the current time in the specified time zone
current_time = datetime.now(timezone)
print("Current time in Karachi:", current_time)
Learn about How to Substring a String in Python.
The dateutil library extends the capabilities of the datetime module. It simplifies parsing, formatting, and manipulating dates and times.
You can install the dateutil library using pip:
pip install python-dateutil
Here’s how you can get the current date and time using the dateutil library:
from datetime import datetime
from dateutil import tz
# Get the current date and time with time zone info
current_time = datetime.now(tz=tz.tzlocal())
print("Current date and time with time zone:", current_time)
The dateutil.parser module can parse dates from strings:
from dateutil import parser
date_str = "2024-12-27 18:56:00"
parsed_date = parser.parse(date_str)
print("Parsed date:", parsed_date)
The arrow library is another powerful third-party package for handling dates and times. It is simple, intuitive, and provides many utilities.
You can install the arrow library using pip:
pip install arrow
Here’s how you can get the current date and time using the arrow library:
import arrow
# Get the current date and time
current_time = arrow.now()
print("Current date and time:", current_time)
You can format the date and time using the format method:
formatted_time = current_time.format('YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss')
print("Formatted date and time:", formatted_time)
The arrow library makes handling time zones easy:
# Get the current time in a specific time zone
karachi_time = arrow.now('Asia/Karachi')
print("Current time in Karachi:", karachi_time)
Python offers a wide range of modules and libraries for working with dates and times. Whether you are using the built-in datetime and time modules or leveraging third-party libraries like pytz, dateutil, and arrow, you have a powerful toolkit at your disposal. Each method has its own benefits and can be used based on your specific needs and preferences. Experiment with these different approaches to find the one that best suits your project requirements.
Choosing a VPS provider can be a difficult task, with so many options available. That’s why Ultahost understands your specific needs and requirements, and brings you a perfect solution. Get the best free VPS servers with a free trial for Linux or Windows, ultra-fast speeds, and immediate setup.
Use datetime.now() from the datetime module to get the current date and time.
No, Python’s built-in datetime module provides everything you need.
Use the strftime() method to format the date and time as needed.
Yes, use date.today() from the datetime module.
Use datetime.now().time() to get the current time.
Yes, it provides precise and accurate date and time data.
Yes, you can use libraries like time or pytz for additional functionality.