Creating a sitemap.xml is a vital phase in creating a website, but many beginners are scared off because it seems and sounds too complicated. So we decided to collect and systematize the available knowledge in this field. Now making a sitemap will be extremely easy!
What is sitemap.xml?
The sitemap is a file containing a list of pages of the website. It helps robots index and reach essential resources, especially those newly created and those difficult to access.
According to Google’s guidelines, the sitemap as a single file should not exceed 50 MB and 50,000 URLs and should be in XML format.
It is not always a good idea to include all subpages in a sitemap, because many of them can have attribute value rel “nofollow” or “noindex”. But no worries, you can learn more about which URLs to include in your sitemap in this article.
What data does sitemap.xml consist of?
The XML format allows you to present your data in a structured way. Using this format means that everyone submits URL information in the same way and crawling robots will read it without problems. The sitemap.xml file should be UTF-8 encoded and consist of 3 obligatory tags.
- <urlset> Contains the file and a reference to the current protocol standard. It is the beginning and ending element for each sitemap.xml file. It contains all the tags.
- <url> The parent tag of each URL entry. You can enrich it with additional tags.
- <loc> The tag represents the location of the subpage. The location tag should contain the URL in full form, i.e. also with the HTTP/HTTPS protocol.
- <lastmod> Informs about the last modification date. The robots know if the content of a given subpage has been changed since the last scan. In lastmod, we use W3C Datetime (YYYY-MM-DD).
- <priority> Tag is supposed to indicate the most important subpages. The range of values in this tag is from 0.0 to 1.0, where the default priority for subpages is 0.5. Unfortunately, Google Robots ignores it (source).
- <changefreq> Tag specifying the frequency of changes. In principle, this element was to help determine the frequency of scanning a given subpage. You can insert one of the following values:
- always – documents that change each time they are opened;
- hourly – changes every hour;
- daily – changes every day;
- weekly – changes every week;
- monthly – changes every month;
- yearly – changes every year;
- never – never changed.
What URLs are included in the sitemap?
As I mentioned at the beginning of this article, not all URLs should be included in your sitemap. Some elements may harm the indexing process. So let’s make sure that the sitemap contains only valuable subpages:
- Pages generating the 200 response code;
- Pages not blocked in robots.txt;
- Canonical links;
- User valuable pages;
- Pages not protected with a password or with difficult access;
Looking at the type of website, these will be the home page, product categories and pages, blog entries, blog categories, FAQ pages, and static pages.
Which URLs should not be in the sitemap?
It is necessary to know which addresses you should avoid when creating a sitemap:
- URLs with redirects;
- Error pages 40X and 50X;
- Pages blocked from robots.txt;
- Pages tagged with noindex;
- Pages of little value for users (regulations, privacy policies);
- Pagination Pages;
- Search result pages;
- Pages with filtering or sorting parameters;
How to generate a sitemap? – The most popular methods
Depending on how big the website is and what CMS you use, generating a sitemap can be done using free tools (sitemap.xml generators) or built-in tools or plugins.
How to generate sitemap.xml for WordPress?
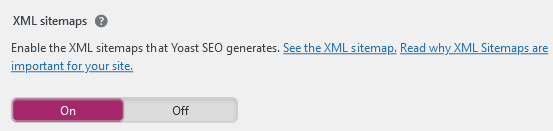
Let’s start with the most popular CMS. The fastest and easiest way to create a sitemap is to use the Yoast SEO plugin. It automatically creates a sitemap for us. We only choose the appropriate settings and decide which resources to include. The plugin is very intuitive and easy to use. Additionally, its basic version has options that are sufficient for most webmasters.
How to generate sitemap.xml for other CMS?
Other popular CMS also have worthy plugin systems. But if you cannot find a plugin or a module that you can use to create your sitemap, that doesn’t mean you need to prepare it manually. There are many free and paid tools that you can use to help.
In this article, I want to cover decisive issues related to sitemap.xml, so the comparison of free sitemap generators won’t fit here but google “free sitemap XML generator” and you will get dozens of results.
The free online generator that creates a sitemap has some limitations. Mostly it is the maximum 500 URLs that you can put in sitemap.xml. So if your website is not too complicated, you will find a free online sitemap.xml generator. If your website is complex, you ought to put more effort into choosing good software.
Manually created sitemaps do not update automatically. Remember to update them after adding new products, entries, or pages.
Where to put the sitemap.xml file?
The generated sitemap.xml file usually is located in the root directory of the website to which it relates and is available at . Usually, but not always. Both the name and the path may differ depending on whether the sitemap was added manually or if we used built-in solutions.
To make it easier for crawlers to get to your sitemap, it’s a good idea to put the path to it in your robots.txt file. All we need to do is add the Sitemap rule.
The most popular types of sitemap.xml
Sitemaps are not always the same. Depending on the type and size of your website, you may need different types of sitemaps. Be sure to find out what a sitemap index is, when it is worth choosing a graphics map, and how your sitemap is related to Google News.
Classic site map
A standard XML sitemap links to pages within your website. Most often known as sitemap.xml
Summary map sitemap-index.xml
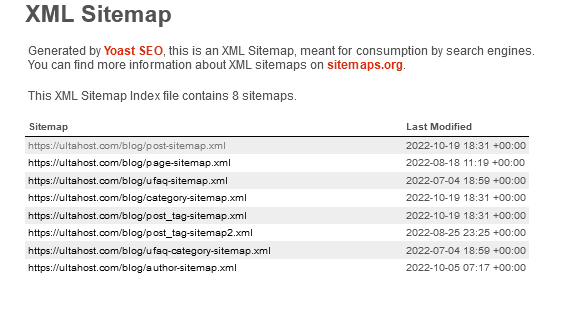
The sitemap index is nothing more than a sitemap containing other sitemaps. It is used for complex websites when one huge sitemap would exceed 50 MB. It has to be divided into several smaller ones and linked together by using the sitemap index.
Also, the previously mentioned Yoast SEO plugin creates a sitemap index for different kinds of pages. Yoast SEO creates a separate sitemap for pages, blog posts, blog categories, or authors.

Sitemap with image files and videos
If you want your image files to appear in the Google image search engine, you can increase the chances of it by creating a dedicated sitemap. While crawling robots have no problem finding and indexing graphic files, settings such as lazyload may make it difficult for them.
The sitemap for articles on Google News
Google News has become a source of information for numerous users. It is worth fighting over a good position there. The sitemap with news articles should contain links to articles not older than two days.
How to submit sitemap.xml in Google Search Console?
We do not create sitemaps for ourselves or users, but crawling robots. I recommend publishing your sitemap and submitting it to Google Search Console so that Google robots can easily reach it.
Step 1: Go to the “Sitemaps” tab in the side menu.
Step 2: Enter the path to your sitemap. Usually it is sitemap.xml or sitemap-index.xml.
Step 3: Verify the sitemap status after uploading it. You need to check the upload date, last read, status and detected URLs. If you see “Failed to Download”, resubmit your sitemap. If the error repeats, check if the file is available at the address indicated.
Why is sitemap.xml so meaningful from the SEO point of view?
The creation of sitemaps in 2005 was a significant step towards better indexing of websites by search engines. Over the years, search engines and their crawling robots have evolved and have been finding resources better on subpages.
Checking and optimizing your sitemap has also become an essential part of SEO audits. The robots with the right website structure and good internal linking will have no problem indexing your subpages, but they do it slowly.
Creating a sitemap is a relatively quick and simple activity that will make it easier to find pages troublesome to access. It may help in the faster discovery of pages by robots. Thanks to submitting your sitemap in Google Search Console you will get SEO results faster.
Conclusion
The sitemap is one of the basic elements of website optimization. You can create a sitemap using the CMS and its built-in functions or using generally available tools. Generating and adding it in GSC will make it easier for robots to reach all the subpages you want to index. Adding a sitemap is especially important for large and new websites.
If you enjoyed this article, then you’ll love UltaHost hosting platform. Get 24/7 support from our support team. Our powered infrastructure focuses on auto-scaling, performance, and security. Let us show you the difference! Check out our plans!










