How to fix the “DNS server not responding�...
When we visit a website, our device talks to a Domain N...
If you are a Linux user, few tools commands is as performant as the grep. As its acronym suggests, grep “global regular expression print” is not just a search engine. It can also target text files, extract information, and navigate specific files in volumes of data. Even for a new Linux user, gaining mastery in command line interface with Linux using terminal can be achieved by mastering The grep Command.
Today, we’ll explore The grep Command and its various techniques. The grep command is a simple but very adaptable tool that can accomplish a lot. As all things, The grep Command comes with options, multitudes, that can tailor its action.
The grep command is an important tool that can be used for a variety of tasks, including:
The power of grep lies in its simplicity and flexibility. It’s a command-line tool, meaning it can be easily integrated into scripts and automated workflows. Additionally, its support for regular expressions allows for powerful and precise pattern matching, enabling users to find exactly what they’re looking for.
Learn more about exploring the ping command in Linux.
To use the grep command simply open your Linux terminal and type the following command:
grep --help
The grep help listed the usage of the command options and patterns, following the image shows how the output looks like:
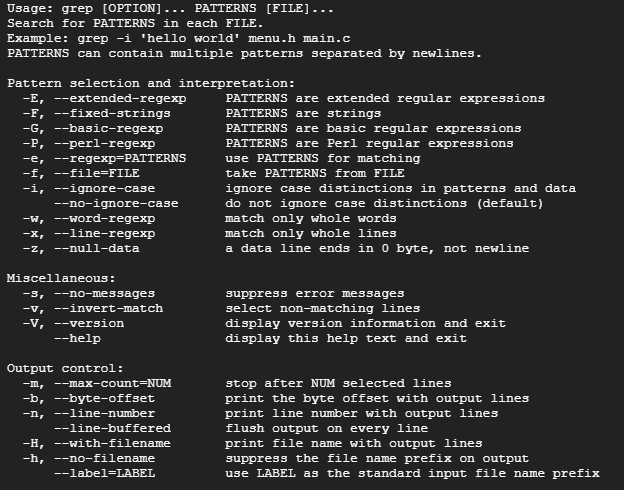
The grep command output includes the following information:
Practice Grep Commands On Our Linux VPS Today!
Ultahost provides Linux hosting with NVME SSD storage. This means your website will load faster and be more responsive.
Grep stands for “global regular expression print”. In simpler terms, it’s a command-line tool used to search for specific patterns in text files. It scans through each line of a file and prints only those lines that match the provided pattern.
The grep command contains two key elements:
When you are creating and managing a file in Linux and you have a bunch of data, The grep command useful to search and optimize your workflow. Here is the basic syntax of the grep command as follows:
grep pattern files
For example, to find all lines containing the word “error” in the “system.log” file:
grep error system.log
The grep command can also count the occurrences of words in directories. For example, In the directory “/var/log” you can use grep for the “warning” message in all log files.
grep -c warning /var/log/*
The grep command can also display lines before and after each match in the “app.log” file:
grep -A 2 -B 2 "critical error" app.log
Grep, the powerful text-searching tool, is important to use when combined with other commands. This combo approach allows you to find complex search tasks efficiently. Let’s explore some ways to use grep with other commands:
Piping output:
The pipe symbol | sends the output of one command as input to the next. Here’s an example:
ps aux | grep firefox
This command uses ps aux to list all processes and pipes the output to grep, which then filters lines containing Firefox.
Using command output as search pattern:
Instead of a static string, you can use the output of another command as your search pattern. Here’s an example:
cat /etc/passwd | grep "$(whoami)"
This command uses cat to read “/etc/passwd” and pipes the output to grep. However, the search pattern is not a string. It is dynamically generated by “whoami” which outputs your username.
Combining with other text processing tools:
Grep often plays well with other text manipulation tools like sed and awk. For instance, you can combine grep and sed to replace all occurrences of a pattern:
grep "error" log.txt | sed 's/error/fixed/g'
The above command can replace “error” with “fixed” in lines containing “error” in log.txt
The grep command is a powerful tool that plays an important role in various technical fields. Its ability to efficiently search for patterns in text makes it an essential skill for anyone working with Unix-like systems. Whether you’re a system administrator, developer, data analyst, or simply someone who wants to work efficiently with text files, grep is a valuable tool to have in your area in every aspect.
The grep command is a powerful tool for searching text in files and matches. You can practice these commands on Ultahost’s Free VPS hosting. This is a great opportunity to try out VPS hosting without having to pay anything upfront. We offer a variety of VPS plans to choose from, so you can find one that meets your needs.