How to Find a File with Find Command in Linux
The find command in Linux allows you to search within a...
The pipe command symbolized as the bar (“|”) enables multi-tasking through the linkage of commands in the execution of a single operation. This function is especially handy in Linux and the rest of the Unix-like operating systems. You can think of it as a pipe that takes the data flowing out of one program and feeds it directly into the next program in the sequence. You can achieve intricate operations using a single command line because it permits the combination of numerous commands.
The current post aims to provide a thorough explanation of the Linux operating system with a special focus on the pipe command. It features the impact of its application, reasoning as to why it is predominantly utilized, and showcases a stepwise guide on its basic and advanced methodologies.
The pipe command in Linux is a step-by-step procedure that allows you to fully exploit the command line capabilities. When you learn the effective use of pipes, you will be able to save more time, create better resources, and accomplish more intricate processes with less difficulty. Below are a few remarks on the functionality of the command Linux pipe:.
Let’s discuss the example in the Linux command pipe with the help of syntax using a command-line interface.
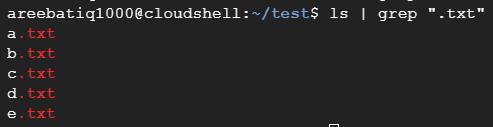
Consider the example, the ”ls” command lists all the files in the current directory. The output of the ls command is then piped to the grep command, which filters the list and only shows lines that contain the pattern “.txt”. The final output is a list of all the files in the current directory that end with the “.txt” extension.
ls | grep ".txt"
Here is an image example of using the pipe command to list all the files in the current directory and then filter them to only show files that end with the “.txt” extension.
Another example of a pipe command is filtering output by finding lines containing a specific word in a file. Type the following command:
cat myfile.txt | grep "keyword"
As the image shows below after creating a Linux file containing an Ultahost keyword filtering out from paragraph.

Beyond the basics
Pipes are not restricted to simple filtering and sorting. They can be used for:
The true form of pipe lies in their ability to chain multiple commands together. Consider a scenario where you want to find all the lines containing “error” in a log file, sort them by date, and finally, extract just the error messages. Without pipes, this would require several independent commands, each demanding individual execution. But with the help of a pipe, you can type the following command:
cat log.txt | grep "error" | sort -k 1 | cut -d " " -f 2-
In this chain, the cat feeds the entire log file to grep, which filters for lines containing “error”. The sorted output then goes to cut, which extracts the second and subsequent fields (containing the actual error messages). Each command receives its input directly from the previous one, creating a streamlined workflow.
Start chaining commands on Linux today!
Ultahost provides Linux hosting with NVME SSD storage. You can practice the pipe command in our Linux VPS to streamline your process.
Here are some uses of the pipe command in the Linux operating system:
The Linux pipe command is a powerful tool that transforms the command line from a series of tasks into a data pipeline. The above post summarizes the key points about the pipe command functionality and its use cases. Whether you are a pro or a newbie, that takes the output of one command and feeds it straight into another which unlocks the chaining abilities.
The pipe command is important for Linux mastery, streamlining workflows, and amplifying command-line efficiency. But even the most streamlined pipeline can be slowed by hardware. That is where Ultahost’s fast and quick VPS comes in, which empowers the full speed of your pipelines with lightning-fast data access. Effortlessly handle complex tasks and large datasets.
The pipe command “|” in Linux is used to send the output of one command as input to another, allowing them to work together.
Simply type a command, followed by a pipe “|”, and then another command. This connects the output of the first command to the input of the second.
Yes, you can chain multiple commands using pipes, creating a sequence of actions that process and manipulate data in a streamlined way.
An example would be ‘ls -l | grep “.txt”,’ where the list of files (ls -l) is filtered by the grep command to show only those containing “.txt.”