How to Fix Duplicate Title Tags in WordPress
Duplicate title tags can be unfavorable for SEO stands ...
Many things can contribute to the decline in performance of a WordPress site and some of those can include heavy plugins, oversized databases, and outdated cached data. When your database expands with unused or expired entries, your page speed suffers, and as a result, your visitors experience delays. One thing that can clutter up your database is called transients.
Transients are examples of cached temporary data that are stored in your database by plugins, themes, and the core system so that they can perform operations faster. Transients can be useful, the problem is that they usually remain in your database after they have expired, or are no longer needed. Eventually, the bloat from this buildup will hurt site performance.
Managing and clearing transients regularly is extremely important when it comes time to optimize your database. As a result of managing and clearing them, you will reduce your server load, increase your WordPress speed, and improve the overall experience of your website, to give your users a fast and seamless experience.
WordPress transients are temporary database entries created through the transient API that are designed to store a specific piece of data with an expiration time, which can serve to minimize repeat processing. Whereas options stored in the database are classified as general and will remain until removed, transients are meant to expire automatically after a set period of time. That is, transients are distinct from permanent options that remain until the developer actively removes them.
Boost WordPress Speed with Smart Optimization
Keep your site running at peak performance by managing transients effectively. Enjoy smoother loading, optimized databases, and a faster user experience—all with simple, reliable steps.
Transients differ from full caching systems as well. Instead of caching entire pages or a larger set of data, a transient speeds up and/or saves money for elements that are smaller like stored queries, remote API responses, or short-term plugin data. For example, instead of fetching a social media feed on every page load, a theme can instead utilize transients to store the social media feed for a few minutes.
By utilizing these ephemeral entries in place of a full database query, developers can cut down on the work done by the server and improve overall performance without putting unnecessary strain on server resources.
Any transients that are expired or never used pile up in the database over time, instead of being removed as designed. Each transient that isn’t cleared contributes to database bloat and wasteful data in the wp_options table. As the wp_options table grows larger, the time it takes to execute any queries on the website grows longer. This negatively affects performance as well.
The larger the wp_options table, the more costly it is to the server resources. Queries that are simple requests like loading a homepage or executing a search, take longer when unnecessary transients exist in the database. This costs more processing on the server during execution and reduces performance.
Visitors can feel the impact of a bloated wp_options table by all pages on the site loading slower, navigation feels slow, and decreases the responsiveness of the website. By clearing these expired transients reduces the size of the wp_options table, reduces server load and keeps the site running as fast as possible for a better user experience.
There’s nothing wrong with being a bit curious about how many transients are stored in a database before deleting them. One way you can check is through phpMyAdmin. At this stage, you may have realized that any transients that are created will show up in the wp_options table, and that when you find that they have names that consist of _transient, if you do a quick search in the options table you will also reveal active and expired transients.
If you want to keep it simple, there are plugins like Query Monitor or Transients Manager that list what is stored as a transient. These plugins will show expiration times too, which means they are helpful to determine what should be deleted.
It is always best to check now rather than to delete it later. You will understand what is present and you will have control over what gets deleted in the cleaning process.
WordPress plugins provide a rapid, low-risk option for users wanting to delete transients without using SQL. Plugins scan the database, provide a list of all the existing transients, and provide you options to delete them with one click, or on a scheduled basis.
For non-technical users or administrators who want the most reliable results with the least amount of manual effort, this is a method that was made for them. However, regardless of the method you choose, always remember to back up your database before doing any cleanup, and perform the action when your site has low activity.
WP-Optimize has a full-service cleanup option. Once you install and activate the plugin, open the plugin and navigate to the Database, or Cleanup area. From there, run the analyzer to find expired transients, as well as enabling any preview options that are available:

After you have checked the results, click the link to start the cleanup and you will receive confirmation when it is complete. Also, WP-Optimizer offers automation, so you can fill it out to regularly have transients removed without any human involvement.
Advanced Database Cleaner provides you with more selective control for those users who want more detail. Once installed, you will first do a database scan which will show you your transients, orphaned entries, and unused post metadata. You can filter the results to show only the expired, or outdated transients:

You can select what you want to delete and perform the clean up. Because it provides more granularity, Advanced Database Cleaner is a good option when you want to delete some transients while retaining others.
Transients Manager gives a detailed look at each transient key and its expiration. Once installed, open the transients listing from the Tools menu to view keys, values, and expiry times.
You can delete individual transients for debugging or remove groups in bulk. This plugin is especially useful when you want to confirm what a transient contains before deleting it.
The process will be similar for all tools: backup your database, install and activate, run the scan to find transients, go through the results, and remove transients that are expired or no longer needed. Then, test your key pages and any plugin function to ensure that everything is still working properly. If you want, you can configure scheduled cleanups at set intervals, to prevent a similar buildup in the future.
There are some advantages to using a plugin-based optimization tool. A plugin minimizes the risk of making SQL errors and gives you scheduling functionality, and transient cleanup functionality is available to those without any coding ability. The downsides of a plugin include adding another plugin, class, or library to your stack.
It may also cause conflicts with caching tools or remove active transients if settings are too aggressive. To keep yourself safe, always run good plugins, use a staging environment to migrate changes when possible, and always have rollback backups ready in case it makes things worse.
If you prefer having direct access to WordPress, phpMyAdmin enables you to delete transients without any plugin dependency. This way is slightly more advanced yet provides complete ownership of the database. However, because you are dealing with core tables, it is essential that you always perform a full database backup prior to running any changes.
Log into your hosting control panel and open phpMyAdmin. Select your WordPress database and open the wp_options table:
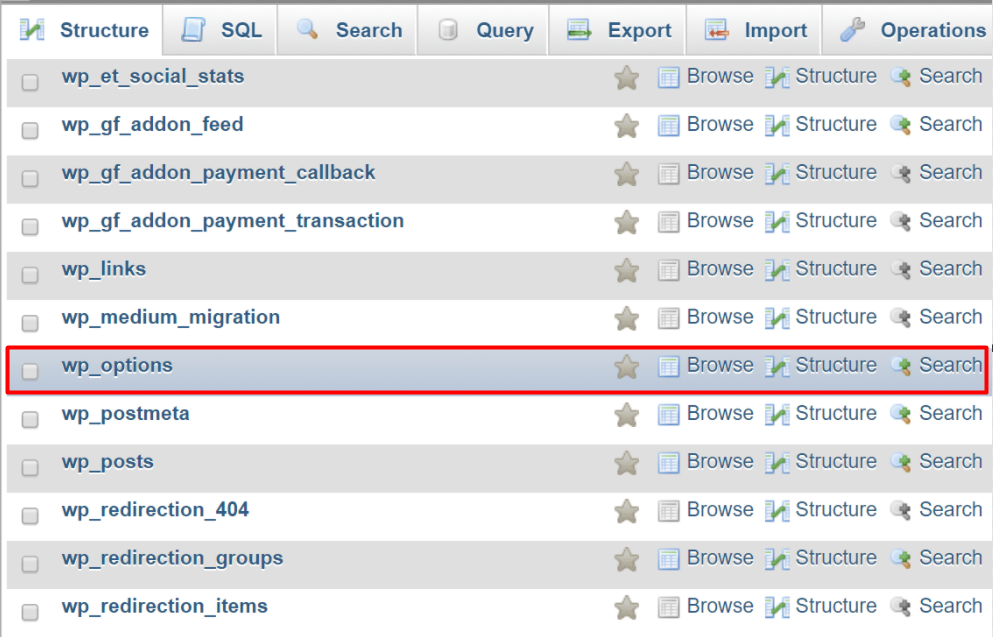
In this table, transients appear with names beginning with _transient or _transient_timeout:
You can run a search to filter these entries and quickly identify which ones are stored.
Expired transients can be removed using a simple SQL query. A common example is:
DELETE FROM wp_options WHERE option_name LIKE ‘_transient_%’ to remove all transient entries:
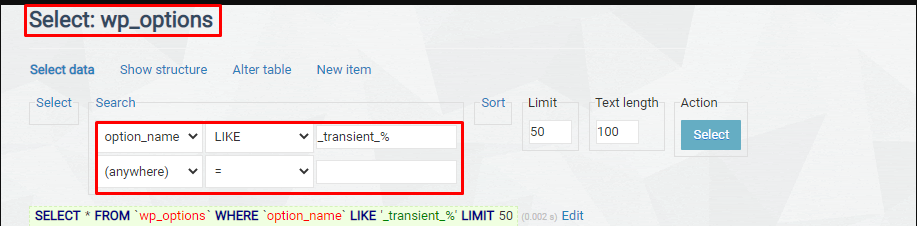
This will delete only expired ones, target _transient_timeout rows with conditions that match outdated timestamps. Always verify your query before running it to avoid deleting unrelated data.
The upside of using phpMyAdmin is that you can be precise. You can delete expired data in bulk or target just a few rows of data to troubleshoot. The downside is that you risk human error; one small mistake of incorrectly running a query can ruin the database or mess up functionality on the site which is vital for the website.
This option may be more ideal for advanced users who are familiar with database management or those working on a staging site that will not merge immediately with an active site.
In this guide, we’ve discussed transients, their impact on WordPress performance, and why they shouldn’t be ignored. We began with an overview of what transients are, what differentiates transients from options and caching, and how expired transients contribute to a bloated database. Then we explored how unchecked transients slow down queries against the wp_options table, increased server load, and result in slower page speeds for site visitors.
We also looked at some practical ways to manage transients. You learned how to find transients that already exist using phpMyAdmin or by using a plugin, how to safely clear transients using tools like WP-Optimize, Advanced Database Cleaner, and Transients Manager, and how to delete transients manually via phpMyAdmin for greater control over which ones to delete. Finally, we explored best practices such as scheduling cleanups, limiting plugin bloat, monitoring database growth, and using persistent caching. Following all of these steps will help keep your WordPress site fast, stable, and optimized.
Easily clean and manage transients with this WordPress optimization guide. Whether you’re preventing database bloat, improving load times, or keeping plugins running smoothly, Ultahost’s managed VPS hosting ensures fast, secure, and reliable performance—helping your site stay optimized with less effort.
UltaAI – Smart AI Assistant for Ultahost Clients
UltaAI is your advisor for anything related to domain or hosting. Experience personalised suggestions.