How to Install Windows 11 on Hyper-V Virtual ...
Hyper-V is a virtualization platform built into Windows...
Permission-denied errors in Linux systems occur when the user does not have permission to access or modify a file or directory. Linux systems require specific permissions to execute commands. Every directory and file is allotted with specific privileges. If you do have not proper access to authorize the file or a directory it will give results as a “permission-denied” error. It can be solved by getting proper access to files and directories in Linux.
In this post, we will guide you in fixing the “permission-denied” error in Linux. This error occurs when you do not have permission to do something, like open a file or run a program. We will explain to you how to use different Linux commands to fix the problem. I am assuming that you already installed Linux on your system.
Learn How to Install Kali Linux on your system: A Step-by-Step Guide
In the security measure of Linux, the Linux permission system is created which means the user does have not access to the superuser in the Linux case which is the root user to help protect data from unauthorized access. There are three types of Linux permission systems.
You can check by typing the following command in your terminal, also you can check by specified folder or file.
ls -la
The following command will display files and folders, as the figure is shown below:
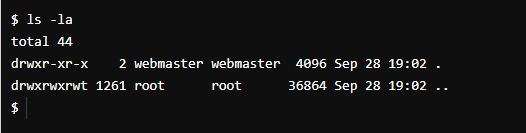
For a specific file or folder, you can also check it by the specified file or folder name, as shown below:
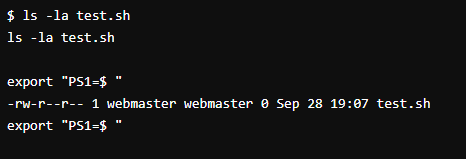
According to the image the test.sh file contains permission to read and write but the file can not have permission to execute.
The reason for “permission-denied errors” is when the user does not have the necessary permissions to access or modify a file or directory. This can be due to a number of reasons, such as:
To fix “permission-denied errors”, you can do the following:
chmod u+rwx test.sh
chown username test.sh
sudo mkdir test
It will ask for the password of your username for creating the directory. You can also use “sudo su” to enter as root. In this case, there is no need to type sudo after login as root.
Checkout when changing file permissions, especially for system files. Changing the wrong permissions can make your system harmful. You can practice these commands on Linux VPS servers. Consider Free VPS for practicing Linux commands for starting out.
When you create a file in the bash you need to change the file permissions, you can use the chmod command to give permission to the file. For example, to give yourself execute permission for a file called “test. sh”, you would run the following command:
chmod +x test.sh
After that, you can run the file by typing the following command:
./test.sh
Linux “permission-denied” errors happen when you do not have permission to access or change files or folders. You can fix these errors by using the chmod command to change permissions or the chown command to change ownership. Be careful when changing permissions, as incorrect changes can be dangerous. It is important to understand Linux file permission concepts like read, write, and execute permissions before making changes.
At Ultahost, we are committed to providing our customers with the best possible service and support, and we are always working to improve our offerings. You can choose us for our Linux VPS hosting plan that are designed to be scalable and flexible, so you can always choose the right amount of resources for your needs.