How to Change RDP Screen Resolution
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) allows you to connect to ...
Docker allows developers to build, ship and run applications on an open-source platform. Applications have dependencies and libraries required for them to run, and containers ensure that there is consistency across different environments by encapsulating everything needed within a single unit.
Docker Hub acts like a cloud repository, but for docker images, and therefore contains a huge collection of them. With docker hub, developers can retrieve perfectly made images for numerous software applications, libraries and frameworks. This in turn saves developers a lot of time that they would otherwise spend building images. It also provides a central place for developers to store, share and work on docker images which improves collaboration.
This article will teach you how to pull and push images from docker hub.
Pushing and pulling stand as core tasks in Docker; they let you send your images to Docker Hub and grab images others have already saved there.
To push an image to Docker Hub means moving a local image from your computer or server into the online Docker registry. You can think of it like handing a completed software package to a public shelf so anyone can pick it up. When you push, the full build of your app, plus all its libraries and settings, travels along. After that, anyone can pull the same image and run it on their machine, confident the container will behave exactly the same everywhere.
To Docker pull image from Docker Hub involves downloading a Docker container image from Docker Hub’s registry onto your local machine or server. It’s similar to fetching a pre-built software package for use in your environment. When you pull an image, you’re retrieving the exact blueprint of an application along with its dependencies. This enables you to deploy the application as a container on your system, ensuring consistency across different environments.
Let’s understand how to push Docker image to Docker hub and further we will discuss how to pull Docker image to Docker hub
Step 1: Install Docker
Before you can push or pull images to and from Docker Hub, you’ll need to set up your environment by installing Docker and creating a Docker Hub account.
The installation of docker depends on the operating system you are using. You can visit this link if you want to install Docker on Windows or if you are a Linux user check out our guide on how to Install Docker on Ubuntu.
Step 2: Log in to Docker Hub
After installing Docker you also need to create a Docker Hub Account.
Signing up for a Docker Hub account is free and grants you access to both public and private repositories.
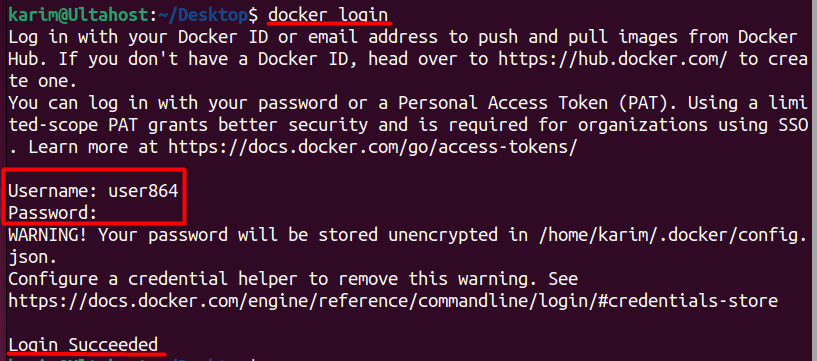
After that, you can sign in directly if you are using Windows. In case you are using Linux then you can execute the below command to log in to Docker:
docker login
This command will prompt you to enter your Docker Hub username and password.
Get an affordable Ubuntu Server for a Docker Instance
Get the reliability of the world’s most popular Linux distro and the flexibility of a virtual server. Enjoy blazing-fast speeds and low latency.
Step 3: Tag the Docker Image
Before pushing an image to Docker Hub, you need to ensure that it’s properly tagged with the repository name, version, and optionally, a specific tag.
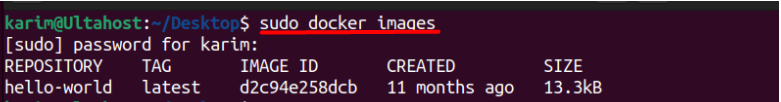
For this, you need to first find the docker image that you want to tag using the below command:
docker images
Now use the following command to tag an image:
docker tag <image_id> <username>/<repository_name>:<tag>
Replace <image_id> with the ID of the Docker image you want to push, <username> with your Docker Hub username, <repository_name> with the name of your repository on Docker Hub, and <tag> with a version tag for the image.
So the actual command in our case could be:
sudo docker tag d2c94e258dcb user864/myhello:latest

Tagging Docker images is crucial for managing versions and organizing repositories. Tags help identify different image versions, facilitating push and pull operations from registries like Docker Hub. They enable version control, allowing easy tracking of changes and reverting to previous states when needed. Overall, tagging ensures clarity, organization, and efficient image management within Docker environments.
Learn about What is Docker and What Benefits Does It Offer?
Step 4. Push the Docker Image
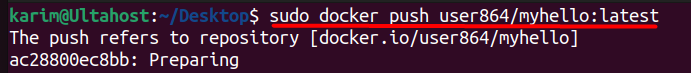
Once the image is tagged, you can run the following command for Docker hub push:
docker push <username>/<repository_name>:<tag>
Replace <username>/<repository_name>:<tag> with the tagged image name you want to push.
sudo docker push user864/myhello:latest
Step 5. Pulling a Docker Image
To pull a Docker image from Docker Hub, you simply need to specify the image name:
docker pull <username>/<repository_name>:<tag>
Replace <username>/<repository_name>:<tag> with the image name you want to Docker hub pull.
Since we want to pull the image from “user864” named “myhello” with the tag “latest”, the command would be:
docker pull user864/myhello:latest

Pulling an image from Docker Hub is a straightforward process facilitated by the Docker command-line interface. You can search for images using keywords and pull the desired image to your local environment.
When working with Docker images, security should be a top priority. Always verify the integrity and authenticity of images before pulling or using them. Utilize Docker Content Trust to enable image signing and verification, ensuring that only trusted images are used in your environment. Regularly update your images to patch any security vulnerabilities and adhere to the principle of least privilege when configuring image permissions.
Docker and Docker Hub streamline the process of building, sharing, and deploying applications through containerization. Docker Hub serves as a comprehensive repository, allowing collaboration and accelerating development by providing access to a wide range of pre-built images.
Learning to push and pull images from Docker Hub empowers developers to efficiently manage their environments, ensuring consistency and reliability across different setups. By following the steps outlined in this article as well as the best security practices, developers can leverage the full potential of Docker and Docker Hub to streamline their workflows and enhance application deployment processes.
Integrate Docker with the best VPS server offered by Ultahost to get the best experience. Enjoy ultra-fast SSD NVMe speeds with no dropouts or slowdowns all at an unbeatable cost.
Docker Hub is a cloud-based registry service that allows you to store and manage Docker images. It provides both public and private repositories for storing Docker images.
Yes, you can push Docker images to both public and private repositories on Docker Hub. Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to push to the private repository, and use the appropriate repository name when tagging your image.
Yes, you can specify a version or tag when pulling a Docker image. Use the : notation followed by the version or tag name after the image name. For example, docker pull ubuntu:latest.
You can search for Docker images using the docker search command followed by keywords related to the image you’re looking for. This command will display a list of matching images available on Docker Hub.
To pull a Docker image from Docker Hub, use the docker pull command followed by the image name and optionally the tag if you want to pull a specific version of the image.