How to Install RabbitMQ in Linux
RabbitMQ is a free and open-source messaging system tha...
In Linux systems, processes are the backbone of system functionality, executing tasks, and providing services. Effective process management is crucial to ensure system stability, performance, and security. The `ps` command, specifically the `ps aux` variant, is a powerful tool in the Linux administrator’s arsenal, providing a snapshot of the system’s process landscape. By mastering the `ps aux` command, administrators can efficiently identify, analyze, and manage processes, troubleshoot system issues, and optimize system resources.
With its ability to display detailed process information, filter output, and integrate with other Linux ps commands, `ps aux` is an indispensable tool for Linux professionals. In this article, we will delve into the capabilities and applications of the `ps aux` command, exploring its options, output, and real-world use cases to help you master process management in Linux.
The Linux ps aux command is a powerful tool for process management in Linux systems. To unlock its full potential, it’s essential to understand the breakdown of the command and its various options.
The ps command stands for “process status,” and it’s used to display information about running processes on a Linux system. The aux options are used to specify the type of information to display.
Start Practice commands on Linux today!
Ultahost provides Linux hosting with NVME SSD storage. You can practice the pipe command in our Linux VPS to streamline your process.
Now lets run the standalone ps aux command in linux:
ps aux
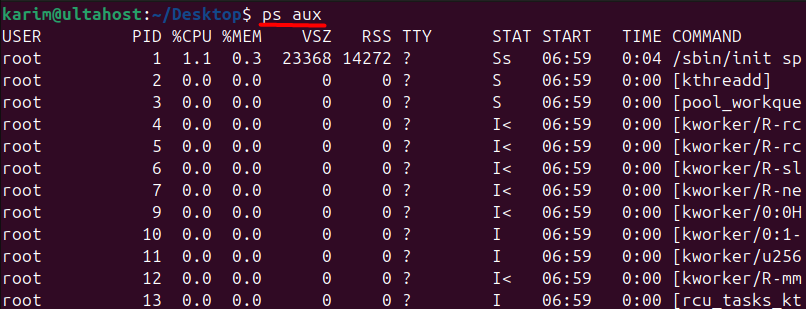
Let’s break down this sample output from the ps aux columns:
Options and Switches
In addition to the aux options, the ps command accepts several other options and switches that can be used to customize the output. Some common options include:
Displaying All Processes
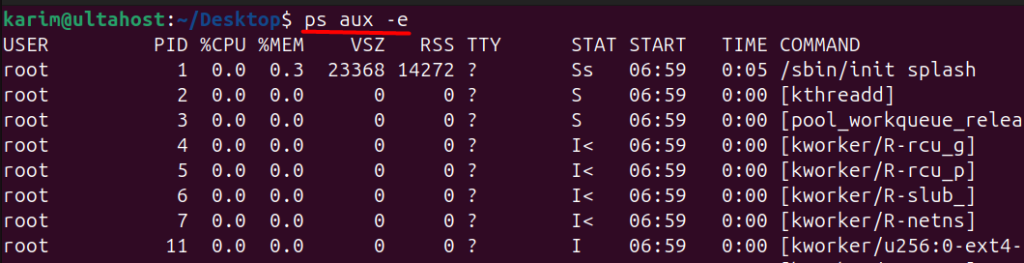
The -e option tells ps to display all processes, including those that do not have a controlling terminal. This is useful for seeing all processes running on the system, even those that are not associated with a specific terminal or user session.
With -e, you’ll see all processes, including system processes, kernel threads, and daemons that don’t have a terminal associated with them:
ps aux -e
Learn more about Exploring the ping command in Linux.
Displays a Full Listing of Information
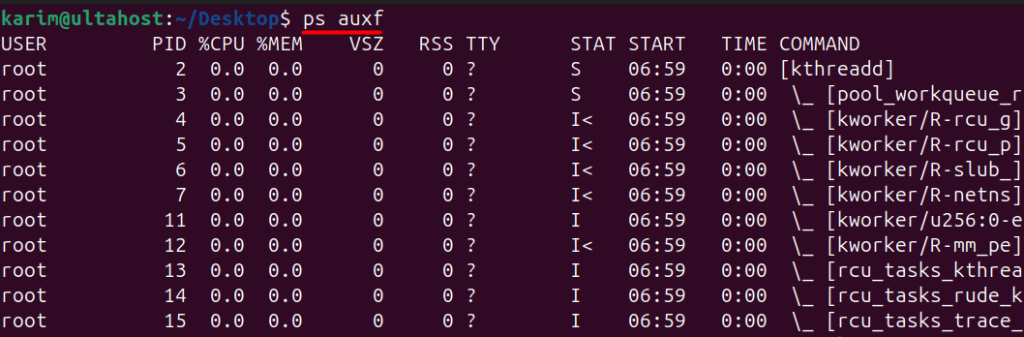
The -f option tells ps to display a full listing of information about each process. This includes additional columns and information that are not shown by default. The output will include columns such as UID, GID, PPID, C, STIME, and TTY, among others:
ps auxf
Filtering and Sorting Processes
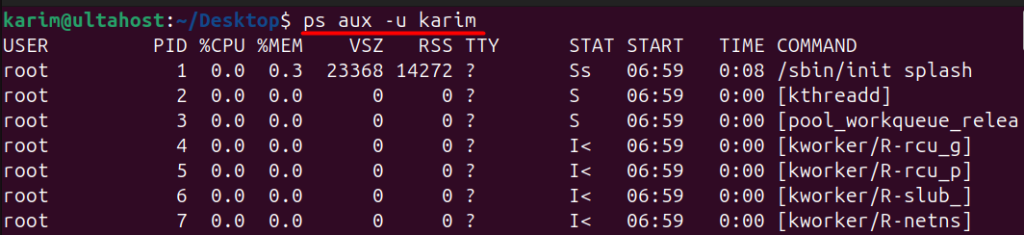
The ps command can be used for filtering and sorting processes based on specific criteria. For example, you can use the -u option followed by a username to display processes owned by a specific user:
ps aux -u karim
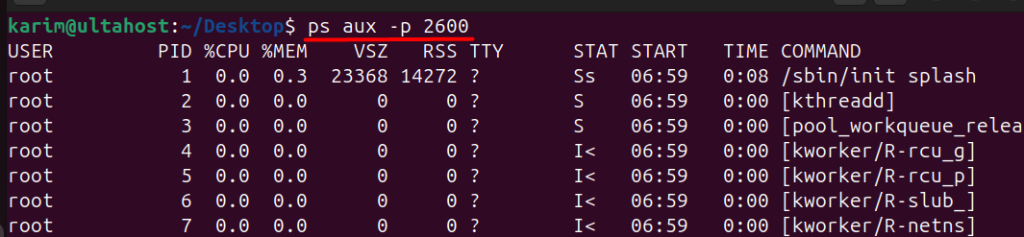
You can also filter the output based on the process ID (PID) using the -p option:
ps aux -p 2600
Sorting and Formatting Output
The ps command also allows you to sort and format the output using various options. For example, you can use the –sort option to sort the output by a specific column:
ps aux --sort %cpu
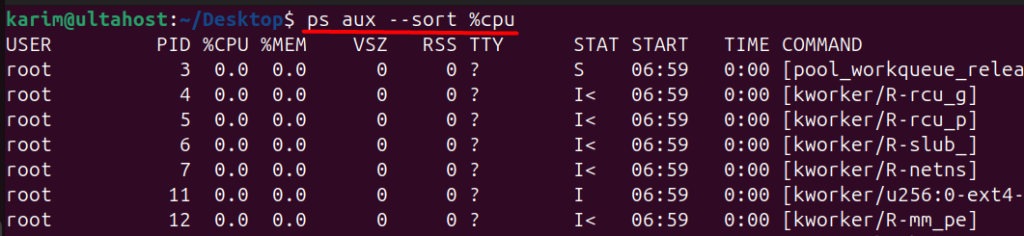
This will sort the output by the %CPU column.
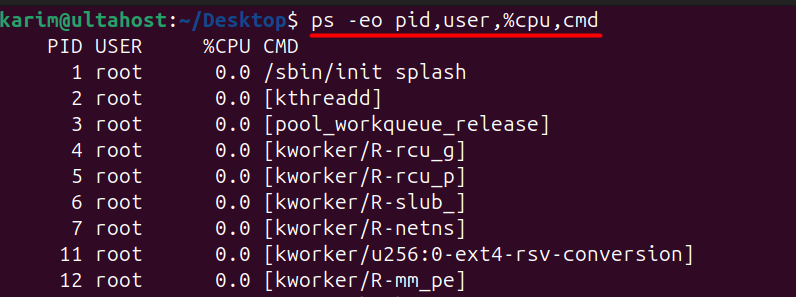
The -eo option in ps allows you to specify exactly which columns you want in your output. This can be used to create a custom view that focuses on the most relevant information.
For example, to display the PID, user, CPU usage, and command for each process, use:
ps -eo pid,user,%cpu,cmd
Now that we’ve explored the capabilities of the ps aux command, let’s examine some real-world use cases that demonstrate its power and versatility.
Identifying Resource-Intensive Processes
Suppose you’re experiencing performance issues on your Linux system, and you suspect that a particular process is consuming excessive resources. You can use the ps aux command to identify the top CPU- or memory-hungry processes:
ps aux --sort %cpu | head -n 5
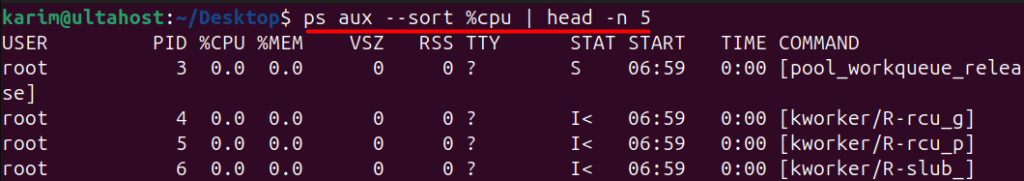
This will display the top 5 processes consuming the most CPU resources.
Identifying Zombie Processes
Zombie processes are processes that have finished executing but still occupy system resources. The ps aux command can be used to identify and terminate these processes:
ps aux | grep defunct

This will display a list of zombie processes, which can then be terminated using the kill command.
Integrating with Other Linux Commands
The ps aux command can be integrated with other Linux commands to create powerful workflows. For example, you can use the ps aux command with the grep command to search for specific processes:
ps aux | grep 2600
This will display information about the specified process, including its current state and CPU usage.
The ps aux command is a key tool for managing monitor Linux processes in your system. It provides detailed information about all running processes, making it essential for system monitoring and management. By learning how to use ps aux effectively, Linux administrators can keep an eye on system performance, identify and fix issues, and ensure the system runs smoothly.
This article has shown how to use ps aux to find processes that use a lot of resources, spot zombie processes, and combine with other Linux pipe commands for better control. For instance, using ps aux –sort %cpu helps identify resource-heavy processes, while ps aux grep defunct detects zombie processes that need to be terminated. Filtering processes by user or PID allows for targeted monitoring and troubleshooting.
This powerful tool provides detailed insights and control, enhancing your system administration skills. For an even more robust and flexible environment, consider Ultahost’s VDS hosting. It offers dedicated resources and optimal performance, perfect for handling your advanced process management tasks. Keep practicing and exploring the options to fully leverage its capabilities.
It lists all processes currently running on the system, providing detailed information such as the user who owns each process, CPU and memory usage, process IDs (PIDs), and more.
You can pipe the output of ps aux to grep to filter for a specific process. For example, to find all processes related to ‘nginx’, you can use ps aux | grep nginx.
Yes, ps aux includes columns for CPU and memory usage (%CPU and %MEM), which can help identify processes consuming the most resources.