How to Install WinGet in Windows
WinGet, the Windows package manager, revolutionizes how...

The ping command is a basic utility used for testing connectivity between two devices. Essentially, it decapsulates data in an ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) echo request packet and waits for a reply. If the echo reply is received from the selected IP address, the connection is considered alive. The ICMP protocol only checks connectivity to the destination; it does not check if services or applications are ‘reachable’ and/or their individual port numbers.
The ping command can only ping a host; you cannot ping a specific port using ping, because ping does not use TCP or UDP to communicate, and TCP or UDP is needed to communicate at the port level. There are various other tools available for testing TCP (and/or UDP) connectivity or testing if a port is open, including PowerShell’s Test-NetConnection cmdlet, Telnet command, Network Mapper (Nmap), and Curl.
Testing specific ports can be helpful when troubleshooting services such as web servers (ports 80/443), remote desktop (port 3389), email servers (port 25), and databases (port 3306). Testing specific open ports can help to verify if services are running and accessible from the network.
The Windows ping port command is in fact an ICMP service, which operates at the OSI model’s network layer and therefore checks whether a device is reachable but does not check whether specific services that run on that device are reachable. Given that services, such as web or database servers, run at the transport layer using either TCP or UDP protocols, those services are assigned designated ports and listen for traffic on those ports.
A port in networking is a number that identifies a specific process or service on a machine. For example: a web server usually listens on port 80 for HTTP-based requests and Remote Desktop Protocol listens on port 3389 for requests. The assignment of ports mean that users can run multiple services on the same IP address of the device and each of those services listen for traffic on its own assigned port.
If I were to “ping port 80”, the standard ping command will not send the request on port 80 to the web server as the ping service will only see, if the host responds to an ICMP request on port 0. To test or check port 80, I would need to send a tcp request from a tool or utility that operates at the transport layer or higher.
Ping Ports Instantly on High-Speed Windows VPS!
Run port checks with zero delay on Ultahost’s performance-optimized Windows VPS. Test connectivity, scan networks fast, and rely on 24/7 expert assistance!
PowerShell includes a built-in cmdlet called Test-NetConnection, available on Windows 8, Windows 10, and Windows Server 2012 or later. It allows users to check the availability of a specific TCP port on a remote system.
Command syntax to check how to ping a port:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName example.com -Port 80
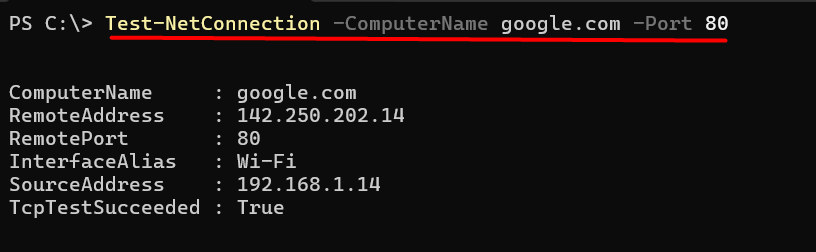
This command attempts a TCP connection to port 80 on example.com. If successful, the output will show TcpTestSucceeded : True, confirming that the port is open and accepting connections. If the port is closed or blocked by a firewall, it will return False.
Additional output includes the IP address of the target, the resolved hostname, and round-trip time. This method is ideal for testing ports like 443 (HTTPS), 1433 (SQL Server), or 3389 (RDP) without needing third-party tools.
Telnet is a legacy command-line tool that can be used to manually test TCP port connectivity. By default, it is not installed on modern Windows systems, but you can enable it via Control Panel:
To enable Telnet:
Go to Control Panel > Programs > Turn Windows features on or off
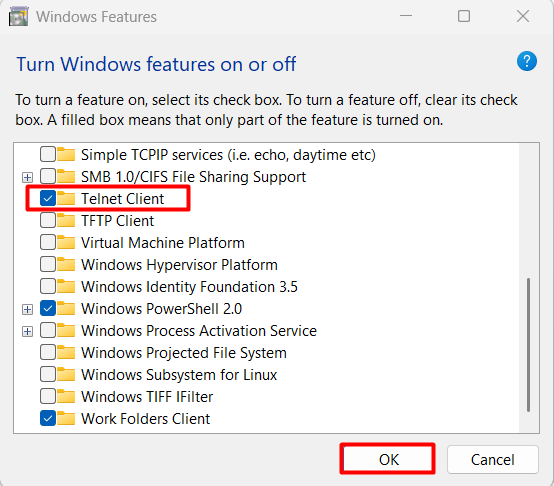
Check Telnet Client, then click OK.
Command syntax to ping port number 80:
telnet example.com 80
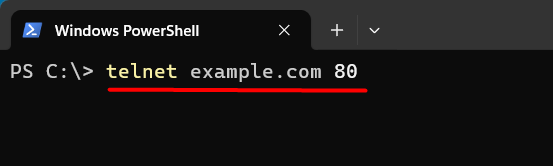
If the connection is successful, the command prompt will go blank. This indicates that the port is open. If the port is closed or filtered, you’ll receive a message like “Could not open connection to the host.”
Telnet is commonly used to test ports like 25 (SMTP), 110 (POP3), 23 (Telnet), or 3389 (RDP). However, it doesn’t support encrypted communication and should be used only in trusted environments.
Nmap is a powerful and widely used network scanning tool. It allows users to detect open, closed, or filtered ports on a remote system. It must be downloaded and installed separately.
Download from nmap official website and then install the Windows version:
Command syntax:
nmap -p 443 example.com
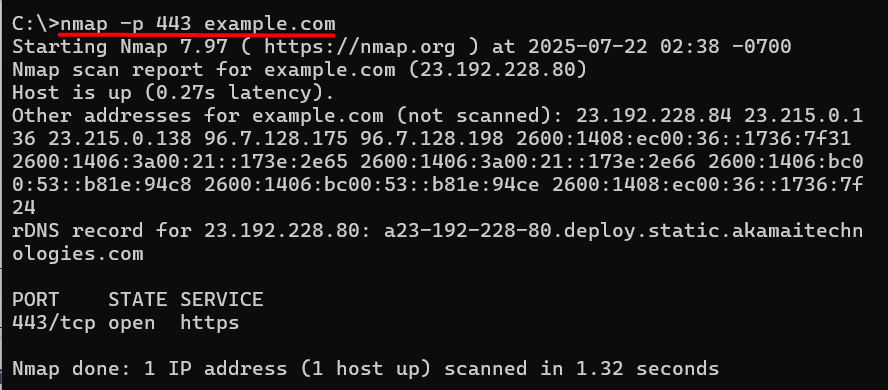
This command scans port 443 on the target system and tells whether it’s open, closed, or filtered. For scanning multiple ports or performing a quick scan:
nmap -F example.com
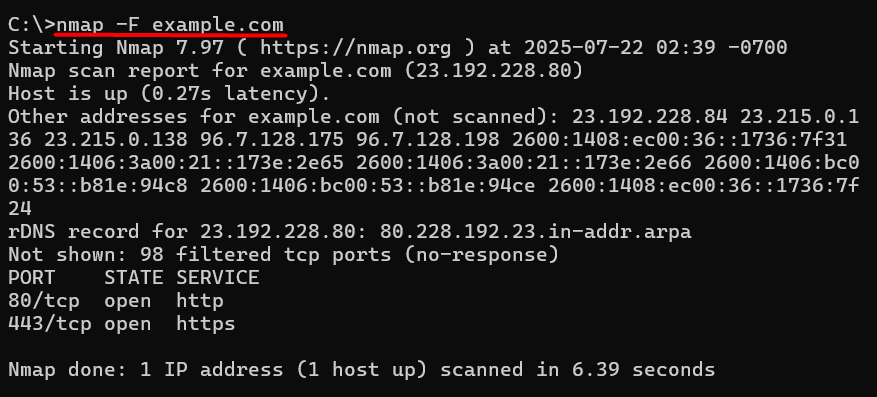
Nmap is preferred for in-depth network diagnostics, but it requires administrator privileges and should only be used on systems you own or are authorized to test.
The response message received when testing a port tells you if the target service is reachable. If you can successfully connect, then the port is open and listening. For example, in PowerShell, you’ll see TcpTestSucceeded : True, in telnet, the command prompt returns blank, and in curl, you see a valid HTTP status code like 200 OK. This confirms that the web server is responding on that port.
A failure message can only mean one thing. If it says “connection refused”, then you reach the host, but no service is listening on that port, usually because the port is closed. If it says “connection timed out,” it usually means a firewall is quietly dropping the request or the host is unreachable altogether.
Ports can be in three states:
Web servers usually listen on port 80 (HTTP) and port 443 (HTTPS). If ports 80 and 443 are responding, that means that a webpage or API is online and serving traffic. If you cannot connect to port 443, there may be an SSL connection issue, or you may see “this site can’t be reached” message.
File transfer services like FTP (21) and SFTP (22) require ports to be open in order to upload or download files. If you run a test and a port check fails, this means that a firewall rule is misconfigured, the service is incorrectly configured, or the service is down altogether.
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) uses port 3389. As a troubleshooting measure, if RDP stops working, the first thing to check is, “What state is the port in?” This clarifies if the issue is a connection issue versus the service itself. Applications also need to access the database on specific ports if connections to the databases are to be established. The default ports for databases are 1433 (SQL Server) and 3306 (MySQL). If you cannot connect to either of those ports, you need to investigate connectivity to the database, furthermore, if you are receiving timeout or login errors, check the connectivity to either port to troubleshoot.
Opening up unnecessary ports creates potential for unauthorized access, and risk of an attack increases with multiple open ports. Always close or block incoming connections on ports not in use and use firewalls, IP whitelisting, or VPNs to restrict access to services that must be open. For example, if a remote service requires access from remote internet users, make it not accessible to the public, only usable on local or internal networks.
Using insecure tools like Telnet expose info in plain text. Always use SSH (port 22) when you are taking remote access (either for login credentials or sensitive commands). Always prefer HTTPS to HTTP to make sure the data in the web traffic is encrypted.
When scanning ports, do it with the intention of only scanning systems and networks which you own or have permission to test. Scanning ports on systems and networks you don’t own or don’t have permission to use may be flagged as malicious activity and may violate laws or company policy. When you follow best practices you can ensure that you use port-checking tools responsibly and reduce the chances of an intrusion detection system or firewall tripping due to your port scanning.
While pinging a port in Windows relies on more than the basic ping, note that ping relies on ICMP and cannot check TCP or UDP ports, but there are great capabilities for checking if a port is open and a service is responding in a reliable way via Test-NetConnection (which is built into PowerShell), Telnet, and Nmap. Each tool brings different levels of detail and is appropriate for different scenarios.
Using PowerShell for an in-and-out review, Telnet (if it’s an available for TCP version), and Nmap for the more advanced port scans on a lan or across a wan is the way to go. Understanding how to interpret the results, such as connection refused, timed out, or connect success; enables effective network troubleshooting. Always be respectful and ethical when using these tools and be sure to put a firewall in front of anything other than a test port you really don’t want to run an open port at a minimum.
Quickly scan and verify open ports using PowerShell, Telnet, or Nmap on UltaHost’s high-performance VPS hosting plans. Get full admin access, fast port response times, and a stable environment ideal for network diagnostics and service monitoring. With NVMe storage, dedicated resources, and 24/7 Ultaai support, our VPS is perfect for IT professionals and developers who need precision, speed, and uptime for port testing and network troubleshooting.
No, the standard ping command only uses ICMP and cannot target specific ports. You need tools like PowerShell or Telnet to test ports.
Use the PowerShell command: Test-NetConnection -ComputerName [host] -Port 80. A successful result shows TcpTestSucceeded : True.
A blank screen means the connection to the port was successful. If it fails, you’ll get a connection error.
It means the device is reachable, but no service is listening on that port. The port is likely closed.
Yes, but only on networks you own or have permission to scan. Unauthorized scanning can be flagged as malicious.
Go to Control Panel → Programs → Turn Windows features on or off → Check “Telnet Client” → Click OK.
PowerShell’s Test-NetConnection is the simplest for most users. Nmap offers more detailed results for advanced diagnostics.
UltaAI – Smart AI Assistant for Ultahost Clients
UltaAI is your advisor for anything related to domain or hosting. Experience personalised suggestions.