How to Fix Update and Upgrade Issues in Kali ...
Kali Linux is a powerful and versatile operating system...
The wall command in Linux is a powerful tool that allows system administrators to broadcast messages to all logged in users. This command is particularly useful in multi user environments where administrators need to communicate important information quickly and efficiently.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the wall command including its syntax options and practical examples.
The wall command short for “write to all command” is used to send messages to all users currently logged into the system. This command is particularly useful for system administrators who need to notify users about system maintenance impending shutdowns or other critical events. The messages sent using wall are displayed on the terminals of all logged in users ensuring that the information reaches everyone promptly.
First, connect your server via SSH. The basic syntax of the wall command Linux is as follows:
wall [options] [message | file]
The Linux wall command comes with several options that allow you to customize its behavior. Here are some of the most commonly used options:
Broadcast Messages on Our Linux VPS!
Ultahost offers Linux hosting with NVMe SSD storage. Use our Linux VPS to practice the command and streamline your processes.
Following are some practical examples of using the wall command in the Linux operating system:
The most basic use of the wall command is to broadcast a simple message to all logged in users. For example:
wall "The system will undergo maintenance at 3 PM."
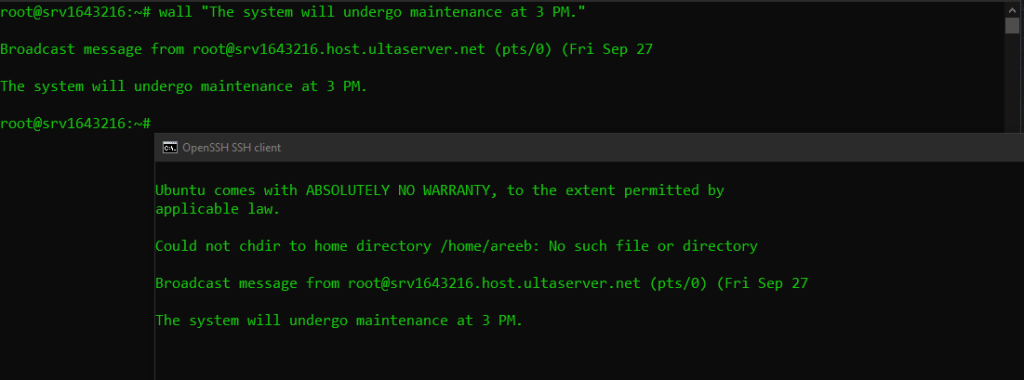
This command will display the message “The system will undergo maintenance at 3 PM.” on the terminals of all logged in users.
You can also broadcast a message from a file. This is useful if you have a long message or if you want to reuse the same message multiple times. For example:
wall /path/to/message.txt
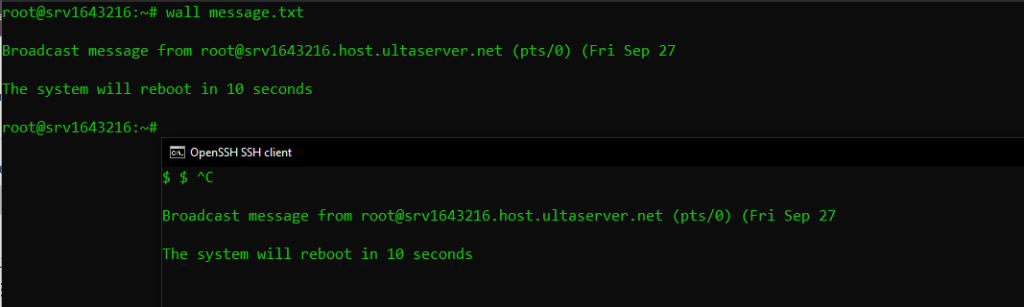
This command will read the contents of message.txt and broadcast it to all logged in users.
The -t option allows you to set a timeout for the message. This means that the message will only be displayed for the specified number of seconds. For example:
wall -t 30 "The system will reboot in 30 seconds."
This command will display the message “The system will reboot in 30 seconds.” for 30 seconds.
By default, the wall command displays a header before the message. You can suppress this header using the -n option. For example:
wall -n "The system will be down for maintenance."
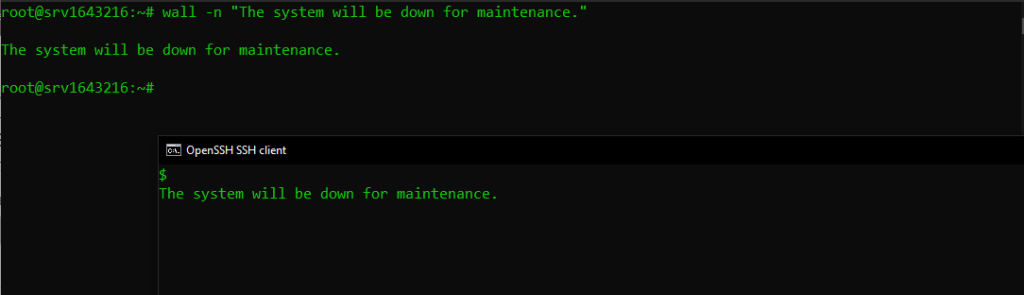
This command will display the message “The system will be down for maintenance.” without the header.
You can send multi line messages using the wall command. To do this simply type the wall command and press Enter. Then type your message pressing Enter after each line. When you are finished press Ctrl+D to send the message. For example:
wall The system will be down for maintenance. Please save your work and log out. Thank you for your cooperation.
This command will display the multi-line message on the terminals of all logged in users.
The -g option allows you to send the message only to users in a specific group. For example:
wall -g admin "The system will be rebooted for maintenance."
This command will display the message “The system will be rebooted for maintenance.” only to users in the admin group.
Learn about Exploring chsh Command in Linux with Examples.
While the wall command is a powerful tool it should be used to avoid disrupting users unnecessarily. Here are some best practices for using the wall command:
The wall command is an essential tool for system administrators in multi user environments. It allows you to broadcast messages to all logged in users quickly and efficiently. By understanding the various options and best practices you can use the wall command effectively to communicate important information to your users.
At Ultahost, we are committed to providing our customers with the best possible service and support, and we are always working to improve our offerings. Our dedicated hosting server is designed to be scalable and flexible so you can always choose the right amount of resources for your needs.
The wall command lets you send a message to all logged in users on a Linux system.
Type wall “Your message” in the terminal and all users will see the message.
All logged in users receive the message sent via the wall command.
Yes, you can send a file by typing wall /path/filename.txt on the terminal.
Yes, only users currently logged in will see the wall message.
Only the root user or users with sudo privileges can send wall messages.
The wall command sends messages to all logged in users, not individuals.