How to Install RubyMine on Ubuntu
RubyMine is an IDE specifically for Ruby and Rails deve...
Drupal is a free and open-source content management framework (CMF) and content management system (CMS) written in PHP. It is known for its flexibility, scalability, and customization capabilities, making it a popular choice for building complex websites and applications. Drupal offers a wide range of features, including user management, content management, and taxonomy, as well as a large community of developers and a vast array of modules and themes. When installed on Ubuntu, Drupal can take advantage of Ubuntu’s reliability, security, and scalability, making it an excellent choice for building robust and high-performance websites.
The benefits of using Drupal on Ubuntu include improved performance, enhanced security, and simplified maintenance. Ubuntu’s package manager, apt, makes it easy to install and manage dependencies, while its community support ensures that any issues are quickly resolved. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to install Drupal on Ubuntu. We will cover the prerequisites, installing the Apache web server, configuring the firewall, installing PHP and database dependencies, creating a Drupal database and user, and completing the Drupal installation.
By following this guide, you will be able to successfully install Drupal Ubuntu 22.04 on your system server.
Preparing Your Ubuntu Server for Drupal Installation
Before you begin installing Drupal on your Ubuntu server, it’s essential to ensure that your system meets the necessary requirements. In this section, we’ll outline the prerequisites and guide you through the process of updating your system and installing the Apache web server.
System Requirements
To install Drupal on Ubuntu, you’ll need:
Moreover, to ensure that your system packages are up-to-date, run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt full-upgrade
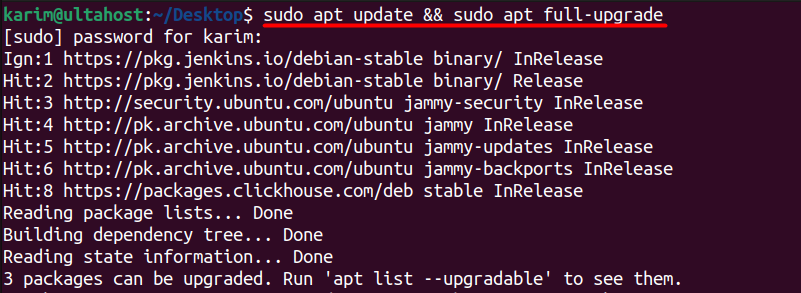
This command will update the package index and upgrade all installed packages to the latest versions available.
Experience the power of Ubuntu VPS
Combine the power of the world’s most trusted Linux distro with the flexibility of a VPS. Experience lightning-fast performance.
Installing the Apache Web Server
Apache is a popular web server software that’s widely used for hosting websites. To install Apache on Ubuntu on your system server, execute the following command:
sudo apt install apache2
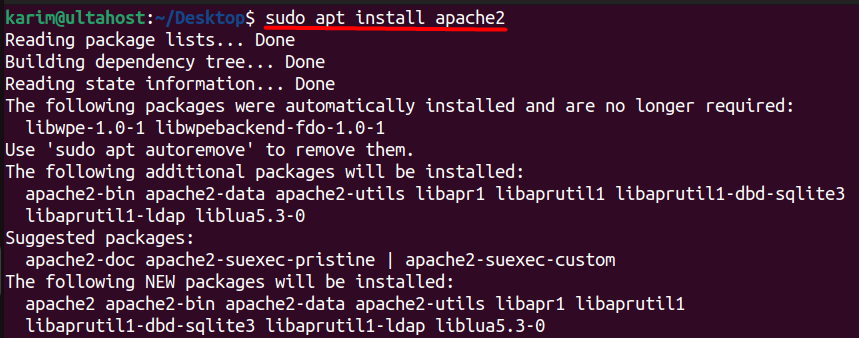
Once the installation is complete, start and enable the Apache service to ensure it runs automatically on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable apache2 && sudo systemctl start apache2
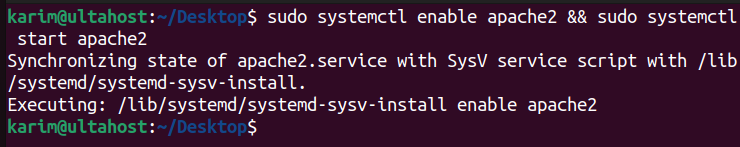
To verify that the Apache service is running, check its status with the following command:
sudo systemctl status apache2
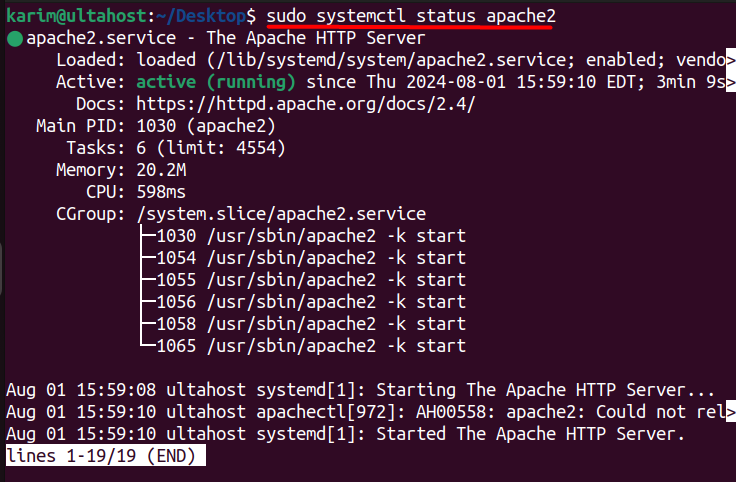
If the service is running correctly, you should see a message indicating that Apache is active and running.
Learn about Install LAMP on Ubuntu 18.04.
Configuring the Firewall
By default, To enable a firewall on your Ubuntu system you can install UFW on Ubuntu system. An Uncomplicated Firewall is a user-friendly configuration tool. To allow incoming traffic on the default Apache port (80), run the following command:
sudo ufw allow http
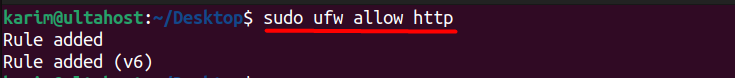
This will allow incoming HTTP traffic, making your Apache server accessible from outside the local network.
In the previous section, we installed the Apache web server and configured the firewall to allow incoming traffic. Now, we’ll focus on installing the PHP and database dependencies required for Drupal.
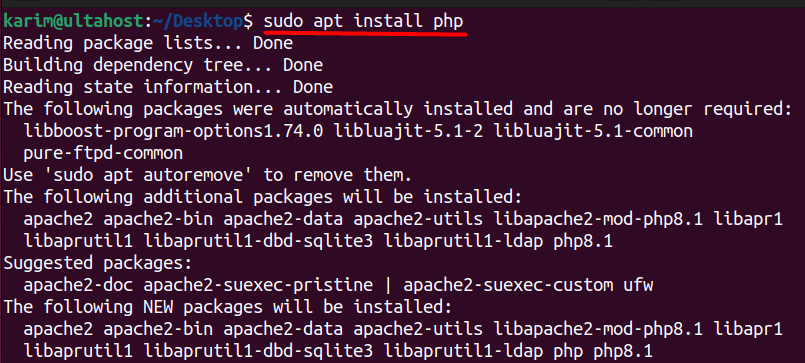
Drupal requires PHP to function correctly. To install PHP 8.1 with the necessary extensions, execute the following command:
sudo apt install php
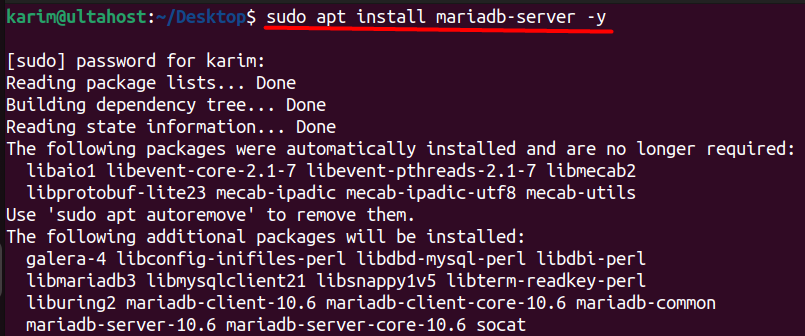
MariaDB is a popular open-source database management system that’s widely used for web applications. To install the MariaDB database server, execute the following command:
sudo apt install mariadb-server -y
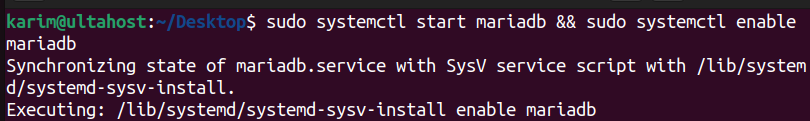
Since the installation is complete, start and enable the MariaDB service to ensure it runs automatically on system boot:
sudo systemctl start mariadb && sudo systemctl enable mariadb
To verify that the MariaDB service is running, check its status with the following command:
sudo systemctl status mariadb
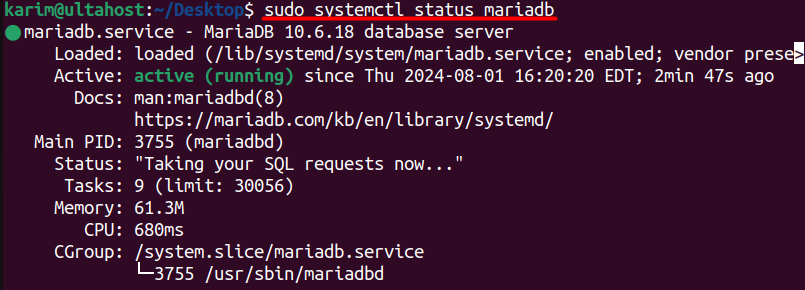
If the service is running correctly, you should see a message indicating that MariaDB is active and running.
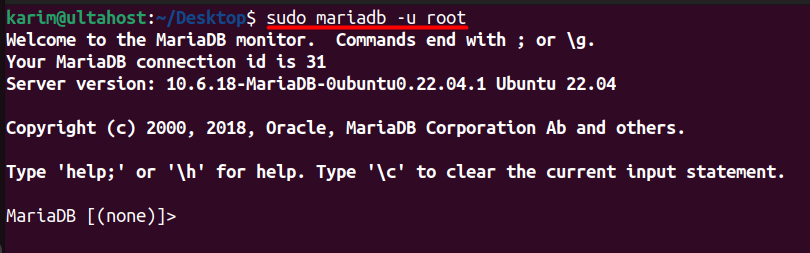
To create a Drupal database and user, you’ll need to access the MariaDB shell. You can do this by running the following command:
sudo mariadb -u root
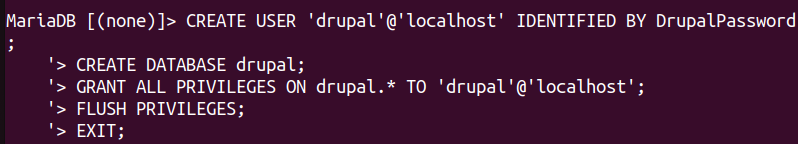
This will open the MariaDB shell, where you can execute the following commands to create a Drupal database and user:
CREATE USER 'drupal'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY DrupalPassword'; CREATE DATABASE drupal; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON drupal.* TO 'drupal'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
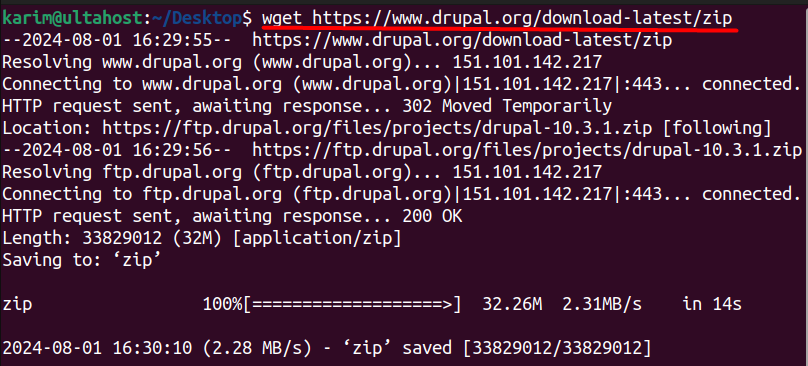
To download Drupal, navigate to the default Apache document root:
cd /var/www/html

Replace your password with a strong password for the Drupal user.
wget https://www.drupal.org/download-latest/zip
Next, unzip the downloaded file:
sudo unzip drupal-10.3.1.zip
Move the extracted files to a new directory named Drupal:
sudo mv drupal-10.3.1/ drupal/

To ensure that Drupal can write to the necessary files and folders, set the correct permissions:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data drupal/

This command sets the ownership of the drupal directory and all its contents to the www-data user and group.
Creating an Apache Virtual Host File
To create a virtual host file for Drupal, navigate to the Apache configuration directory:
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/

Create a new file named drupal.conf:
sudo touch drupal.conf

Next, open the file and paste the following configuration:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName yourdomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/drupal
<Directory /var/www/html/drupal>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
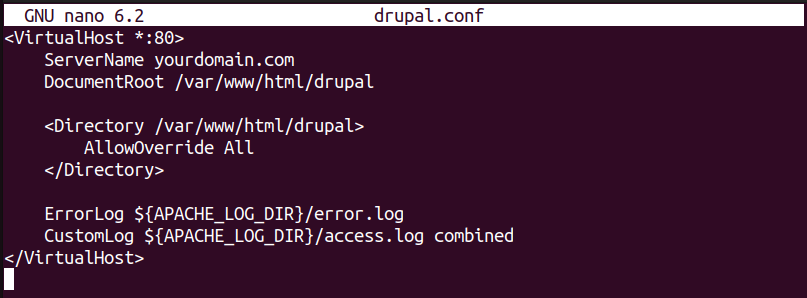
Replace yourdomain.com with your actual domain name then save and close the file.
Enabling the Apache Configuration and Rewrite Module
To enable the Apache configuration for Drupal, run the following command:
systemctl reload apache2

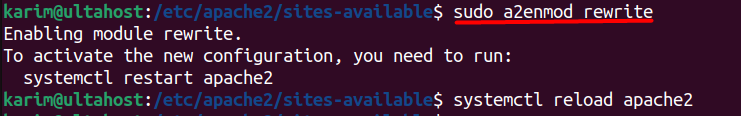
Next, enable the Apache rewrite module:
sudo a2enmod rewrite
Checking the Syntax and Restarting Apache
To check the syntax of the Apache configuration, run the following command:
apachectl -t

Completing the Drupal Installation
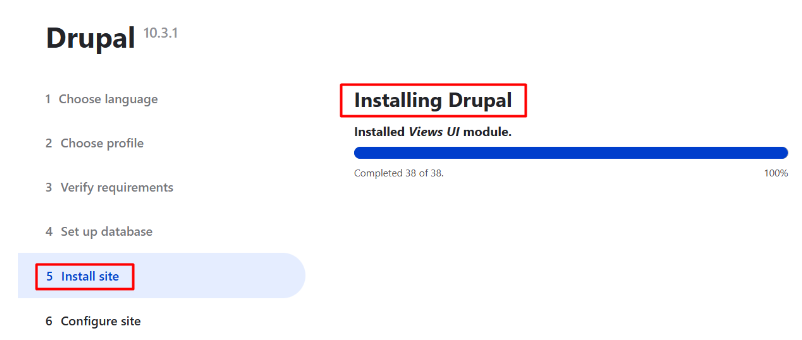
Once the Apache service is restarted, you can complete the Drupal installation by accessing http://yourdomain.com in your web browser. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation:
In this article, we have provided a comprehensive guide on how to install Drupal on Ubuntu. The steps performed to install and set up Drupal on Ubuntu include installing the Apache web server, configuring the firewall, and installing PHP and database dependencies.
Next, we created a Drupal database and user, downloading and unzipping the Drupal installation files, creating an Apache virtual host file, enabling the Apache configuration and rewrite module, and restarting the Apache service.
Finally, we completed the Drupal installation by accessing the website in a web browser and following the on-screen instructions. By following these steps, you should now have a fully functional Drupal installation on your Ubuntu server, ready to be customized and developed into a robust and high-performance website.
You can install Drupal on the Linux system. For this, you need a powerful platform to host your Drupal projects Look no further than Ultahost’s VPS hosting! Our VPS plans offer to ensure fast loading times for your applications and easily upgrade your resources as your needs grow. Experience the freedom and flexibility of a VPS today.
Drupal is an open-source content management system (CMS) that allows users to build and manage websites. It’s highly flexible and customizable, suitable for a range of applications from blogs to complex enterprise sites.
Drupal generally supports recent LTS (Long Term Support) versions of Ubuntu. As of now, Ubuntu 20.04 LTS or Ubuntu 22.04 LTS are recommended due to their stability and extended support.
Drupal requires a web server (Apache or Nginx), PHP, and a database server (MySQL/MariaDB or PostgreSQL). Specific PHP version requirements depend on the Drupal version being installed.
You can install these components using the following commands:
Commonly required PHP modules include php-xml, php-gd, php-mbstring, php-json, and php-zip. You can install them with:
sudo apt install php-xml php-gd php-mbstring php-json php-zip