Linux is an open-source operating system that offers a wide range of distributions, each with its unique features and characteristics. Knowing your Linux version is crucial for various tasks, including troubleshooting, ensuring software compatibility, and keeping your system secure with the latest updates.
In this article, we’ll explore three methods to check Linux version, including using the uname command, accessing the /etc/os-release file, and utilizing the lsb_release command. We’ll also troubleshoot common issues that may arise during the process.
Why Check Your Linux Version?
Before we dive into the methods, it’s essential to understand the importance of knowing your Linux version. Here are some compelling reasons to check your Linux version:
- Ensuring Compatibility: Knowing your Linux version helps you ensure that the software and hardware you use are compatible with your system. This is particularly crucial when installing new software or drivers, as incompatible versions can lead to system crashes or errors.
- Troubleshooting Issues: Identifying your Linux version helps you troubleshoot issues specific to your distribution. For instance, if you’re experiencing issues with a particular package or service, knowing your Linux version can help you find the correct solution or patch.
- Staying Up to Date: Linux distributions regularly release security patches and updates to fix vulnerabilities and improve performance. Knowing your Linux version ensures you receive the correct updates and stay protected from potential threats.
- Optimizing Performance: Understanding your Linux version can help you optimize your system’s performance. By knowing the kernel version, you can fine-tune your system’s settings to improve performance, reduce latency, and enhance overall user experience.
Unleash the power of Ubuntu VPS
Get the reliability of the world’s most popular Linux distro and the flexibility of a virtual server. Enjoy blazing-fast speeds and low latency.
Methods to Check Linux Version
Method 1: Using the uname Command
The uname command is a built-in Linux utility that displays information about your system, including the linux kernel version, architecture, and operating system.
To find Linux version, you need to open a terminal on your Linux system. You can do this by searching for “terminal” in your application launcher or by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + T.
Next, type the following Linux version command and press Enter:
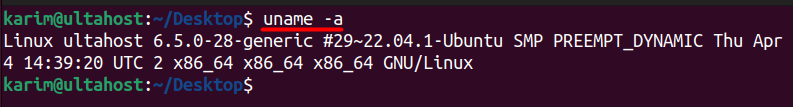
uname -a
Let’s discuss the output:
- Linux: Indicates that the operating system is Linux.
- ultahost: This is the hostname of the system.
- 6.5.0-28-generic: This is the kernel version of the Linux operating system.
- #29~22.04.1-Ubuntu SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu Apr 4 14:39:20 UTC 2: This part provides additional information about the kernel, such as the build number, whether it’s from Ubuntu, the SMP (Symmetric Multiprocessing) status, and the date and time of the kernel build.
- x86_64: Indicates the architecture of the system, in this case, it’s 64-bit.
- x86_64: Refers to the processor architecture.
- x86_64: Indicates the hardware platform.
- GNU/Linux: Denotes that the system is based on the GNU operating system and the Linux kernel.
Method 2: Using the /etc/os-release File
The /etc/os-release file contains information about your Linux distribution, including the version, name, and ID. To access this file, write the below command on the terminal:
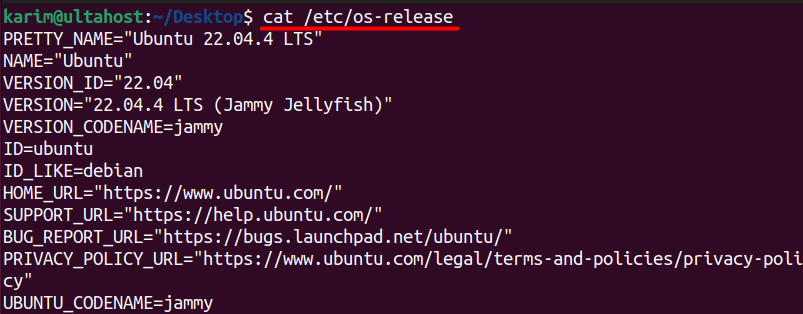
cat /etc/os-release
Let’s understand the output:
- PRETTY_NAME: Describes the pretty or user-friendly name of the operating system, in this case, “Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS”.
- NAME: Specifies the name of the operating system, which is “Ubuntu”.
- VERSION_ID: Indicates the version of the operating system, which is “22.04”.
- VERSION: Provides additional version information, including the release codename, which is “Jammy Jellyfish”, and the LTS (Long-Term Support) status.
- VERSION_CODENAME: Specifies the codename of the version, which is “jammy”.
- ID: Identifies the distribution ID, which is “ubuntu”.
- ID_LIKE: Indicates which distribution this one is similar to, in this case, “Debian”.
- HOME_URL: Provides the URL of the Ubuntu homepage.
- SUPPORT_URL: Specifies the URL for Ubuntu support.
- BUG_REPORT_URL: Indicates the URL where bugs in Ubuntu can be reported.
- PRIVACY_POLICY_URL: Provides the URL for the privacy policy of Ubuntu.
- UBUNTU_CODENAME: Reiterates the codename of the version, which is “jammy”.
Method 3: Using the lsb_release Command
The lsb_release command is a part of the Linux Standard Base (LSB) package, which provides information about your Linux distribution, including the version, name, and ID. To use the lsb_release command, execute the below command:
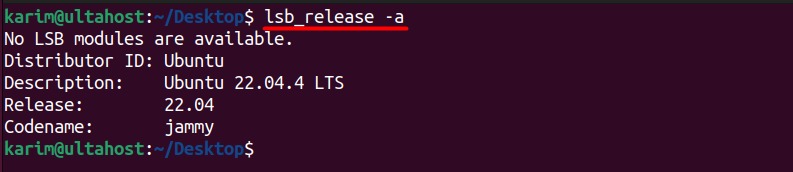
lsb_release -a
Let’s evaluate the output:
- No LSB modules are available: This message indicates that no LSB (Linux Standard Base) modules are installed or available on the system. LSB modules provide a standard interface for Linux distributions, but they’re not always present on every system.
- Distributor ID: Ubuntu: Specifies the distributor or vendor of the Linux distribution, which is Ubuntu in this case.
- Description: Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS: Provides a brief description of the Ubuntu release, including the version number (22.04.4) and the fact that it’s a Long-Term Support (LTS) release.
- Release: 22.04: Specifies the version number of the Ubuntu release.
- Codename: jammy: Identifies the codename associated with the Ubuntu release, which is “jammy”.
Method 4: Using the hostnamectl Command
The hostnamectl command is a part of the systemd suite, which provides information about the system and its hostname. To see Linux version, use the below command:
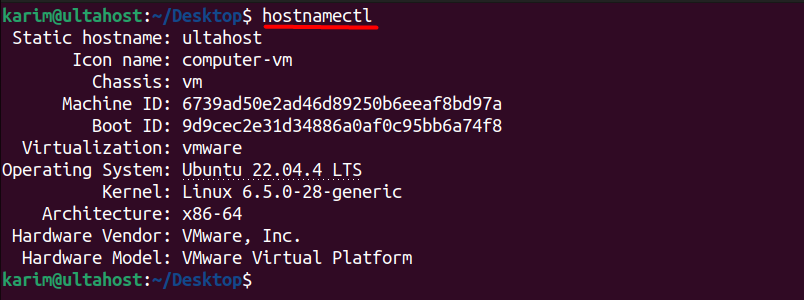
hostnamectl
Let’s evaluate the output:
- Static hostname: Specifies the static hostname of the system, which is “ultahost” in this case.
- Icon name: Describes an icon name associated with the system, indicating it’s a virtual machine (“computer-vm”).
- Chassis: Specifies the chassis type of the system, which is a virtual machine (“vm”).
- Machine ID: Represents a unique identifier assigned to the machine.
- Boot ID: Represents a unique identifier assigned to the boot instance of the system.
- Virtualization: Indicates the virtualization technology being used, which is VMware in this case.
- Hardware Vendor: Indicates the vendor of the hardware, which is VMware, Inc.
- Hardware Model: Describes the hardware model, which is a VMware Virtual Platform.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored some methods to check your Linux version, including using the uname command, accessing the /etc/os-release file, utilizing the lsb_release and hostnamectl command.
By following these methods, you’ll be able to easily check your Linux version and ensure compatibility, troubleshoot issues, and stay up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
If you are a developer or starting your journey and trying to dive into the Linux operating system consider that you ensure your current setup can handle the demands of your specific needs. This is where you need a powerful and reliable platform like Ultahost. We provide affordable Linux VPS hosting which helps to manage your server and dedicated resources for guaranteed speed and stability to perform your required task.
FAQ
How do I check the version of Linux I’m running?
You can check the Linux version using the lsb_release -a command or by viewing the /etc/os-release file.
What does the lsb_release -a command do?
This command displays various information about the Linux distribution, including its version number, description, codename, and more.
Is there another way to check the Linux version?
Yes, you can also use the cat /etc/os-release command to view the contents of the /etc/os-release file, which contains information about the Linux distribution, including its version.
Can I check the Linux version without using the terminal?
Yes, you can usually find information about the Linux version in the system settings or by using graphical tools provided by your distribution.
Why is it important to know the Linux version?
Knowing the Linux version can help you determine compatibility with software, find support resources, and troubleshoot issues effectively.