How to Install Chromium on Ubuntu 22.04
Chromium is an open-source web browser project that ser...
The “Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock” error message in Ubuntu can occur especially when you are trying to install or update software. This error comes when another process is already using the package manager and has acquired a lock on the important /var/lib/dpkg/lock file. This file makes sure that only one package management operation occurs at a time, preventing conflicts and maintaining system integrity.
While the error message itself shows a package management error. This guide explores various methods to diagnose and fix could not get lock error Ubuntu allowing you to resume your package management tasks easily.
The /var/lib/dpkg/lock file serves as a gatekeeper for package management operations. When you initiate an action like the update command, the package manager usually apt or aptitude acquires this lock to ensure exclusive access during the update or installed deb packages process. This prevents potential conflicts if another program tries to modify packages simultaneously.
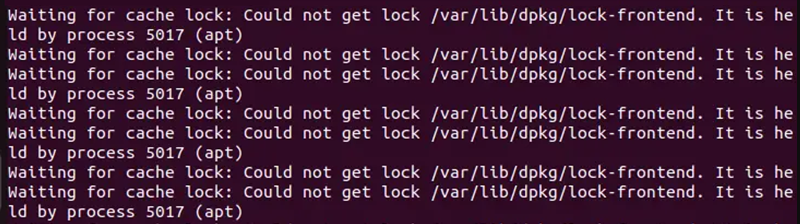
The “Could not get lock” error surfaces when another process already holds the lock. This could be due to:
apt, aptitude, synaptic, or a graphical package manager like Ubuntu Software Center might be running in the background, performing updates or installations.unattended-upgrades could be in progress holding the lock.Here’s a step-by-step approach to resolve this error starting with the most straightforward methods and progressing to more advanced solutions:
Method 1: Check Running Applications
Close any program that might be involved in package management:
apt update, apt install, aptitude, etc.Try your package management command again.
Method 2: Wait it Out
In some cases, the conflicting process might finish shortly, releasing the lock. Give it a few minutes and try your command again.
Method 3: Reboot Your System
A reboot will forcefully terminate all running processes, including any that might be holding the lock. To restart the Ubuntu system use the following command:
reboot

After rebooting attempt your package management operation.
Method 4: Clear Package Cache
A corrupted package cache can sometimes lead to unexpected behavior. Try clearing the cache using:
sudo apt clean

Run your desired package management command.
Unlock Seamless Performance with Ubuntu VPS!
Experience superior reliability and flexibility with Ubuntu VPS, offering a powerful and personalized hosting solution.
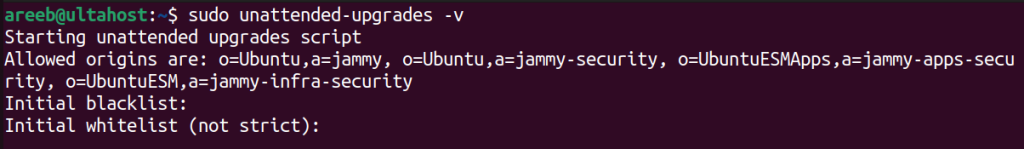
Method 5: Check for Software Updates
Automatic updates might be using the lock. Use the following command:
sudo unattended-upgrades -v
to check if automatic updates are configured and if they are currently running. If updates are in progress wait for them to finish or consider disabling automatic updates temporarily.
Method 6: Identify Running Processes
Use the lsof command to view open files and the processes holding them. Run the following command:
lsof /var/lib/dpkg/lock
This will display the process ID (PID) of the program using the lock. Terminating processes can have unintended consequences. Proceed with caution and only if you are comfortable identifying the issue. Use the following command for detailed usage information.
man lsof
Method 7: Address Stuck Services
If lsof identifies a system service you can attempt to restart it using:
sudo systemctl restart <service_name>
Replace the service_name with the actual service name. If restarting does not work consider more advanced troubleshooting specific to the identified service.
Method 8: Using Kill Command
Improper usage of kill can corrupt your package database and render your system unstable. Do not use kill carelessly. Use lsof to identify the exact process that is holding the lock. The output will display the process ID (PID). Analyze the results to ensure you’re targeting the correct procedure. There are different kill signal options. We will focus on two commonly used ones:
If you are confident about the identified process attempt to terminate it gracefully using SIGTERM:
sudo kill <PID>
Replace with the actual process ID obtained from lsof. Wait a few minutes to see if the process terminates and releases the lock.
If the process does not terminate after a reasonable wait or if you are certain it’s stuck consider using SIGKILL:
sudo kill -KILL <PID>
This forceful termination can lead to data loss or system instability.
Method 9: Delete Lock Files
This method should be the last option as improperly deleting lock files can corrupt your package database. Use the following command to remove the dpkg lock error Ubuntu:
sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/lock
Now run your desired package management command.
Following are some important preventions on how to fix could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock-frontend error on Ubuntu:
The “Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock” error can be resolved by following the methods outlined in this guide and you should be able to diagnose and resolve the issue effectively. Remember to start with simpler solutions and progress to more advanced methods only if necessary. By understanding the cause and utilizing the appropriate techniques you can keep your Ubuntu system’s package management running smoothly.
Resolving the “Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock” error on Ubuntu can involve checking for other running package managers which can be time-consuming. Upgrading to an Ultahost cheap Linux VPS hosting plan offers a more efficient solution that grants you root access and eliminates the limitations and no conflicting processes using the package manager lock allowing you to install or update software smoothly.
This error occurs when another process is using the package manager, preventing new package installations or updates.
Use the command sudo lsof /var/lib/dpkg/lock to see which process is holding the lock.
Removing the lock file with sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/lock can be safe if no package manager processes are running, but use caution.
Restart your computer to ensure no processes are holding the lock and try again.
Avoid running multiple package managers at the same time to prevent this error from occurring.